|
Hysteroid Dysphoria
Hysteroid dysphoria is a name given to repeated episodes of depressed mood in response to feeling rejected. Hysteroid dysphoria has been described in outpatient populations and is thought to be a subtype of atypical depression involving rejection sensitivity and therapeutic response to monoamine oxidase inhibitors. While some research shows that hysteroid dysphoria responds well to MAOIs, other research has suggested that the difference actually comes from the condition being less sensitive to tricyclic antidepressants. Other studies have examined the symptoms associated with hysteroid dysphoria and found that while the symptoms are observable, they are not unique or distinct enough to be considered their own condition. See also * Dysphoria Dysphoria (; ) is a profound state of unease or dissatisfaction. It is the semantic opposite of euphoria. In a psychiatric context, dysphoria may accompany depression, anxiety, or agitation. In psychiatry Intense states of distress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypical Depression
Atypical depression is defined in the '' DSM IV'' as depression that shares many of the typical symptoms of major depressive disorder or dysthymia but is characterized by improved mood in response to positive events. In contrast to those with atypical depression, people with melancholic depression generally do not experience an improved mood in response to normally pleasurable events. Atypical depression also often features significant weight gain or an increased appetite, hypersomnia, a heavy sensation in the limbs, and interpersonal rejection sensitivity that results in significant social or occupational impairment.American Psychiatric Association. (2000). Mood Disorders. In Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (4th ed., text rev.) Washington, DC: Author. Despite its name, "atypical" depression does not mean it is uncommon or unusual. The reason for its name is twofold: it was identified with its "unique" symptoms subsequent to the identification of melanchol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rejection Sensitivity
Social rejection occurs when an individual is deliberately excluded from a interpersonal relationship, social relationship or social interaction. The topic includes ''interpersonal rejection'' (or peer rejection), ''romantic rejection'' and ''familial estrangement''. A person can be rejected or shunned by individuals or an entire group of people. Furthermore, rejection can be either ''active'', by bullying, teasing, or ridiculing, or ''passive-aggressive behaviour, passive'', by ignoring a person, or giving the "silent treatment". The experience of being rejected is subjectivity, subjective for the recipient, and it can be perception, perceived when it is not actually present. The word "ostracism" is also commonly used to denote a process of social exclusion (in Ancient Greece, ''ostracism'' was a form of temporary banishment following a people's vote). Although humans are society, social beings, some level of rejection is an inevitable part of life. Nevertheless, rejection can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
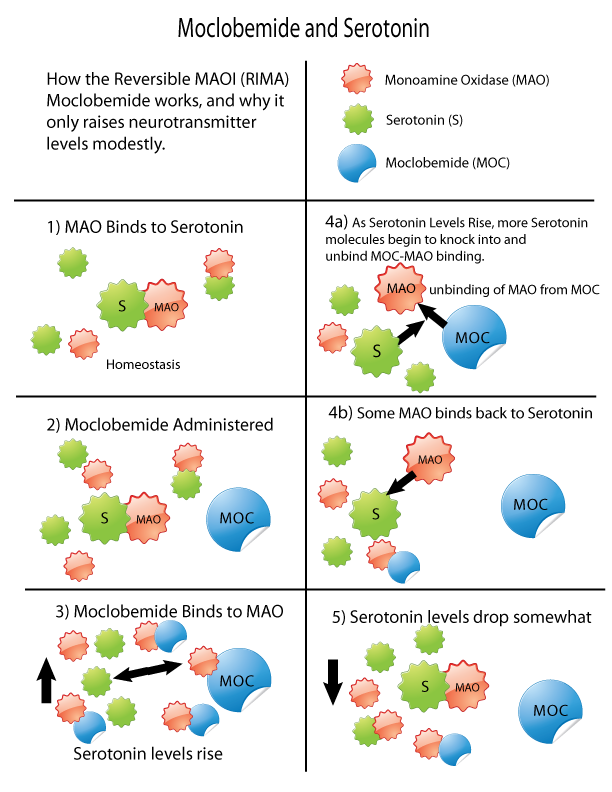
MAOI
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders. Reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase A (RIMAs) are a subclass of MAOIs that selectively and reversibly inhibit the MAO-A enzyme. RIMAs are used clinically in the treatment of depression and dysthymia. Due to their reversibility, they are safer in single-drug overdose than the older, irreversible MAOIs, and weaker in increasing the monoamines important in depressive disorder. RIMAs have not gained widespread market share in the United States. Medical uses MAOIs have been found to be effective in the treatment of panic disorder with agoraphobia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysphoria
Dysphoria (; ) is a profound state of unease or dissatisfaction. It is the semantic opposite of euphoria. In a psychiatric context, dysphoria may accompany depression, anxiety, or agitation. In psychiatry Intense states of distress and unease increase the risk of suicide, as well as being unpleasant in themselves. Relieving dysphoria is therefore a priority of psychiatric treatment. One may treat underlying causes such as depression or bipolar disorder as well as the dysphoric symptoms themselves. The '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM-5) categorizes specific dysphoria in the obsessive–compulsive spectrum. Dissatisfaction with being able-bodied can be diagnosed as body integrity dysphoria in the ICD-11. Gender dysphoria Gender dysphoria is discomfort, unhappiness or distress due to one's assigned sex. The current edition (DSM-5) of the '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' uses the term "gender dysphoria" where it pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low mood and aversion to activity, which affects more than 280 million people of all ages (about 3.5% of the global population). Classified medically as a mental and behavioral disorder, the experience of depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, motivation, feelings, and sense of well-being. The core symptom of depression is said to be anhedonia, which refers to loss of interest or a loss of feeling of pleasure in certain activities that usually bring joy to people. Depressed mood is a symptom of some mood disorders such as major depressive disorder and dysthymia; it is a normal temporary reaction to life events, such as the loss of a loved one; and it is also a symptom of some physical diseases and a side effect of some drugs and medical treatments. It may feature sadness, difficulty in thinking and concentration and a significant increase or decrease in appetite and time spent sleeping. People experiencing depression may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |