|
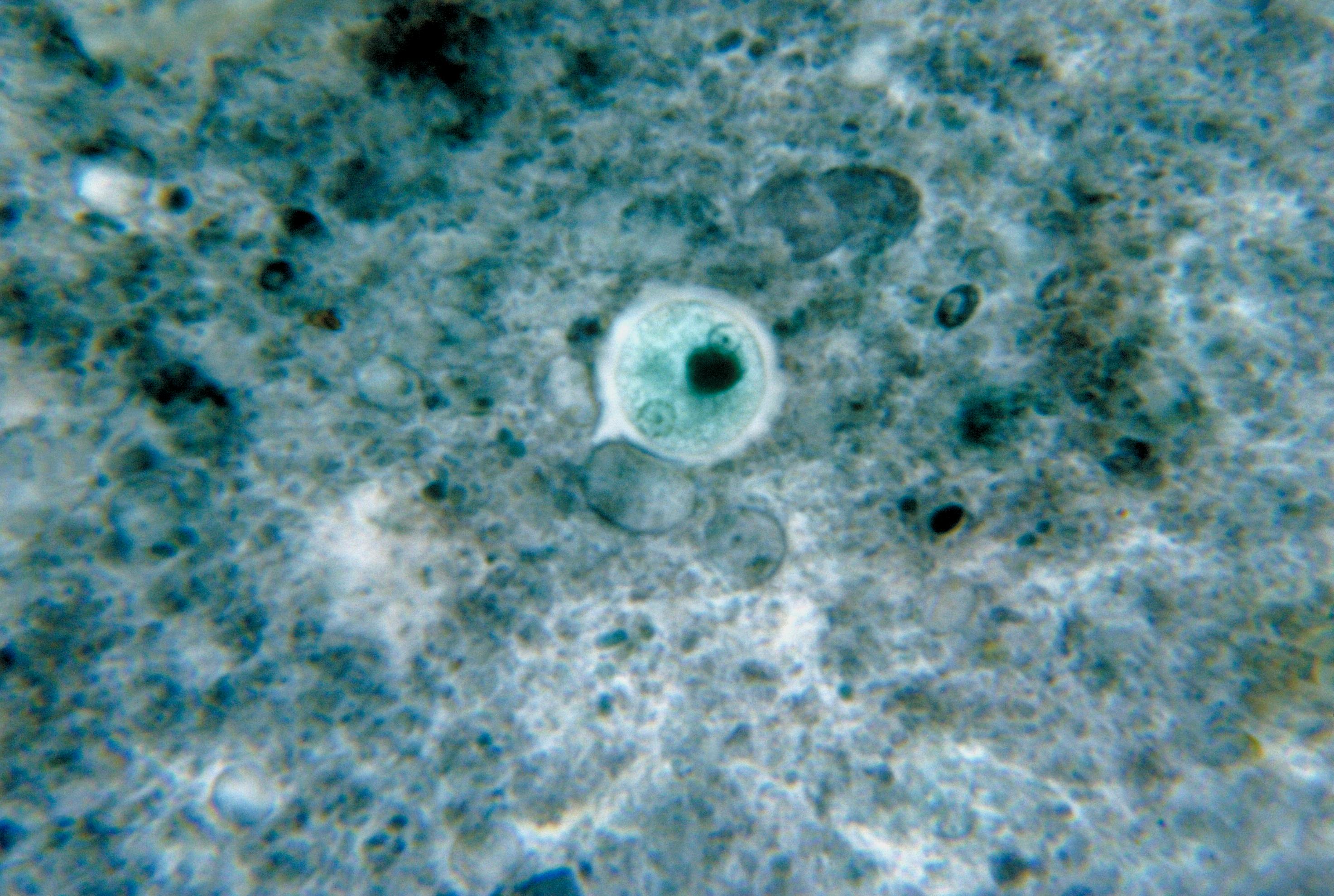
Hypnozygote
A hypnozygote is a resting cyst A cyst is a closed sac, having a distinct envelope and division compared with the nearby tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubb ... resulting from sexual fusion; it is commonly thick-walled. A synonym of zygotic cyst. Hypnozygotes have the ability to remain dormant in mud and other sediments until conditions become more favorable for growth. References Cysts Microbiology {{microbiology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Cyst
A microbial cyst is a resting or dormant stage of a microorganism, that can be thought of as a state of suspended animation in which the metabolic processes of the cell are slowed and the cell ceases all activities like feeding and locomotion. Many groups of single-celled, microscopic organisms, or microbes, possess the ability to enter this dormant state. Encystment, the process of cyst formation, can function as a method for dispersal and as a way for an organism to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. These two functions can be combined when a microbe needs to be able to survive harsh conditions between habitable environments (such as between hosts) in order to disperse. Cysts can also be sites for nuclear reorganization and cell division, and in parasitic species they are often the infectious stage between hosts. When the encysted microbe reaches an environment favorable to its growth and survival, the cyst wall breaks down by a process known as excystation. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygotic
A zygote (; , ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism. The sexual fusion of haploid cells is called karyogamy, the result of which is the formation of a diploid cell called the zygote or zygospore. History German zoologists Oscar and Richard Hertwig made some of the first discoveries on animal zygote formation in the late 19th century. In multicellular organisms The zygote is the earliest developmental stage. In humans and most other anisogamous organisms, a zygote is formed when an egg cell and sperm cell come together to create a new unique organism. The formation of a totipotent zygote with the potential to produce a whole organism depends on epigenetic reprogramming. DNA demethylation of the paternal genome in the zygote appears to be an important part of epigenetic reprogramming. In the patern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysts
A cyst is a closed Wikt:sac, sac, having a distinct Cell envelope, envelope and cell division, division compared with the nearby Biological tissue, tissue. Hence, it is a cluster of Cell (biology), cells that have grouped together to form a sac (like the manner in which water molecules group together to form a bubble); however, the distinguishing aspect of a cyst is that the cells forming the "shell" of such a sac are distinctly abnormal (in both appearance and behaviour) when compared with all surrounding cells for that given location. A cyst may contain air, fluids, or semi-solid material. A collection of pus is called an abscess, not a cyst. Once formed, a cyst may resolve on its own. When a cyst fails to resolve, it may need to be removed surgically, but that would depend upon its type and location. Cancer-related cysts are formed as a defense mechanism for the body following the development of mutations that lead to an uncontrolled cellular division. Once that mutation has o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |