|
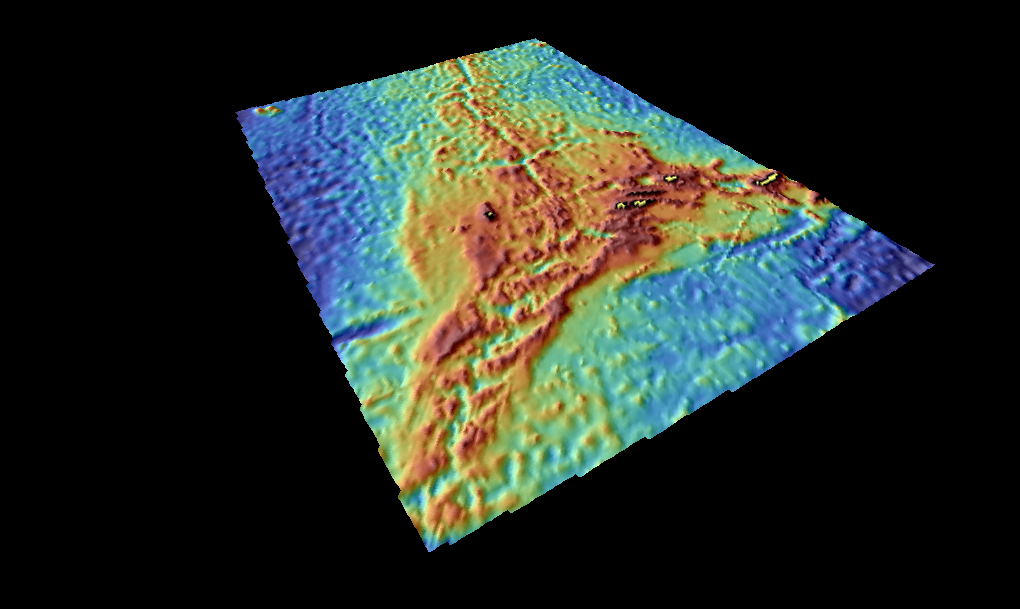
Hydrothermal Vents And Seamounts Of The Azores
The hydrothermal vents and seamounts of the Azores (') are a series of Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic seamounts and hydrothermal vents that are part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge system, giving rise to the archipelago and bathymetric region of the Azores. These geological structures, formed from masses of basalt (typical of mid-ocean regions), are of a geomorphological interest due to their rich deposits of ore. In addition it fosters a rich ecosystem of diverse subaquatic plant and animal life. There are food chains within this environment, for example, that are purely chemosynthesis, chemosynthetic, and do not need sunlight for photosynthesis. Geography The Azores consists of an extensive marine and terrestrial system of hundreds of active submarine mounts and volcanoes that extend from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The islands of the Azores are the visible representation of the complex ridge of undersea mountains that extend from Iceland to Antarctic. Below the waters of the Azores are unders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and because most of Earth's plate boundaries are underwater, most volcanoes are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes resulting from divergent tectonic activity are usually non-explosive whereas those resulting from convergent tectonic activity cause violent eruptions."Mid-ocean ridge tectonics, volcanism and geomorphology." Geology 26, no. 455 (2001): 458. https://macdonald.faculty.geol.ucsb.edu/papers/Macdonald%20Mid-Ocean%20Ridge%20Tectonics.pdf Volcanoes can also form where there is str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycara Saldanhai
''Pachycara'' is a genus of marine ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Zoarcidae, the eelpouts. The fishes in this genus are found in the Atlantic, Indian, Southern and Pacific Ocean. Species There are currently 29 recognized species in this genus: * '' Pachycara alepidotum'' M. E. Anderson & Mincarone, 2006 * '' Pachycara angeloi'' Thiel, Kneblsberger, Kihara & Gerdes, 2021 * '' Pachycara andersoni'' Møller, 2003 (Anderson's eelpout) * '' Pachycara arabica'' Møller, 2003 (Arabian eelpout) * '' Pachycara brachycephalum'' (Pappenheim, 1912) * '' Pachycara bulbiceps'' (Garman, 1899) (Snub-nose eelpout) * '' Pachycara caribbaeum'' M. E. Anderson, R. N. Somerville & Copley, 2016Anderson, M.E., Somerville, R. & Copley, J.T. (2016): A new species of ''Pachycara'' Zugmayer, 1911 (Teleostei: Zoarcidae) from deep-sea chemosynthetic environments in the Caribbean Sea. ''Zootaxa, 4066 (1): 71-77.'' * '' Pachycara cousinsi'' Møller & N. J. King 2007 (Brown eelpout) * '' Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
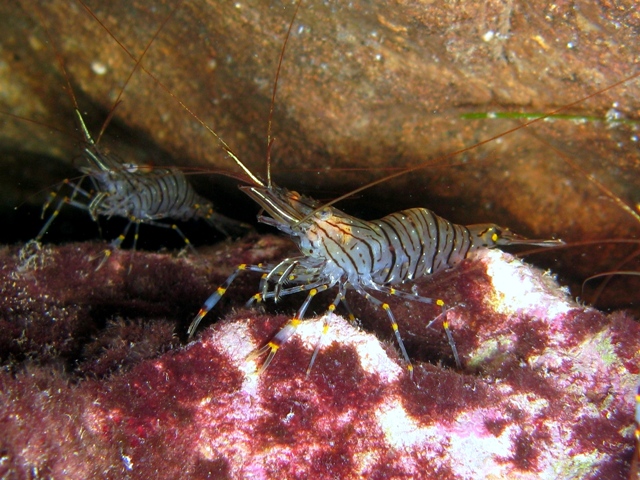
Rimicaris Exoculata
''Rimicaris exoculata'', commonly known as the 'blind shrimp', is a species of shrimp. It thrives on active hydrothermal edifices at deep-sea vents of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This species belongs to the Alvinocarididae family of shrimp, named after the DSV Alvin, the vessel that collected the original samples described by M. L. Christoffersen in 1986. The genus name ''Rimicaris'' is composed of ''rima'' (Latin for "rift" or "fissure", referring to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge) + ''karis'' ("shrimp" in Greek), while the species epithet benign is Latin for "rendered eyeless", referring to the highly modified, non-image-forming eyes. Description ''Rimicaris exoculata'' typically measures between in length and weighs an average of . During the moult cycle of their exoskeleton, this species transitions from white to translucent due to mineral deposits in the branchial chamber. Both sides of their body are covered in many long bacteriophore setae, and they possess an enlarged cephaloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata, although some Shrimp#Non-decapods, crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp". Any small crustacean may also be referred to as "shrimp", regardless of resemblance. More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either of the aforementioned groups, or only the Marine life, marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (Abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomens), long whiskers (Antenna (biology), antennae), and slender, Biramous, biramous legs. They swim forward by paddling the swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other edible clams, which are often more or less rounded or oval. The word "mussel" is frequently used to mean the bivalves of the marine family Mytilidae, most of which live on exposed shores in the intertidal zone, attached by means of their strong Byssus, byssal threads ("beard") to a firm substrate. A few species (in the genus ''Bathymodiolus'') have colonised hydrothermal vents associated with deep ocean ridges. In most marine mussels the shell is longer than it is wide, being wedge-shaped or asymmetrical. The external colour of the shell is often dark blue, blackish, or brown, while the interior is silvery and somewhat nacreous. The common name "mussel" is also used for many freshwater bivalves, including the freshwater pearl mussels. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exclusive Economic Zone
An exclusive economic zone (EEZ), as prescribed by the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, is an area of the sea in which a sovereign state has exclusive rights regarding the exploration and use of marine natural resource, resources, including energy production from water and wind. It stretches from the outer limit of the territorial sea (22.224 kilometres or 12 nautical miles from the baseline) out 370.4 kilometres (or 200 nautical miles) from the coast of the state in question. It is also referred to as a maritime continental margin and, in colloquial usage, may include the continental shelf. The term does not include either the Territorial waters#Territorial sea, territorial sea or the continental shelf beyond the 200 nautical mile limit. The difference between the territorial sea and the exclusive economic zone is that the first confers full sovereignty over the waters, whereas the second is merely a "sovereign right" which refers to the coastal state's righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Fund For Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is a Swiss-based international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the World Wildlife Fund, which remains its official name in Canada and the United States. WWF is the world's largest conservation organization, with over 5 million supporters worldwide, working in more than 100 countries and supporting around 3,000 conservation and environmental projects. It has invested over $1 billion in more than 12,000 conservation initiatives since 1995. WWF is a foundation with 65% of funding from individuals and bequests, 17% from government sources (such as the World Bank, FCDO, and USAID) and 8% from corporations in 2020. WWF aims to "stop the degradation of the planet's natural environment and to build a future in which humans live in harmony with nature." '' Living Planet Report'' has been published every two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faial Island
Faial Island (), also known as Fayal Island, is a Portugal, Portuguese island of the Central Group or ''Grupo Central'' of the Azores, in the Atlantic Ocean. The Capelinhos volcano is the westernmost point of the island and is considered the westernmost point of Europe other than the Monchique Islet. The largest town on the island is Horta, Azores, Horta with a population of approximately 7,000 inhabitants. The nearby islands of Pico Island, Pico and São Jorge Island, São Jorge form an area commonly known as the ''Triângulo'' or ''Triangle''. Faial Island has also been referred to as the Ilha Azul or ''Blue Island,'' a name derived from the writings of Portuguese poet Raul Brandão describing the large number of hydrangeas that bloom during the summer months: History Early records During the Middle Ages,Many stories have been told in the history of Portuguese discovery related to the Azores of the land of Atlantis, Sete Cidades, lands of São Brandão, the Ilhas Afo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terceira Island
Terceira () is a volcanic island in the Azores archipelago, about a third of the way across the North Atlantic Ocean at a similar latitude to Portugal's capital Lisbon, with the island group forming an insular part of Portugal. It is one of the larger islands of the archipelago, with a population of 53,311 inhabitants in an area of approximately . Terceira is the location of the Azores' oldest city, Angra do Heroísmo, the historical capital of the archipelago and UNESCO World Heritage Site; the seat of the judicial system (Supreme Court); and the main insular Portuguese Air Force base, Lajes Field, Base Aérea nº 4 at Lajes, with a United States Air Force detachment. Terceira island has two main sea ports, one at Angra do Heroísmo and the other at Praia da Vitória, and a commercial airport integrated with the flight operations at Lajes Field, Base Aérea nº 4. The Portuguese bullfight is popular on the island, coming in two variations: the traditional equestrian bullfight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
São Miguel Island
São Miguel Island (; ), nicknamed "The Green Island" (), is the largest and most populous island in the Portugal, Portuguese archipelago of the Azores. The island covers and has around 140,000 inhabitants, with 45,000 people residing in Ponta Delgada, the archipelago's largest city. History In 1427, São Miguel became the second of the islands discovered by Gonçalo Velho Cabral to be settled by colonists from continental Portugal. This date is uncertain, as it is believed that the island was discovered between 1426 and 1437 and inscribed in portolans from the middle of the 15th century. Its discovery was later recorded by Priesthood (Catholic Church), Father Gaspar Frutuoso in the seminal history of the Azores, ''Saudades da Terra'', as he began: "This island of São Miguel where...we are, is mountainous and covered in ravines, and it was, when we discovered it, covered in trees...due to its humidity, with its water showers and ravines warm with sun..." It was sometime afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dom João De Castro Bank
Dom João de Castro Bank () is a large submarine volcano located in the central north Atlantic Ocean, between the islands of São Miguel and Terceira in the archipelago of the Azores. History The first historical reference correlated with the submarine volcanoes between São Miguel and Terceira occurred after two ships of the French corsair Henry Tourin sank in the spring of 1718. The last major eruption associated with this region occurred on 31 December 1720.Sérgio Paulo Ávila (1997), p.1 Beginning as a submarine eruption, it eventually built into a Surtseyan eruption that resulted in the formation of a circular island long and in altitude. Smoke and steam released by the eruption was visible from the islands of São Miguel and Terceira. The eruption also caused multiple small earthquakes felt on those islands. Designated the ''Ilha Nova'' (New Island), it remained above sea-level for only two years, reaching a height of and diameter of . Marine erosion and ocean swells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |