|
Hypoglycin B
Hypoglycin B is a naturally occurring organic compound in the species '' Blighia sapida''. It is particularly concentrated in the fruit of the plant especially in the seeds. Hypoglycin B is toxic if ingested and is one of the causative agents of Jamaican vomiting sickness. It is a dipeptide of glutamic acid Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can ... and hypoglycin A. References Alpha-Amino acids Dipeptides Dicarboxylic acids Toxic amino acids {{OrganicAcid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blighia Sapida
The ackee (''Blighia sapida''), also known as acki, akee, or ackee apple, is a fruit of the Sapindaceae ( soapberry) family, as are the lychee and the longan. It is native to tropical West Africa. The scientific name honours Captain William Bligh who took the fruit from Jamaica to the Royal Botanic Gardens in Kew, England, in 1793. The English common name is derived from the West African Akan-language name . Although having a long-held reputation as being poisonous with potential fatalities, the fruit arils are renowned as delicious when ripe, prepared properly, and cooked and are a feature of various Caribbean cuisines. Ackee is the national fruit of Jamaica and is considered a delicacy. Botany Ackee is an evergreen tree that grows about 10 metres tall, with a short trunk and a dense crown. The leaves are paripinnately, compound long, with 6–10 elliptical to oblong leathery leaflets. Each leaflet is long and wide. The inflorescences are fragrant, up to 20& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamaican Vomiting Sickness
Jamaican vomiting sickness, also known as toxic hypoglycemic syndrome (THS), acute ackee fruit intoxication, or ackee poisoning, is an acute illness caused by the toxins hypoglycin A and hypoglycin B, which are present in fruit of the ackee tree. Unripe arils contain concentrations of hypoglycin A that are 20-fold higher than those of ripe arils, and can cause vomiting and even death. Some countries in the Caribbean and Western Africa experience frequent cases. Presentation Abdominal discomfort begins two to six hours after eating unripe ackee fruit, followed by sudden onset vomiting. In severe cases, profound dehydration, seizures, coma, and death may ensue. Children and those who are malnourished are more susceptible to the disease. Pathophysiology When ingested, hypoglycin A is metabolized to produce methylenecyclopropylacetic acid (MCPA). MCPA acts to inhibit the beta-oxidation of fatty acids in two ways. First, it interferes with the transport of long-chain fatty acids i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medscape
Medscape is a website providing access to medical information for clinicians and medical scientists; the organization also provides continuing education for physicians and other health professionals. It references medical journal articles, Continuing Medical Education (CME), a version of the National Library of Medicine's MEDLINE database, medical news, and drug information (Medscape Drug Reference, or MDR). At one time Medscape published seven electronic peer reviewed journals. History Medscape launched May 22, 1995, by SCP Communications, Inc. under the direction of its CEO Peter Frishauf. The first editor of Medscape was a P.A. named Stephen Smith. In 1999, George D. Lundberg became the editor-in-chief of Medscape. For seventeen years before joining Medscape he served as editor of the ''Journal of the American Medical Association''. In September 1999, Medscape, Inc. went public and began trading on NASDAQ under the symbol MSCP. In 2000, Medscape merged with MedicaLogic, In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipeptide
A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener. Dipeptides are white solids. Many are far more water-soluble than the parent amino acids. For example, the dipeptide Ala-Gln has the solubility of 586 g/L more than 10x the solubility of Gln (35 g/L). Dipeptides also can exhibit different stabilities, e.g. with respect to hydrolysis. Gln does not withstand sterilization procedures, whereas this dipeptide does. Because dipeptides are prone to hydrolysis, the high solubility is exploited in infusions, i.e. to provide nutrition. Examples Commercial value About six dipeptides are of commercial interest. *Aspartame (''N''-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glutamic Acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; known as glutamate in its anionic form) is an α- amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synthesize enough for its use. It is also the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system. It serves as the precursor for the synthesis of the inhibitory gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in GABAergic neurons. Its molecular formula is . Glutamic acid exists in two optically isomeric forms; the dextrorotatory -form is usually obtained by hydrolysis of gluten or from the waste waters of beet-sugar manufacture or by fermentation.Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language Unabridged, Third Edition, 1971. Its molecular structure could be idealized as HOOC−CH()−()2−COOH, with two carboxyl groups −COOH and one amino group −. However, in the solid state and mildly acidic water s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycin A
Hypoglycin A is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative found in the unripened fruit of the Ackee tree ('' Blighia sapida'') and in the seeds of the box elder tree (''Acer negundo''). It is toxic if ingested, and is the causative agent of Jamaican vomiting sickness. A 2017 Lancet report established a link between the consumption of unripened lychees (containing hypoglycin A or methylenecyclopropylglycine (MCPG)) resulting in hypoglycaemia and death from acute toxic encephalopathy. Sources The entirety of the unripe Ackee fruit is toxic and contains large amounts of hypoglycin. The fruit is safe to eat only when the fruit is allowed to fully open and expose the large black seeds while on the tree. The levels of the toxin decrease over time though from approximately 1000 ppm to around 0.1 ppm in the mature fruit. Relatives of Ackee, including lychee, longan, and rambutan, can contain enough α-(methylenecyclopropyl)glycine, a homologue of hypoglycin A, in their fruit to caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-Amino Acids
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipeptides
A dipeptide is an organic compound derived from two amino acids. The constituent amino acids can be the same or different. When different, two isomers of the dipeptide are possible, depending on the sequence. Several dipeptides are physiologically important, and some are both physiologically and commercially significant. A well known dipeptide is aspartame, an artificial sweetener. Dipeptides are white solids. Many are far more water-soluble than the parent amino acids. For example, the dipeptide Ala-Gln has the solubility of 586 g/L more than 10x the solubility of Gln (35 g/L). Dipeptides also can exhibit different stabilities, e.g. with respect to hydrolysis. Gln does not withstand sterilization procedures, whereas this dipeptide does. Because dipeptides are prone to hydrolysis, the high solubility is exploited in infusions, i.e. to provide nutrition. Examples Commercial value About six dipeptides are of commercial interest. *Aspartame (''N''-L-α-aspartyl-L-phenylal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
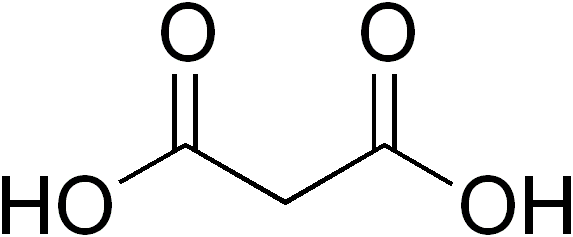
Dicarboxylic Acids
In organic chemistry, a dicarboxylic acid is an organic compound containing two carboxyl groups (). The general molecular formula for dicarboxylic acids can be written as , where R can be aliphatic or Aromatic compound, aromatic.Boy Cornils, Peter Lappe "Dicarboxylic Acids, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2014, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. In general, dicarboxylic acids show similar chemical behavior and reactivity to carboxylic acid, monocarboxylic acids. Dicarboxylic acids are usually colorless solids. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are used in industry. Adipic acid, for example, is a precursor to certain kinds of nylon. A wide variety of dicarboxylic acids are found in nature. Aspartic acid and glutamic acid are two amino acids found in all life. Succinic and fumaric acids are essential for metabolism. A large inventory of derivatives are known including many mono- and diesters, amides, etc. Partial list of saturated dicarboxylic acids Some common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |