|
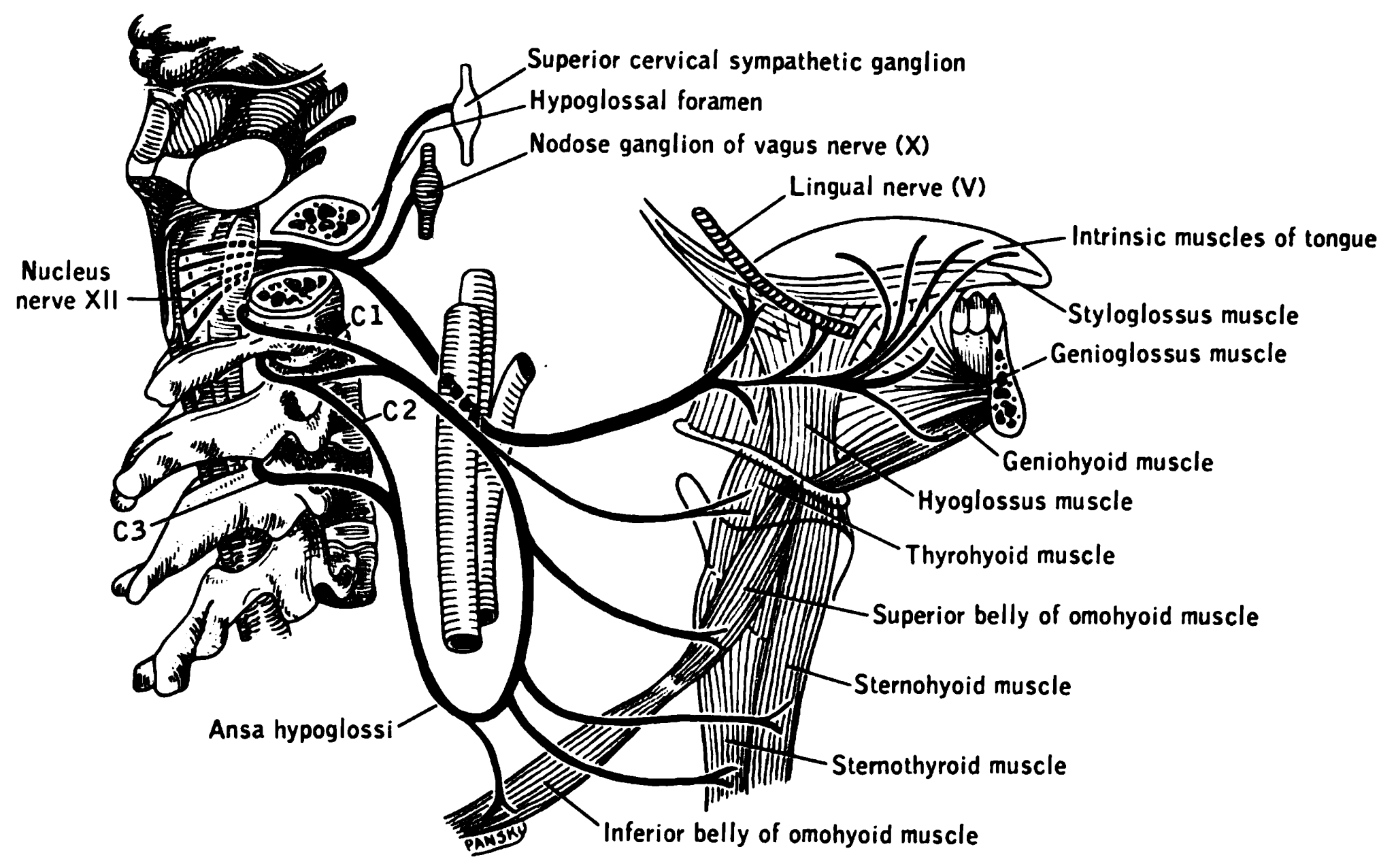
Hyoglossi
The hyoglossus is a thin and quadrilateral extrinsic muscle of the tongue. It originates from the hyoid bone; it inserts onto the side of the tongue. It is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve (cranial nerve XII). It acts to depress and retract the tongue. Structure It forms a part of the floor of submandibular triangle. Origin from the side of the body and from the whole length of the greater cornu of the hyoid bone. The fibers arising from the body of the hyoid bone overlap those from the greater cornu. Insertion Its fibres pass almost vertically upward to enter the side of the tongue, inserting between the styloglossus and the inferior longitudinal muscle of the tongue. Relations Structures that are medial/deep to the hyoglossus are the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX), the stylohyoid ligament and the lingual artery and lingual vein. The lingual vein passes medial to the hyoglossus. The lingual artery passes deep to the hyoglossus. Laterally, in between the hyoglo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tongue
The tongue is a Muscle, muscular organ (anatomy), organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for chewing and swallowing as part of the digestive system, digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste buds housed in numerous lingual papillae. It is sensitive and kept moist by saliva and is richly supplied with nerves and blood vessels. The tongue also serves as a natural means of cleaning the teeth. A major function of the tongue is to enable speech in humans and animal communication, vocalization in other animals. The human tongue is divided into two parts, an oral cavity, oral part at the front and a pharynx, pharyngeal part at the back. The left and right sides are also separated along most of its length by a vertical section of connective tissue, fibrous tissue (the lingual septum) that results in a groove, the median sulcus, on the tongue's surface. There are two groups of glossal muscles. The f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyoid
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical vertebra. Unlike other bones, the hyoid is only distantly articulated to other bones by muscles or ligaments. It is the only bone in the human body that is not connected to any other bones. The hyoid is anchored by muscles from the anterior, posterior and inferior directions, and aids in tongue movement and swallowing. The hyoid bone provides attachment to the muscles of the floor of the mouth and the tongue above, the larynx below, and the epiglottis and pharynx behind. Its name is derived . Structure The hyoid bone is classed as an irregular bone and consists of a central part called the body, and two pairs of horns, the greater and lesser horns. Body The body of the hyoid bone is the central part of the hyoid bone. *At the front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Vein
The lingual veins are veins of the tongue with two distinct courses: one group drains into the lingual vein, while another group drains either into the lingual artery, (common) facial vein, or internal jugular vein. Clinical significance The lingual veins are clinically significant due to their ability to rapidly absorb drugs. For this reason, nitroglycerin is administered sublingually to patients experiencing angina pectoris Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of part .... See also * Deep lingual vein * Dorsal lingual veins External links Photo of model (frog) References * Moore NA and Roy W. Rapid Review: Gross Anatomy. Elsevier, 2010. Veins of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylohyoid Muscle
The mylohyoid muscle or diaphragma oris is a paired muscle of the neck. It runs from the Human mandible, mandible to the hyoid bone, forming the floor of the oral cavity of the human mouth, mouth. It is named after its two attachments near the molar (tooth), molar teeth. It forms the floor of the submental triangle. It elevates the hyoid bone and the tongue, important during swallowing and Speech, speaking. Structure The mylohyoid muscle is flat and triangular, and is situated immediately Anatomical terms of location#Superior and inferior, superior to the digastric muscle, anterior belly of the digastric muscle. It is a pharyngeal musculature, pharyngeal muscle (derived from the first pharyngeal arch) and classified as one of the suprahyoid muscles. Together, the paired mylohyoid muscles form a muscular floor for the oral cavity of the human mouth, mouth. The two mylohyoid muscles arise from the mandible at the mylohyoid line, which extends from the mandibular symphysis in front ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salivary Gland
The salivary glands in many vertebrates including mammals are exocrine glands that produce saliva through a system of ducts. Humans have three paired major salivary glands ( parotid, submandibular, and sublingual), as well as hundreds of minor salivary glands. Salivary glands can be classified as serous, mucous, or seromucous (mixed). In serous secretions, the main type of protein secreted is alpha-amylase, an enzyme that breaks down starch into maltose and glucose, whereas in mucous secretions, the main protein secreted is mucin, which acts as a lubricant. In humans, 1200 to 1500 ml of saliva are produced every day. The secretion of saliva (salivation) is mediated by parasympathetic stimulation; acetylcholine is the active neurotransmitter and binds to muscarinic receptors in the glands, leading to increased salivation. A proposed fourth pair of salivary glands, the tubarial glands, were first identified in 2020. They are named for their location, being positione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglossal Nerve
The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve. CN XII is a nerve with a sole motor function. The nerve arises from the hypoglossal nucleus in the medulla as a number of small rootlets, pass through the hypoglossal canal and down through the neck, and eventually passes up again over the tongue muscles it supplies into the tongue. The nerve is involved in controlling tongue movements required for speech and swallowing, including sticking out the tongue and moving it from side to side. Damage to the nerve or the neural pathways which control it can affect the ability of the tongue to move and its appearance, with the most common sources of damage being injury from trauma or surgery, and motor neuron disease. The first recorded description of the nerve was by Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vena Comitans
Vena comitans (Latin for accompanying vein, also known as a satellite vein) refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes. Venae comitantes are usually found with certain smaller arteries, especially those in the extremities. Larger arteries, on the other hand, generally do not have venae comitantes. They usually have a single, similarly sized vein which is not as intimately associated with the artery. Function As the vein is found in close proximity to an artery the pulsations of the artery aid venous return. Claude Bernard suggested the interchange of heat between the arteries and adjacent veins might moderate cooling of the arterial blood, for which there is experimental evidence. Examples Examples of arteries and their venae comitantes: * Radial artery and radial veins * Ulnar artery and ulnar veins * Brachial artery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Nerve
The lingual nerve carries sensory innervation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue. It contains fibres from both the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V) and from the facial nerve (CN VII). The fibres from the trigeminal nerve are for touch, pain and temperature (general sensation), and the ones from the facial nerve are for taste (special sensation). Structure Origin The lingual nerve arises from the posterior trunk of mandibular nerve (CN V) within the infratemporal fossa. Course The lingual nerve first courses deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle and superior to the tensor veli palatini muscle; while passing between these two muscle, it is joined by the chorda tympani, and often by a communicating branch from the inferior alveolar nerve. The nerve then comes to pass inferoanteriorly upon the medial pterygoid muscle towards the medial aspect of the ramus of mandible, eventually meeting the mandible at the junction of the ramus and body of mandibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submandibular Duct
The submandibular duct (also Wharton's duct or historically submaxillary duct) is one of the salivary excretory ducts. It is about 5 cm long, and its wall is much thinner than that of the parotid duct. It drains saliva from each bilateral submandibular gland and sublingual gland to the sublingual caruncle in the floor of the mouth. Structure 270px, Picture of the mouth showing the sublingual caruncle and related anatomical structures The submandibular duct arises from deep part of submandibular gland, a salivary gland. It begins by numerous branches from the superficial surface of the gland, and runs forward between the mylohyoid, hyoglossus, and genioglossus muscles. It then passes between the sublingual gland and the genioglossus and opens by a narrow opening on the summit of a small papilla (the "sublingual caruncle") at the side of the frenulum of the tongue. It lies superior to lingual and hypoglossal nerves. Variation The submandibular duct may be duplicated on one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublingual Gland
The sublingual gland (''glandula sublingualis'') is a seromucous polystomatic exocrine gland. Located underneath the oral diaphragm (''diaphragma oris''), the sublingual gland is the smallest and most diffuse of the three major salivary glands of the oral cavity, with the other two being the submandibular and parotid. The sublingual gland provides approximately 3-5% of the total salivary volume. Structure The submandibular glands are located anterior and superior to the submandibular gland and inferior and lateral to the tongue, as well as inferior to the mucous membrane of the floor of the mouth. They are bound laterally by the bone of the mandible and inferolaterally by the mylohyoid muscle. The glands can be palpated posteriorly to each mandibular canine. Placing one index finger within the mouth and the fingertips of the opposite hand outside it, the compressed gland is manually palpated between the inner and outer fingers.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylohyoid Ligament
The stylohyoid ligament is a ligament that extends between the hyoid bone, and the temporal styloid process (of the temporal bone of the skull). Anatomy Attachments It attaches at the lesser horn of the hyoid bone inferiorly, and (the apex of) the styloid process of the temporal bone superiorly. The ligament gives attachment to the superior-most fibres of the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle. Relations The ligament is adjacent to the lateral wall of the oropharynx. Inferiorly, it is adjacent to the hyoglossus. Clinical significance The stylohyoid ligament frequently contains a little cartilage in its center, which is sometimes partially ossified Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in t ... in Eagle syndrome. Other animals In many animals, the epihyal i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingual Artery
The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue. Structure The lingual artery first branches off from the external carotid artery. It runs obliquely upward and medially to the greater horns of the hyoid bone. It then curves downward and forward, forming a loop which is crossed by the hypoglossal nerve. It then passes beneath the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle running horizontally forward, beneath the hyoglossus. This takes it through the sublingual space. Finally, ascending almost perpendicularly to the tongue, it turns forward on its lower surface as far as the tip of the tongue, now called the deep lingual artery ( profunda linguae). Branches The lingual artery gives 4 main branches: the deep lingual artery, the sublingual artery, the suprahyoid branch, and the dorsal lingual branch. Deep lingual artery The deep lingual artery (or ranine artery) is the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |