|
Hydrometalation
Hydrometalation (hydrometallation) is a type of chemical reaction in organometallic chemistry in which a chemical compound with a hydrogen to metal bond (M-H, metal hydride) adds to compounds with an unsaturated bond like an alkene (RC=CR) forming a new compound with a carbon to metal bond (RHC-CRM).Elschenbroich, C. ”Organometallics” (2006) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. The metal is less electronegative than hydrogen, the reverse reaction is beta-hydride elimination. The reaction is structurally related to carbometalation. When the substrate is an alkyne the reaction product is a vinylorganometallic. : Examples are hydroboration, hydroalumination, hydrosilylation, hydrozirconation, and hydrocupration A hydrocupration is a chemical reaction whereby a ligated copper hydride species (Cu(I)H), reacts with a carbon-carbon or carbon-oxygen pi-system; this insertion is typically thought to occur via a four-membered ring transition state, producing a ne .... References {{Reflist Organome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (Metal carbonyl, metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganics, metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrozirconation
Schwartz's reagent is the common name for the organozirconium compound with the formula (C5H5)2ZrHCl, sometimes called zirconocene hydrochloride or zirconocene chloride hydride, and is named after Jeffrey Schwartz, a chemistry professor at Princeton University. This metallocene is used in organic synthesis for various transformations of alkenes and alkynes. Preparation The complex was first prepared by Wailes and Weigold. It can be purchased or readily prepared by reduction of zirconocene dichloride with lithium aluminium hydride: : (C5H5)2ZrCl2 + LiAlH4 → (C5H5)2ZrHCl + LiAlCl4 This reaction also affords (C5H5)2ZrH2, which is treated with methylene chloride to give Schwartz's reagent An alternative procedure that generated Schwartz's reagent from dihydride has also been reported. Moreover, it's possible to perform an ''in situ'' preparation of (C5H5)2ZrHCl from zirconocene dichloride by using LiH. This method can also be used to synthesize isotope-labeled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins. The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) Preferred IUPAC name, recommends using the name "alkene" only for Open-chain compound, acyclic hydrocarbons with just one double bond; alkadiene, alkatriene, etc., or polyene for acyclic hydrocarbons with two or more double bonds; cycloalkene, cycloalkadiene, etc. for Cyclic compound, cyclic ones; and "olefin" for the general class – cyclic or acyclic, with one or more double bonds. Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups (also known as mono-enes) form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula with ''n'' being a >1 natural number (which is two hydrogens less than the corresponding alkane). When ''n'' is four or more, isomers are possible, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrosilylation
Hydrosilylation, also called catalytic hydrosilation, describes the addition of Si-H bonds across unsaturated bonds."Hydrosilylation A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances" B. Marciniec (ed.), Advances in Silicon Science, Springer Science, 2009. Ordinarily the reaction is conducted catalytically and usually the substrates are unsaturated organic compounds. Alkenes and alkynes give alkyl and vinyl silanes; aldehydes and ketones give silyl ethers, while esters provide alkyl silyl mixed acetals. Hydrosilylation has been called the "most important application of platinum in homogeneous catalysis." Scope and mechanism Hydrosilylation of alkenes represents a commercially important method for preparing organosilicon compounds. The process is mechanistically similar to the hydrogenation of alkenes. In fact, similar catalysts are sometimes employed for the two catalytic processes. The prevalent mechanism, called the Chalk-Harrod mechanism, assumes an intermediate metal complex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroboration
In organic chemistry, hydroboration refers to the addition of a hydrogen-boron bond to certain double and triple bonds involving carbon (, , , and ). This chemical reaction is useful in the organic synthesis of organic compounds. Hydroboration produces organoborane compounds that react with a variety of reagents to produce useful compounds, such as alcohols, amines, or alkyl halides. The most widely known reaction of the organoboranes is oxidation to produce alcohols from alkenes. The development of this technology and the underlying concepts were recognized by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Herbert C. Brown. Borane adducts Much of the original work on hydroboration employed diborane as a source of BH3. Usually however, borane dimethylsulfide complex BH3S(CH3)2 (BMS) is used instead. It can be obtained in highly concentrated forms. The adduct BH3(THF) is also commercially available as THF solutions. Its shelf life is less than BMS. In terms of synthetic results, dibor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrometalation
Hydrometalation (hydrometallation) is a type of chemical reaction in organometallic chemistry in which a chemical compound with a hydrogen to metal bond (M-H, metal hydride) adds to compounds with an unsaturated bond like an alkene (RC=CR) forming a new compound with a carbon to metal bond (RHC-CRM).Elschenbroich, C. ”Organometallics” (2006) Wiley-VCH: Weinheim. The metal is less electronegative than hydrogen, the reverse reaction is beta-hydride elimination. The reaction is structurally related to carbometalation. When the substrate is an alkyne the reaction product is a vinylorganometallic. : Examples are hydroboration, hydroalumination, hydrosilylation, hydrozirconation, and hydrocupration A hydrocupration is a chemical reaction whereby a ligated copper hydride species (Cu(I)H), reacts with a carbon-carbon or carbon-oxygen pi-system; this insertion is typically thought to occur via a four-membered ring transition state, producing a ne .... References {{Reflist Organome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyne
\ce \ce Acetylene \ce \ce \ce Propyne \ce \ce \ce \ce 1-Butyne In organic chemistry, an alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon containing at least one carbon—carbon triple bond. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general chemical formula . Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name ''acetylene'' also refers specifically to , known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature. Like other hydrocarbons, alkynes are generally hydrophobic. Structure and bonding In acetylene, the H–C≡C bond angles are 180°. By virtue of this bond angle, alkynes are rod-like. Correspondingly, cyclic alkynes are rare. Benzyne cannot be isolated. The C≡C bond distance of 118 picometers (for C2H2) is much shorter than the C=C distance in alkenes (132 pm, for C2H4) or the C–C bond in alkanes (153 pm). : The triple bond is very strong with a bond strength of 839 kJ/mol. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
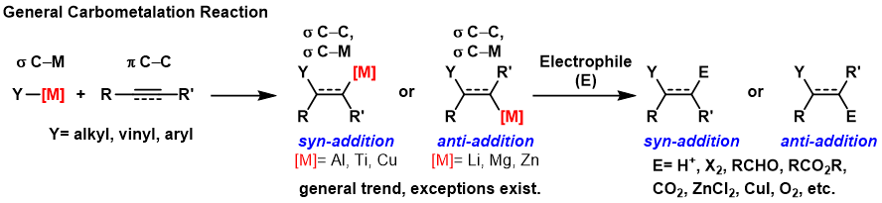
Carbometalation
A carbometallation is any reaction where a carbon-metal bond reacts with a carbon-carbon π-bond to produce a new carbon-carbon σ-bond and a carbon-metal σ-bond. The resulting carbon-metal bond can undergo further carbometallation reactions (oligomerization or polymerization see Ziegler-Natta polymerization) or it can be reacted with a variety of electrophiles including halogenating reagents, carbonyls, oxygen, and inorganic salts to produce different organometallic reagents. Carbometallations can be performed on alkynes and alkenes to form products with high geometric purity or enantioselectivity, respectively. Some metals prefer to give the ''anti''-addition product with high selectivity and some yield the syn-addition product. The outcome of ''syn'' and ''anti''- addition products is determined by the mechanism of the carbometallation. Carboboration Carboboration is one of the most versatile carbometallation reactions. See '' Carboboration''. Carboalumination The car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronegative
Electronegativity, symbolized as , is the tendency for an atom of a given chemical element to attract shared electrons (or electron density) when forming a chemical bond. An atom's electronegativity is affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from the charged nucleus. The higher the associated electronegativity, the more an atom or a substituent group attracts electrons. Electronegativity serves as a simple way to quantitatively estimate the bond energy, and the sign and magnitude of a bond's chemical polarity, which characterizes a bond along the continuous scale from covalent to ionic bonding. The loosely defined term electropositivity is the opposite of electronegativity: it characterizes an element's tendency to donate valence electrons. On the most basic level, electronegativity is determined by factors like the nuclear charge (the more protons an atom has, the more "pull" it will have on electrons) and the number and locatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three Isotopes of carbon, isotopes occur naturally, carbon-12, C and carbon-13, C being stable, while carbon-14, C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the timeline of chemical element discoveries#Pre-modern and early modern discoveries, few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th abundance of elements in Earth's crust, most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the abundance of the chemical elements, fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual abi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |