|
Hydrogen Sensors
A hydrogen sensor is a gas detector that detects the presence of hydrogen. They contain micro-fabricated point-contact hydrogen sensors and are used to locate hydrogen leaks. They are considered low-cost, compact, durable, and easy to maintain as compared to conventional gas detecting instruments. Key issues There are five key issues with hydrogen detectors: * Reliability: Functionality should be easily verifiable. * Performance: Detection 0.5% hydrogen in air or better * Response time < 1 second. * Lifetime: At least the time between scheduled maintenance. * : Goal is $5 per sensor and $30 per controller. Additional requirements * Measurement range coverage of 0.1–10.0% concentration * Operation in temperatures of −30 °C to 80 °C * Accuracy with ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greg Glatzmaier Determines The High-temperature Thermal And Mechanical Stability Of Sealants Used In A Lab Prototype Of The Integrated Hydrogen Sensor Separator Module
Greg is a masculine given name, and often a shortened form of the given name Gregory (given name), Gregory. Greg (sometimes spelled "Gregg (surname), Gregg") is also a surname. People with the name *Greg Abbott (other), multiple people *Greg Abel (born 1961/1962), Canadian businessman *Greg Adams (other), multiple people *Greg Allen (other), multiple people *Greg Anderson (other), multiple people *Greg Austin (other), multiple people *Greg Ball (other), multiple people *Greg Bell (other), multiple people *Greg Bennett (other), multiple people *Greg Berlanti (born 1972), American writer and producer *Greg Biffle (born 1969), American NASCAR driver *Greg Blankenship (born 1954), American football player *Greg Boyd (other), multiple people *Greg Boyer (other), multiple people *Greg Brady (broadcaster) (born 1971), Canadian sports radio host *Greg Brock (baseball) (born 1957), American baseball pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical filter to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Kenneth O. Hill, Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the #Interference, interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by the Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Diode
The Schottky diode (named after the German physicist Walter H. Schottky), also known as Schottky barrier diode or hot-carrier diode, is a semiconductor diode formed by the junction of a semiconductor with a metal. It has a low forward voltage drop and a very fast switching action. The cat's-whisker detectors used in the early days of wireless and metal rectifiers used in early power applications can be considered primitive Schottky diodes. When sufficient forward voltage is applied, a current flows in the forward direction. A silicon p–n diode has a typical forward voltage of 600–700 mV, while the Schottky's forward voltage is 150–450 mV. This lower forward voltage requirement allows higher switching speeds and better system efficiency. Construction A metal–semiconductor junction is formed between a metal and a semiconductor, creating a Schottky barrier (instead of a semiconductor–semiconductor junction as in conventional diodes). Typical metals used ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
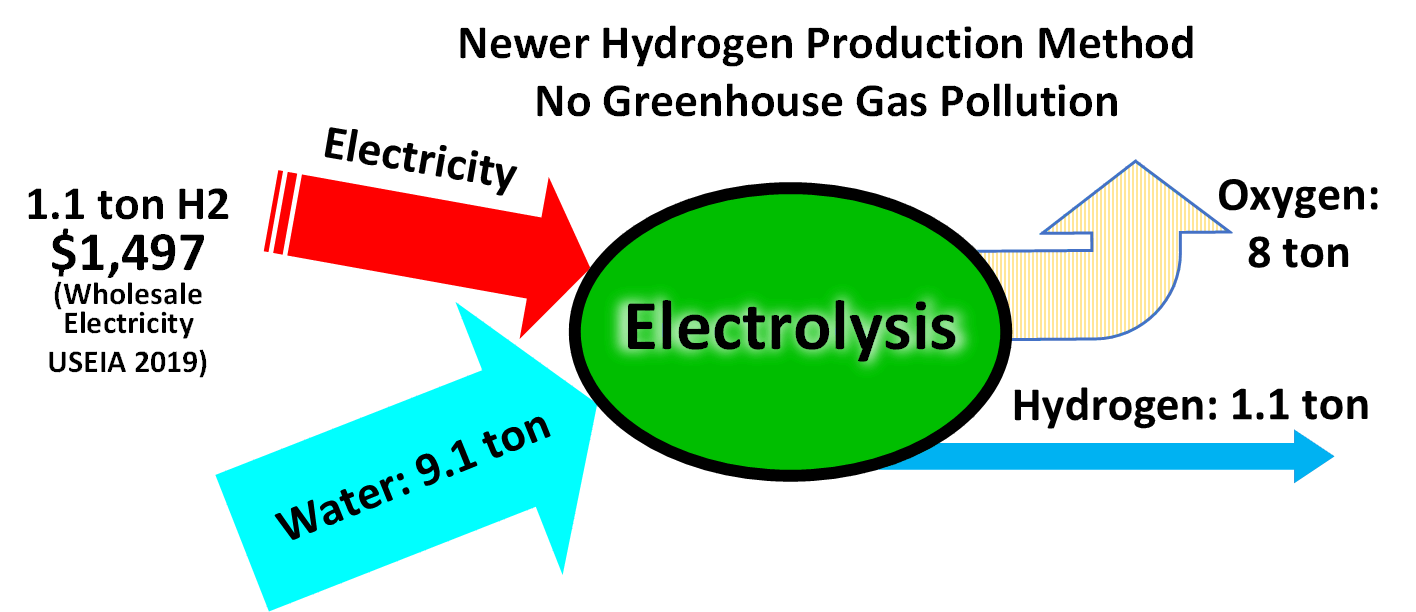
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. When carbon capture and storage is used to remove a large fraction of these emissions, the product is known as ''blue hydrogen''. ''Green hydrogen'' is usually understood to be produced from Renewable energy, renewable electricity via electrolysis of water. Less frequently, definitions of ''green hydrogen'' include hydrogen produced from other low-emission sources such as Biomass (energy), biomass. Producing green hydrogen is currently more expensive than producing gray hydrogen, and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Film
A thin film is a layer of materials ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. A familiar example is the household mirror, which typically has a thin metal coating on the back of a sheet of glass to form a reflective interface. The process of silvering was once commonly used to produce mirrors, while more recently the metal layer is deposited using techniques such as sputtering. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, integrated passive devices, light-emitting diodes, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage ( thin-film bat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanomechanical Resonator
A nanomechanical resonator is a nanoelectromechanical systems ultra-small resonator that oscillates at a specific frequency depending on its mass and stiffness. See also *Quartz crystal microbalance *Atomic force microscopy Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opti ... References Further reading * * Nanoelectronics {{Physics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Oxide
Tin oxide may refer to: * Tin(II) oxide (stannous oxide), a black powder with the formula SnO * Tin(IV) oxide Tin(IV) oxide, also known as stannic oxide, is the inorganic compound with the formula SnO2. The mineral form of SnO2 is called cassiterite, and this is the main ore of tin. With many other names, this oxide of tin is an important material in ti ... (tin dioxide, stannic oxide), a white powder with the formula SnO2 {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium(III) Oxide
Indium(III) oxide ( In2 O3) is a chemical compound, an amphoteric oxide of indium. Physical properties Crystal structure Amorphous indium oxide is insoluble in water but soluble in acids, whereas crystalline indium oxide is insoluble in both water and acids. The crystalline form exists in two phases, the cubic ( bixbyite type) and rhombohedral ( corundum type). Both phases have a band gap of about 3 eV. The parameters of the cubic phase are listed in the infobox. The rhombohedral phase is produced at high temperatures and pressures or when using non-equilibrium growth methods. It has a space group Rc No. 167, Pearson symbol hR30, a = 0.5487 nm, b = 0.5487 nm, c = 1.4510 nm, Z = 6 and calculated density 7.31 g/cm3. Conductivity and magnetism Thin films of chromium- doped indium oxide (In2−xCrxO3) are a magnetic semiconductor displaying high-temperature ferromagnetism, single- phase crystal structure, and semiconductor behavior with high concentration of ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectromechanical Systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the large surface area to volume ratio of MEMS, forces produced by ambient electromagnetism (e.g., electrostatic charges and magnetic moments), and fluid dynamics (e.g., surface tension and viscosity) are more important design considerations than with larger scale mechanical devices. MEMS technology is distinguished from molecular nanotechnol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |