|
Hypoglossal Nerve Stimulation
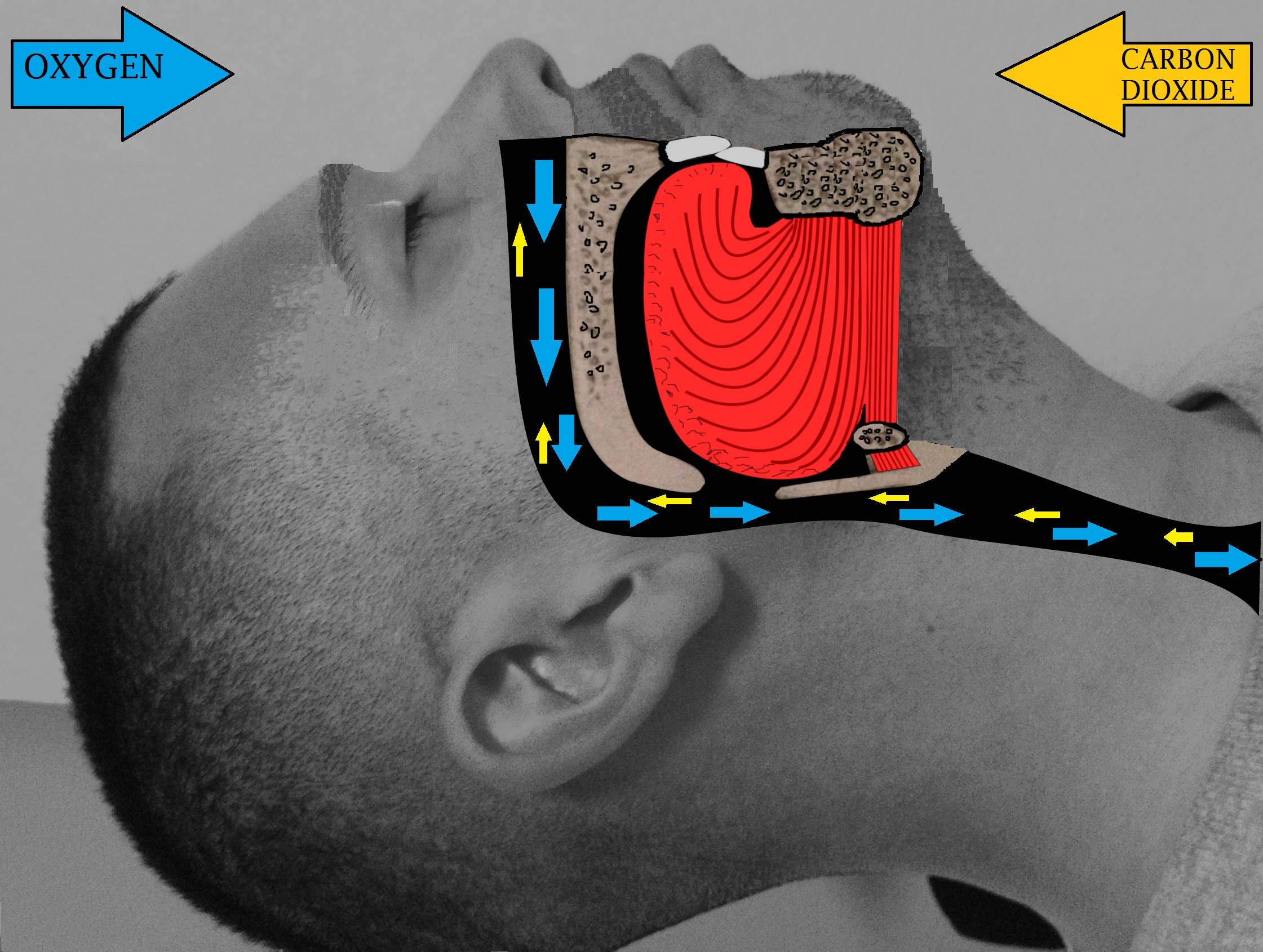
Hypoglossal nerve stimulation (HNS) is a treatment for obstructive sleep apnea. It involves implanting a small device that sends electrical impulses to the hypoglossal nerve (the twelfth cranial nerve) during sleep, causing the tongue to move forward and preventing airway blockage. The first HNS device was approved for use in Europe in 2013 and by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2014, and since then the treatment has been adopted in multiple countries for thousands of patients. Eligibility criteria HNS therapy is intended for adults with moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea who meet specific medical criteria. Candidates typically have an apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) between about 15 and 65 events per hour, indicating moderate or severe OSA. Patients should first have attempted CPAP therapy, and either failed to achieve adequate results or been unable to tolerate CPAP use. Because obesity can contribute to poor outcomes with HNS, candidates are usually re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway leading to reduced or absent breathing during sleep. These episodes are termed "apneas" with complete or near-complete cessation of breathing, or "hypopneas" when the reduction in breathing is partial. In either case, a fall in oxygen saturation (medicine), blood oxygen saturation, a disruption in sleep, or both, may result. A high frequency of apneas or hypopneas during sleep may interfere with the quality of sleep, whichin combination with disturbances in blood oxygenationis thought to contribute to negative consequences to health and quality of life. The terms obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) or obstructive sleep apnea–hypopnea syndrome (OSAHS) may be used to refer to OSA when it is associated with symptoms during the daytime (e.g. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genioglossus
The genioglossus is one of the paired extrinsic muscles of the tongue. It is a fan-shaped muscle that comprises the bulk of the body of the tongue. It arises from the mental spine of the mandible; it inserts onto the hyoid bone, and the bottom of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). The genioglossus is the major muscle responsible for protruding (or sticking out) the tongue. Structure Genioglossus is the fan-shaped extrinsic tongue muscle that forms the majority of the body of the tongue. The muscle is paired, having a left and right portion, which are divided at the midline of the tongue by a septum made of connective tissue. Origin The large part of the muscle arises from the mental spine of the mandible, but some fibers originate directly from the hyoid bone and connect vertically to the tongue. Insertion Its insertions are the hyoid bone and the bottom of the tongue. Innervation The genioglossus is innervated by the hypoglos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Surgery
Sleep surgery is a range of surgical procedures to treat sleep-related breathing disorders (sleep-disordered breathing), especially obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). The spectrum of sleep-related breathing disorders also includes Snoring, primary snoring (non apneic snoring), upper airway resistance syndrome, and obesity hypoventilation syndrome. These surgeries are performed by surgeons trained in otolaryngology, oral maxillofacial surgery, and craniofacial surgery. Background Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is defined as either cessation of breathing (apnea) for 10 seconds, or a decrease in normal breathing (hypopnea) with an associated desaturation in oxygen and arousal during sleep that lasts at least 10 seconds. In adults, it is typical to have up to 4.9 events per hour. In OSA, affected individuals are categorized based on how many apneas or hypopneas (apnea-hypopnea index or AHI) or events they have per hour. * Normal: <5 events per hour * Mild: 5 to <15 events per hour * M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Devices
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of Archaeology, archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it was not until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleep Disorders
A sleep disorder, or somnipathy, is a medical disorder affecting an individual's sleep patterns, sometimes impacting physical, mental, social, and emotional functioning. Polysomnography and actigraphy are tests commonly ordered for diagnosing sleep disorders. Sleep disorders are broadly classified into dyssomnias, parasomnias, circadian rhythm sleep disorders involving the timing of sleep, and other disorders, including those caused by medical or psychological conditions. When a person struggles to fall asleep or stay asleep without any obvious cause, it is referred to as insomnia, which is the most common sleep disorder. Other sleep disorders include sleep apnea, narcolepsy, hypersomnia (excessive sleepiness at inappropriate times), sleeping sickness (disruption of the sleep cycle due to infection), sleepwalking, and night terrors. Sleep disruptions can be caused by various issues, including teeth grinding (bruxism) and night terrors. Managing sleep disturbances that are seconda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implants (medicine)
Implant can refer to: Medicine *Implant (medicine), or specifically: ** Brain implant **Breast implant ** Buttock implant **Cochlear implant ** Contraceptive implant **Dental implant ** Fetal tissue implant ** Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator ** Orthopedic implant ** Prosthetic implant ** Retinal implant ** Subdermal implant ** Transdermal implant Alternative * Alien implants * Extraocular implant * Implant (body modification) * Implant (thought insertion) *Microchip implant (animal) (human) *'' The Implant'', a television episode of ''Seinfeld ''Seinfeld'' ( ) is an American television sitcom created by Larry David and Jerry Seinfeld that originally aired on NBC from July 5, 1989, to May 14, 1998, with a total of nine seasons consisting of List of Seinfeld episodes, 180 episodes. It ...'' See also * History of dental treatments * Implantation (other) * Osseointegration * Osseoincorporation {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otorhinolaryngology
Otorhinolaryngology ( , abbreviated ORL and also known as otolaryngology, otolaryngology–head and neck surgery (ORL–H&N or OHNS), or ear, nose, and throat (ENT)) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the surgical and medical management of conditions of the head and neck. Doctors who specialize in this area are called otorhinolaryngologists, otolaryngologists, head and neck surgeons, or ENT surgeons or physicians. Patients seek treatment from an otorhinolaryngologist for diseases of the ear, Human nose, nose, throat, base of skull, base of the skull, head, and neck. These commonly include functional diseases that affect the senses and activities of eating, drinking, speaking, breathing, swallowing, and hearing. In addition, ENT surgery encompasses the surgical management of cancers and benign tumors and reconstruction of the head and neck as well as plastic surgery of the face, scalp, and neck. Etymology The term is a combination of Neo-Latin classic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treatment Of Sleep Disorders
Treatment may refer to: * "Treatment" (song), a 2012 song by * Film treatment, a prose telling of a story intended to be turned into a screenplay * Medical treatment also known as "therapy" * Sewage treatment * Surface treatment or surface finishing * Water treatment * Treatment group in design of experiments See also * ''In Treatment'', an American drama television series * ''In Treatment'' (Italian TV series), an Italian drama television series * National treatment, an economic concept focused on grantings to foreigners of rights similar to those of domestic nationals * Silent treatment, a form of social rejection * The Treatment (other) * Treatment group, the collection of items or individuals receiving the same treatment in an experiment * Window treatment Window coverings are considered any type of materials used to cover a window to manage sunlight, privacy, additional weatherproofing or for purely decorative purposes. Description and design Window cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
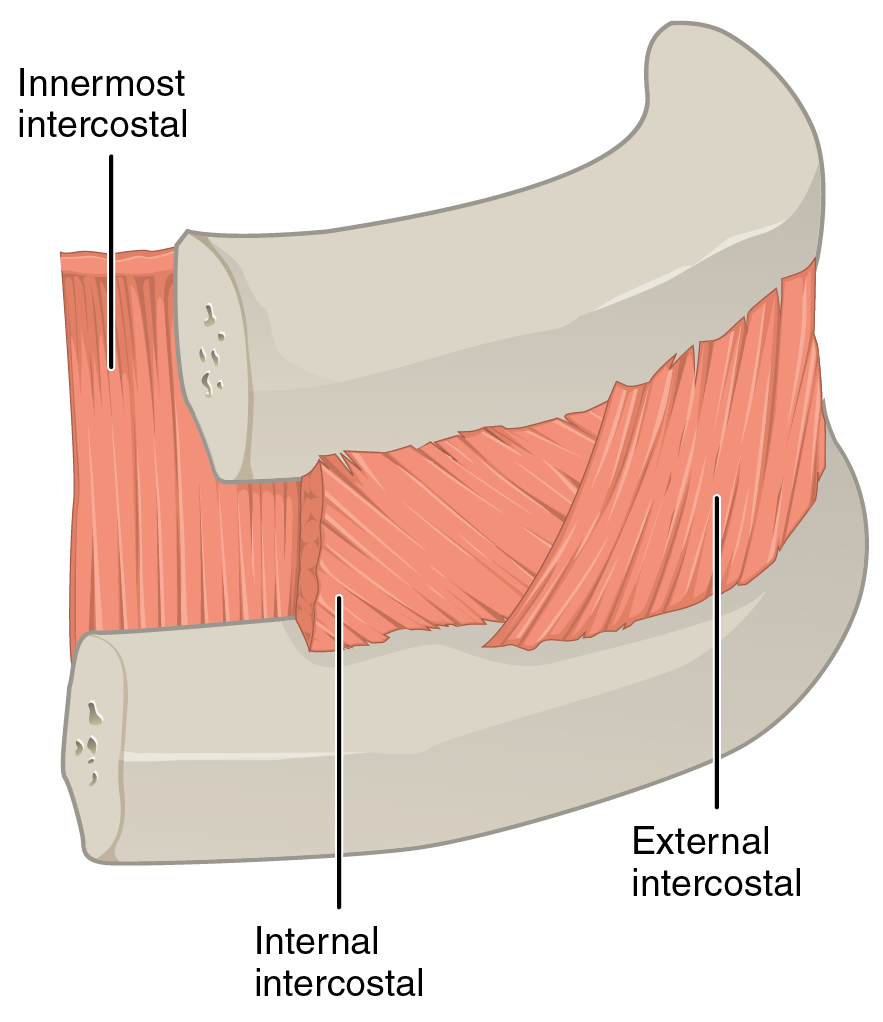
External Intercostal Muscles
The external intercostal muscles or external intercostals (intercostales externi) are eleven in number on both sides. Structure The muscles extend from the tubercles of the ribs behind, to the cartilages of the ribs in front, where they end in thin membranes, the external intercostal membranes, which are continued forward to the sternum. These muscles work in unison when inhalation occurs. The internal intercostal muscles relax while the external muscles contract causing the expansion of the chest cavity and an influx of air into the lungs. Each arises from the lower border of a rib, and is inserted into the upper border of the rib below. In the two lower spaces they extend to the ends of the cartilages, and in the upper two or three spaces they do not quite reach the ends of the ribs. They are thicker than the internal intercostals, and their fibers are directed obliquely downward and laterally on the back of the thorax, and downward, forward, and medially on the front. V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Intercostal Muscles
The internal intercostal muscles (intercostales interni) are a group of skeletal muscles located between the ribs. They are eleven in number on either side. They commence anteriorly at the sternum, in the intercostal spaces between the cartilages of the true ribs, and at the anterior extremities of the cartilages of the false ribs, and extend backward as far as the angles of the ribs, hence they are continued to the vertebral column by thin aponeuroses, the posterior intercostal membranes. They pull the sternum and ribs upward and inward. Structure Their fibers are also directed obliquely, but pass in a direction opposite to those of the external intercostal muscles. The internal intercostal muscles originate from the costal groove of the rib and insert into the superior aspect of the rib below in a direction perpendicular to the external intercostal muscles. It is this arrangement that allows these muscles to facilitate exhalation. For the most part, they are muscles of exh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib Cage
The rib cage or thoracic cage is an endoskeletal enclosure in the thorax of most vertebrates that comprises the ribs, vertebral column and sternum, which protect the vital organs of the thoracic cavity, such as the heart, lungs and great vessels and support the shoulder girdle to form the core part of the axial skeleton. A typical human thoracic cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs and the adjoining costal cartilages, the sternum (along with the manubrium and xiphoid process), and the 12 thoracic vertebrae articulating with the ribs. The thoracic cage also provides attachments for extrinsic skeletal muscles of the neck, upper limbs, upper abdomen and back, and together with the overlying skin and associated fascia and muscles, makes up the thoracic wall. In tetrapods, the rib cage intrinsically holds the muscles of respiration ( diaphragm, intercostal muscles, etc.) that are crucial for active inhalation and forced exhalation, and therefore has a major ventilatory fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soft Palate
The soft palate (also known as the velum, palatal velum, or muscular palate) is, in mammals, the soft biological tissue, tissue constituting the back of the roof of the mouth. The soft palate is part of the palate of the mouth; the other part is the hard palate. The soft palate is distinguished from the hard palate at the front of the mouth in that it does not contain bone. Structure Muscles The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: # Tensor veli palatini, which is involved in swallowing # Palatoglossus, involved in swallowing # Palatopharyngeus, involved in breathing # Levator veli palatini, involved in swallowing # Musculus uvulae, which moves the palatine uvula, uvula These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus of vagus nerve, pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini. The tensor veli palatini is innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |