|
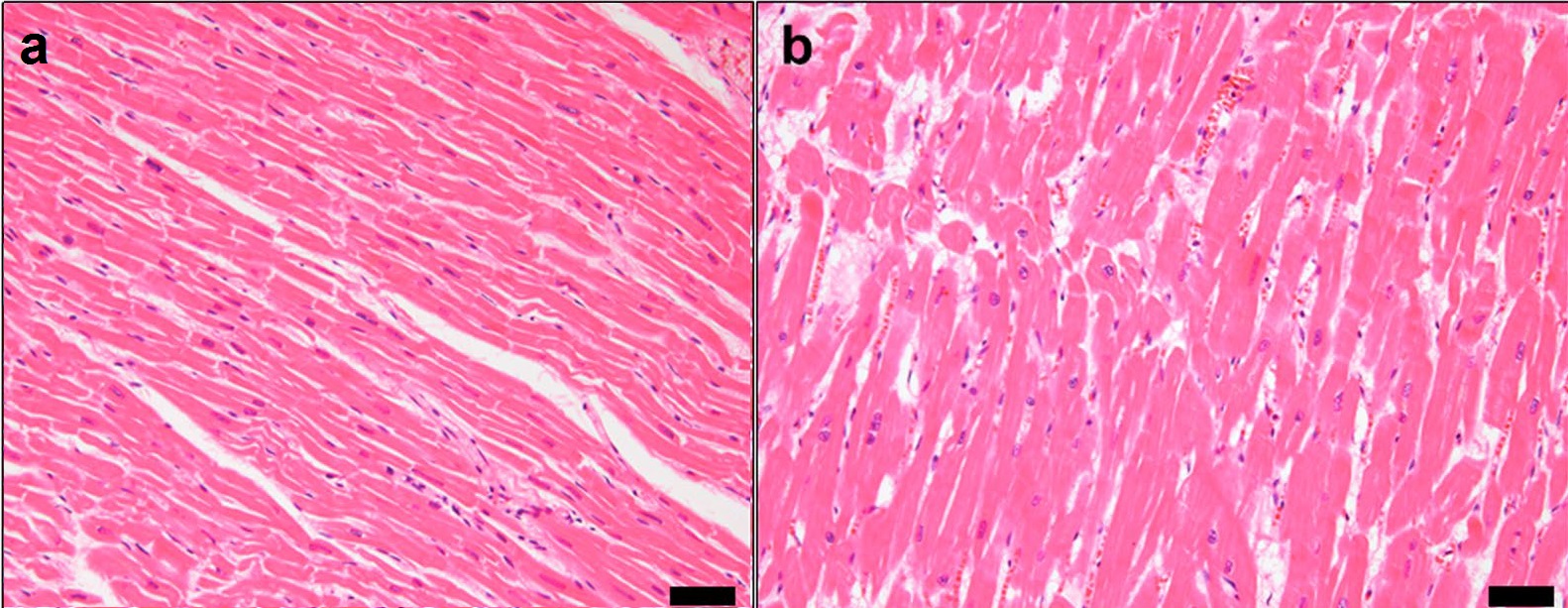
Hypertrophic
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery Gould Pyle 234.jpg, Breasts Hypertrophied clitoris.jpg, Clitoris Head of a boy with hypertrophy of the ear Wellcome L0062496.jpg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM, or HOCM when obstructive) is a condition in which muscle tissues of the heart become thickened without an obvious cause. The parts of the heart most commonly affected are the interventricular septum and the ventricles. This results in the heart being less able to pump blood effectively and also may cause electrical conduction problems. Specifically, within the bundle branches that conduct impulses through the interventricular septum and into the Purkinje fibers, as these are responsible for the depolarization of contractile cells of both ventricles. People who have HCM may have a range of symptoms. People may be asymptomatic, or may have fatigue, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Symptoms may be worse when the person is dehydrated. Complications may include heart failure, an irregular heartbeat, and sudden cardiac death. HCM is most commonly inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athlete's Heart
Athletic heart syndrome (AHS) is a non-pathological condition commonly seen in sports medicine in which the human heart is enlarged, and the resting heart rate is lower than normal. The athlete's heart is associated with physiological cardiac remodeling as a consequence of repetitive cardiac loading. Athlete's heart is common in athletes who routinely exercise more than an hour a day, and occurs primarily in endurance athletes, though it can occasionally arise in heavy weight trainers. The condition is generally considered benign, but may occasionally hide a serious medical condition, or may even be mistaken for one. Signs and symptoms Athlete's heart most often does not have any physical symptoms, although an indicator would be a consistently low resting heart rate. Athletes with AHS often do not realize they have the condition unless they undergo specific medical tests, because athlete's heart is a normal, physiological adaptation of the body to the stresses of physical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both ventricles can also occur. Ventricular hypertrophy can result from a variety of conditions, both adaptive and maladaptive. For example, it occurs in what is regarded as a physiologic, adaptive process in pregnancy in response to increased blood volume; but can also occur as a consequence of ventricular remodeling following a heart attack. Importantly, pathologic and physiologic remodeling engage different cellular pathways in the heart and result in different gross cardiac phenotypes. Presentation In individuals with eccentric hypertrophy there may be little or no indication that hypertrophy has occurred as it is generally a healthy response to increased demands on the heart. Conversely, concentric hypertrophy can make itself known in a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentric Hypertrophy
Concentric hypertrophy is a hypertrophic growth of a hollow organ without overall enlargement, in which the walls of the organ are thickened and its capacity or volume is diminished. Sarcomeres are added in parallel, as for example occurs in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In the heart, concentric hypertrophy is related to increased pressure overload of the heart, often due to hypertension and/or aortic stenosis. The consequence is a decrease in ventricular compliance and diastolic dysfunction Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the ..., followed eventually by ventricular failure and systolic dysfunction. Laplace's law for a sphere states wall stress (T) is proportionate to the product of the transmural pressure (P) and cavitary radius (r) and inversely proportionate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Causes While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular disease, or high blood pressure. It is one aspect of ventricular remodeling. While LVH itself is not a disease, it is usually a marker for disease involving the heart. Disease processes that can cause LVH include any disease that increases the afterload that the heart has to contract against, and some primary diseases of the muscle of the heart. Causes of increased afterload that can cause LVH include aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency and hypertension. Primary disease of the muscle of the heart that cause LVH are known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, which can lead into heart failure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, prevent injuries, hone athletic skills, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many people choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, usually, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week is recommended for reducing the risk of health problems. At the same time, even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Only doing an hour and a quarter (11 minutes/day) of exercise could reduce the risk of early death, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Hypertrophy
Muscle hypertrophy or muscle building involves a hypertrophy or increase in size of skeletal muscle through a growth in size of its component cells. Two factors contribute to hypertrophy: sarcoplasmic hypertrophy, which focuses more on increased muscle glycogen storage; and myofibrillar hypertrophy, which focuses more on increased myofibril size. It is the primary focus of bodybuilding-related activities. Hypertrophy stimulation A range of stimuli can increase the volume of muscle cells. These changes occur as an adaptive response that serves to increase the ability to generate force or resist fatigue in anaerobic conditions. Strength training Strength training (resistance training) causes neural and muscular adaptations which increase the capacity of an athlete to exert force through voluntary muscular contraction: After an initial period of neuro-muscular adaptation, the muscle tissue expands by creating sarcomeres (contractile elements) and increasing non-contractile ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the right lower chamber of the heart and it receives deoxygenated blood from the right upper chamber (right atrium) and pumps blood into the lungs. Since RVH is an enlargement of muscle it arises when the muscle is required to work harder. Therefore, the main causes of RVH are pathologies of systems related to the right ventricle such as the pulmonary artery, the tricuspid valve or the airways. RVH can be benign and have little impact on day-to-day life or it can lead to conditions such as heart failure, which has a poor prognosis. Signs and symptoms Symptoms Although presentations vary, individuals with right ventricular hypertrophy can experience symptoms that are associated with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and/or a reduced cardiac output. These i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Biological Development Disorders
The following is a list of terms used to describe biological disorders of development, arranged by root word and shared prefix: References Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Biological development disorders Lists of diseases Disability-related lists Biological nomenclature Medical terminology Lists of biology lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingival Enlargement
Gingival enlargement is an increase in the size of the gingiva (gums). It is a common feature of gingival disease. Gingival enlargement can be caused by a number of factors, including inflammatory conditions and the side effects of certain medications. The treatment is based on the cause. A closely related term is epulis, denoting a localized tumor (i.e. lump) on the gingiva. Classification The terms gingival hyperplasia and gingival hypertrophy have been used to describe this topic in the past. These are not precise descriptions of gingival enlargement because these terms are strictly histologic diagnoses, and such diagnoses require microscopic analysis of a tissue sample. Hyperplasia refers to an increased number of cells, and hypertrophy refers to an increase in the size of individual cells. As these identifications cannot be performed with a clinical examination and evaluation of the tissue, the term ''gingival enlargement'' is more properly applied. Gingival enlargement ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroglossia
Macroglossia is the medical term for an unusually large tongue. Severe enlargement of the tongue can cause cosmetic and functional difficulties in speaking, eating, Dysphagia, swallowing and sleeping. Macroglossia is uncommon, and usually occurs in children. There are many causes. Treatment depends upon the exact cause. Signs and symptoms Although it may be asymptomatic, symptoms usually are more likely to be present and more severe with larger tongue enlargements. Signs and symptoms include: * Dyspnea – difficult, noisy breathing, obstructive sleep apnea or airway obstruction * Dysphagia – difficulty swallowing and eating * Dysphonia – disrupted speech, possibly manifest as lisping * Sialorrhea – drooling * Angular cheilitis – sores at the corners of the mouth * Crenated tongue – indentations on the lateral borders of the tongue caused by pressure from teeth ("pie crust tongue") * Open bite malocclusion – a type of malocclusion of the teeth * Mandibular prognathis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |