|
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition in which a person exhibits excessive perspiration, sweating, more than is required for the Thermoregulation, regulation of body temperature. Although it is primarily a physical burden, hyperhidrosis can deteriorate the quality of life of the people who are affected, frequently leading to psychological, physical, and social consequences. Hyperhidrosis can lead to difficulties in professional fields, with more than 80% of patients experiencing moderate to severe emotional effects from the disease. This excess of sweat happens even if the person is not engaging in tasks that require muscular effort, and it does not depend on the exposure to heat. Common places to sweat can include underarms, face, neck, back, groin, feet, and hands. It has been called by some researchers 'the silent handicap'. Both ''diaphoresis'' and ''hidrosis'' can mean either ''perspiration'' (in which word sense, sense they are synonymous with ''sweating'') or ''excessive per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidrosis
Hyperhidrosis is a medical condition in which a person exhibits excessive sweating, more than is required for the regulation of body temperature. Although it is primarily a physical burden, hyperhidrosis can deteriorate the quality of life of the people who are affected, frequently leading to psychological, physical, and social consequences. Hyperhidrosis can lead to difficulties in professional fields, with more than 80% of patients experiencing moderate to severe emotional effects from the disease. This excess of sweat happens even if the person is not engaging in tasks that require muscular effort, and it does not depend on the exposure to heat. Common places to sweat can include underarms, face, neck, back, groin, feet, and hands. It has been called by some researchers 'the silent handicap'. Both '' diaphoresis'' and '' hidrosis'' can mean either ''perspiration'' (in which sense they are synonymous with ''sweating'') or ''excessive perspiration'', in which case they refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
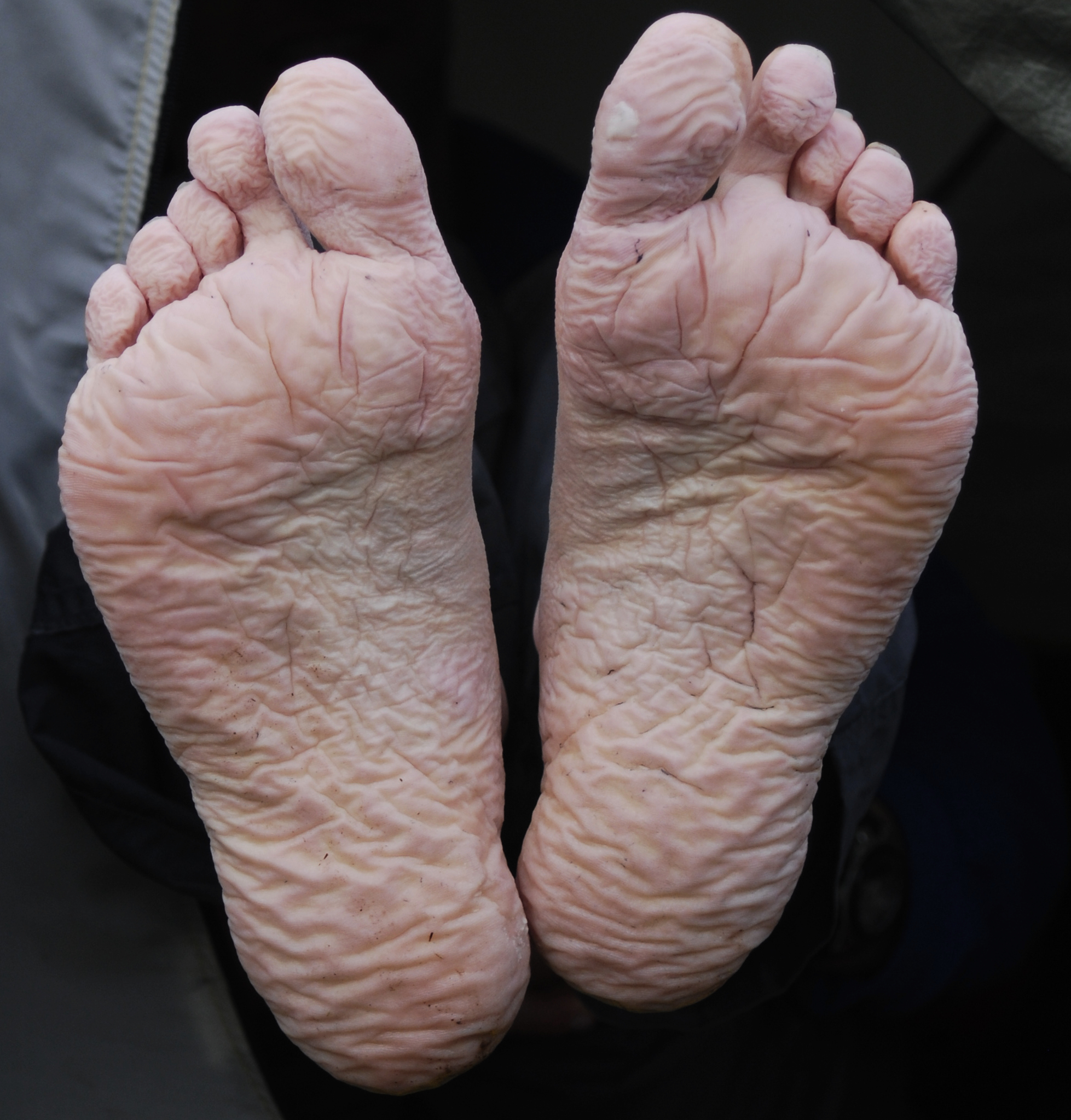
Focal Hyperhidrosis
Focal hyperhidrosis, also known as primary hyperhidrosis, is a disease characterized by an excessive sweating localized in certain body regions (particularly palms, feet and underarms). Studies suggest that this condition, affecting between 1% and 3% of the US population, seems to have a genetic predisposition in about two thirds of those affected. Focal hyperhidrosis is sometimes referred to as ''The Silent Handicap'', as it has a significant impact on the quality of life, affecting the individual socially, psychologically, emotionally and professionally. Genetics In 2006, researchers uncovered that primary palmar hyperhidrosis, referring to excess sweating on the palms of the hands and feet, maps to the gene locus 14q11.2-q13. Based on previous research using mice and rats, researchers looked towards the role of aquaporin 5 (AQP5), a water channel protein, in human individuals with primary focal hyperhidrosis. AQP5 has been identified as a candidate gene in many hyperhidr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspiration
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and Apocrine sweat gland, apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the body and are responsible for secreting the watery, brackish sweat most often triggered by excessive body temperature. Apocrine sweat glands are restricted to the armpits and a few other areas of the body and produce an odorless, oily, opaque secretion which then gains its characteristic odor from bacterial decomposition. In humans, sweating is primarily a means of thermoregulation, which is achieved by the water-rich secretion of the eccrine glands. Maximum sweat rates of an adult can be up to per hour or per day, but is less in children prior to puberty. Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface has a cooling effect due to evaporative cooling. Hence, in Temperature, hot weather, or when the individual's muscles hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphoresis
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the body and are responsible for secreting the watery, brackish sweat most often triggered by excessive body temperature. Apocrine sweat glands are restricted to the armpits and a few other areas of the body and produce an odorless, oily, opaque secretion which then gains its characteristic odor from bacterial decomposition. In humans, sweating is primarily a means of thermoregulation, which is achieved by the water-rich secretion of the eccrine glands. Maximum sweat rates of an adult can be up to per hour or per day, but is less in children prior to puberty. Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface has a cooling effect due to evaporative cooling. Hence, in hot weather, or when the individual's muscles heat up due to exertion, more sweat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sweat Gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. There are two main types of sweat glands that differ in their structure, function, secretory product, mechanism of excretion, anatomic distribution, and distribution across species: * Eccrine sweat glands are distributed almost all over the human body, in varying densities, with the highest density in palms and soles, then on the head, but much less on the trunk and the extremities. Their water-based secretion represents a primary form of cooling in humans. * Apocrine sweat glands are mostly limited to the axillae (armpits) and perineal area in humans. They are not significant for cooling in humans, but are the sole effective sweat glands in hoofed animals, such as the camels, donkeys, horses, and cattle. Ceru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachydermoperiostosis
Pachydermoperiostosis (PDP) is a rare genetic disorder that affects both bones and skin. Other names are primary hypertrophic osteoarthropathy or Touraine-Solente-Golé syndrome. It is mainly characterized by pachyderma (thickening of the skin), periostosis (excessive bone formation) and finger clubbing (swelling of tissue with loss of normal angle between nail and nail bed). This disease affects more men than women. After onset, the disease stabilizes after about 5–20 years. Life of PDP patients can be severely impaired. Currently, symptomatic treatments are NSAIDs and steroids or surgical procedures. In 1868, PDP was first described by Friedreich as 'excessive growth of bone of the entire skeleton'. Touraine, Solente and Golé described PDP as the primary form of bone disease hypertrophic osteoarthropathy in 1935 and distinguished its three known forms. Symptoms and signs PDP has a number of visible signs. Most important clinical features are: pachydermia (thickening and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Foot
Trench foot, also known by #Names, other names, is a type of immersion foot syndromes, foot damage due to moisture. Initial symptoms often include tingling or itching which can progress to numbness. The feet may become erythema, red or cyanosis, bluish in color. As the condition worsens the feet can start to swell and smell of decay. Complications may include skin breakdown or infection. Trench foot occurs due to prolonged exposure of the feet to cold, damp, and often unsanitary conditions. Unlike frostbite, trench foot usually occurs at temperatures above freezing, and can be classed as a form of non-freezing cold injury. Onset can be as rapid as 10 hours. Risk factors include overly tight boots and not moving. The underlying mechanism is believed to involve vasoconstriction, constriction of blood vessels resulting in insufficient blood flow to the feet. Diagnosis is based on symptoms and physical examination, examination. Prevention involves keeping the feet warm, dry, and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eccrine Sweat Gland
Eccrine sweat glands (; from Greek '' ek(s)+krinein'' 'out(wards)/external+ secrete') are the major sweat glands of the human body. Eccrine sweat glands are found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in the palms of the hands, and soles of the feet, and on the head, but much less on the torso and the extremities. In other mammals, they are relatively sparse, being found mainly on hairless areas such as foot pads. They reach their peak of development in humans, where they may number 200–400/cm2 of skin surface.Bolognia, J., Jorizzo, J., & Schaffer, J. (2012). Dermatology (3rd ed., pp. 539-544). hiladelphia Elsevier Saunders. They produce sweat, a merocrine secretion which is clear, odorless substance, consisting primarily of water. These are present from birth. Their secretory part is present deep inside the dermis. Eccrine glands are composed of an intraepidermal spiral duct, the "acrosyringium"; a dermal duct, consisting of a straight and coiled portion; and a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustatory Hyperhidrosis
Frey's syndrome (also known as Baillarger's syndrome, Dupuy's syndrome, auriculotemporal syndrome, or Frey-Baillarger syndrome) is a rare neurological disorder resulting from damage to or near the parotid glands responsible for making saliva, and from damage to the auriculotemporal nerve often from surgery. The symptoms of Frey's syndrome are redness and sweating on the cheek area adjacent to the ear (see focal hyperhidrosis). They can appear when the affected person eats, sees, dreams, thinks about, or talks about certain kinds of food which produce strong salivation. Observing sweating in the region after eating a lemon wedge may be diagnostic. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms include erythema (redness or flushing) and sweating in the cutaneous distribution of the auriculotemporal nerve, usually in response to gustatory stimuli. There is sometimes pain in the same area, often burning in nature. Between attacks of pain, there may be numbness or other altered sensations (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burning Feet Syndrome
Burning feet syndrome, also known as Grierson-Gopalan syndrome, is a medical condition that causes severe burning and aching of the feet, hyperesthesia, and vasomotor changes of the feet that lead to excessive sweating. It can even affect the eyes, causing scotoma and amblyopia. The condition occurs more frequently in women, and usually manifests itself when a person is between twenty and forty years old. Presentation The burning heat is usually limited to the soles of the feet, but may extend up to the ankles or lower legs of some patients. The burning can sometimes be accompanied by feelings of 'pins and needles' or tingling in these regions. Nighttime is when almost all people with this syndrome report the heat symptoms being the worst, with the condition getting better as morning comes. Those who have psychosomatic disorders sometimes display psychological symptoms along with the burning of feet associated with the syndrome. For most, there is no redness of the skin of their f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
POEMS Syndrome
POEMS syndrome (also termed osteosclerotic myeloma, Crow–Fukase syndrome, Takatsuki disease, or PEP syndrome) is a rare paraneoplastic syndrome caused by a clone of aberrant plasma cells. The name POEMS is an acronym for some of the disease's major signs and symptoms (polyneuropathy, polyneuropathy, organomegaly, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, endocrinopathy, myeloma protein, myeloma protein, and cutaneous condition, skin changes), as is PEP (polyneuropathy, polyneuropathy, endocrinopathy, endocrinopathy, plasma cell dyscrasia, plasma cell dyscrasia). The signs and symptoms of most neoplasms (excessive, abnormal tissue growths) are due to their Mass effect (medicine), mass effects (compression of surrounding tissue by the mass of the growth) caused by the invasion and destruction of tissues by the neoplasms' cells. Signs and symptoms of a cancer causing a paraneoplastic syndrome result from the release of humoral factors such as hormones, cytokines, or immunoglobulins by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine chemical classification, class and is the most commonly consumed Psychoactive drug, psychoactive substance globally. It is mainly used for its eugeroic (wakefulness promoting), ergogenic (physical performance-enhancing), or nootropic (cognitive-enhancing) properties. Caffeine acts by blocking the binding of adenosine at a number of adenosine receptor types, inhibiting the centrally depressant effects of adenosine and enhancing the release of acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, cyclic AMP levels through nonselective Phosphodiesterase inhibitor, inhibition of phosphodiesterase, increases calcium release from intracellular stores, and Receptor antagonist, antagonizes GABA receptor, GABA receptors, although these mechanisms typically occur at concentrati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |