|
Hydrogen Purity
Hydrogen purification is any technology used to purify hydrogen. The impurities in hydrogen gas depend on the source of the H2, e.g., petroleum, coal, electrolysis, etc. The required purity is determined by the application of the hydrogen gas. For example, ultra-high purified hydrogen is needed for applications like proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Purification technologies Low temperature methods The default large-scale purification of H2 produced in oil refineries exploits its very low boiling point of −253 °C. Most impurities have boiling points well above this temperature. Low temperature methods can be complemented by scrubbing to remove particular impurities. Palladium membrane hydrogen purifiers Hydrogen can be purified by passing through a membrane composed of palladium and silver. Permeability of the former to hydrogen was discovered back in the 1860s. An alloy with a ca. 3:1 ratio for Pd:Ag is more structural robust than pure Pd, which is the active compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter. Under standard conditions, hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules with the chemical formula, formula , called dihydrogen, or sometimes hydrogen gas, molecular hydrogen, or simply hydrogen. Dihydrogen is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Stars, including the Sun, mainly consist of hydrogen in a plasma state, while on Earth, hydrogen is found as the gas (dihydrogen) and in molecular forms, such as in water and organic compounds. The most common isotope of hydrogen (H) consists of one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. Hydrogen gas was first produced artificially in the 17th century by the reaction of acids with metals. Henry Cavendish, in 1766–1781, identified hydrogen gas as a distinct substance and discovere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is an organic compound with the chemical formula and structure , more precisely . The compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde. It is stored as aqueous solutions (formalin), which consists mainly of the hydrate CH2(OH)2. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). As a precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds, in 2006 the global production of formaldehyde was estimated at 12 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Formaldehyde also occurs naturally. It is derived from the degradation of serine, dimethylglycine, and lipids. Demethylases act by converting N-methyl groups to formaldehyde. Formaldehyde is classified as a group 1 carcinogen and can cause respiratory and skin irritation upon exposure. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Gases
Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also available in gas cylinders. The industry producing these gases is also known as industrial gas, which is seen as also encompassing the supply of equipment and technology to produce and use the gases. Their production is a part of the wider chemical Industry (where industrial gases are often seen as " specialty chemicals"). Industrial gases are used in a wide range of industries, which include oil and gas, petrochemicals, chemicals, power, mining, steelmaking, metals, environmental protection, medicine, pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, food, water, fertilizers, nuclear power, electronics and aerospace. Industrial gas is sold to other industrial enterprises; typically comprising large orders to corporate industrial clients, covering a size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Equipment
A chemical substance is a unique form of matter with constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Chemical substances may take the form of a single element or chemical compounds. If two or more chemical substances can be combined without reacting, they may form a chemical mixture. If a mixture is separated to isolate one chemical substance to a desired degree, the resulting substance is said to be chemically pure. Chemical substances can exist in several different physical states or phases (e.g. solids, liquids, gases, or plasma) without changing their chemical composition. Substances transition between these phases of matter in response to changes in temperature or pressure. Some chemical substances can be combined or converted into new substances by means of chemical reactions. Chemicals that do not possess this ability are said to be inert. Pure water is an example of a chemical substance, with a constant composition of two hydrogen atoms bonded to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Technologies
Hydrogen technologies are technologies that relate to the production and use of hydrogen as a part hydrogen economy. Hydrogen technologies are applicable for many uses. Some hydrogen technologies are carbon neutral and could have a role in preventing climate change and a possible future hydrogen economy. Hydrogen is a chemical widely used in various applications including ammonia production, oil refining and energy. The most common methods for producing hydrogen on an industrial scale are: Steam reforming, oil reforming, coal gasification, water electrolysis. Hydrogen is not a primary energy source, because it is not naturally occurring as a fuel. It is, however, widely regarded as an ideal energy storage medium, due to the ease with which electricity can convert water into hydrogen and oxygen through electrolysis and can be converted back to electrical power using a fuel cell or hydrogen turbine. There are a wide number of different types of fuel and electrolysis ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton-exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
Proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC), also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells, are a type of fuel cell being developed mainly for transport applications, as well as for stationary fuel-cell applications and portable fuel-cell applications. Their distinguishing features include lower temperature/pressure ranges (50 to 100 °C) and a special proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membrane. PEMFCs generate electricity and operate on the opposite principle to PEM electrolysis, which consumes electricity. They are a leading candidate to replace the aging alkaline fuel-cell technology, which was used in the Space Shuttle. Science PEMFCs are built out of membrane electrode assemblies (MEA) which include the electrodes, electrolyte, catalyst, and gas diffusion layers. An ink of catalyst, carbon, and electrode are sprayed or painted onto the solid electrolyte and carbon paper is hot pressed on either side to protect the inside of the cell and also act a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Fuel
The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not available. In this context, ''hydrogen economy'' encompasses the production of hydrogen and the use of hydrogen in ways that contribute to phasing-out fossil fuels and limiting climate change. Hydrogen can be produced by several means. Most hydrogen produced today is ''gray hydrogen'', made from natural gas through steam methane reforming (SMR). This process accounted for 1.8% of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2021.Greenhouse gas emissions totalled 49.3 Gigatonnes CO2e in 2021. ''Low-carbon hydrogen'', which is made using SMR with carbon capture and storage ('' blue hydrogen''), or through electrolysis of water using renewable power ('' green hydrogen''), accounted for less than 1% of production. Virtually all of the 100 million tonnes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Station
A hydrogen infrastructure is the infrastructure of points of hydrogen production, truck and pipeline transport, and hydrogen stations for the distribution and sale of hydrogen fuel, and thus a crucial prerequisite before a successful commercialization of fuel cell technology. Hydrogen stations which are not situated near a hydrogen pipeline get supply via hydrogen tanks, Compressed hydrogen tube trailer, compressed hydrogen tube trailers, Liquid hydrogen trailer, liquid hydrogen trailers, liquid hydrogen tank trucks or dedicated onsite production. Pipelines are the cheapest way to move hydrogen over long distances compared to other options. Hydrogen gas piping is routine in large oil-refineries, because hydrogen is used to Hydrocracking, hydrocrack fuels from crude oil. The IEA recommends existing industrial ports be used for production and natural gas pipelines for transport, international co-operation and shipping. South Korea and Hydrogen highway (Japan), Japan, which as of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
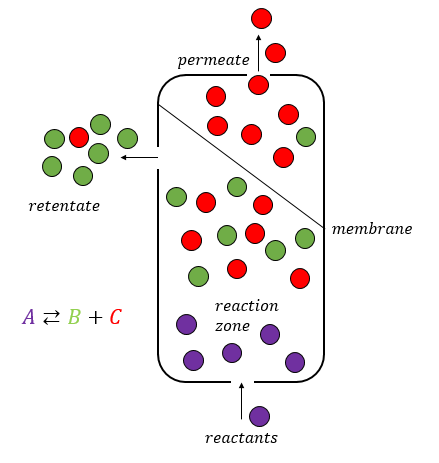
Membrane Reactor
A membrane reactor is a physical device that combines a chemical conversion process with a membrane separation process to add reactants or remove products of the reaction. Chemical reactors making use of membranes are usually referred to as membrane reactors. The membrane can be used for different tasks: * Separation ** Selective extraction of products ** Retention of the catalyst * Distribution/dosing of a reactant * Catalyst support (often combined with distribution of reactants) Membrane reactors are an example for the combination of two unit operations in one step, e.g., membrane filtration with the chemical reaction. The integration of reaction section with selective extraction of a reactant allows an enhancement of the conversions compared to the equilibrium value. This characteristic makes membrane reactors suitable to perform equilibrium-limited endothermic reactions. Benefits and critical issues Selective membranes inside the reactor lead to several benefits: reacto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Membrane Gas Separation
Gas mixtures can be effectively separated by synthetic membranes made from polymers such as polyamide or cellulose acetate, or from ceramic materials. While polymeric membranes are economical and technologically useful, they are bounded by their performance, known as the Robeson limit (permeability must be sacrificed for selectivity and vice versa). This limit affects polymeric membrane use for CO2 separation from flue gas streams, since mass transport becomes limiting and CO2 separation becomes very expensive due to low permeabilities. Membrane materials have expanded into the realm of Silicon dioxide, silica, zeolites, metal-organic frameworks, and perovskites due to their strong thermal and chemical resistance as well as high tunability (ability to be modified and functionalized), leading to increased permeability and selectivity. Membranes can be used for separating gas mixtures where they act as a permeable barrier through which different compounds move across at different rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Pinch
Hydrogen pinch analysis (HPA) is a hydrogen management method that originates from the concept of heat pinch analysis. HPA is a systematic technique for reducing hydrogen consumption and hydrogen generation through integration of hydrogen-using activities or processes in the petrochemical industry, petroleum refineries hydrogen distribution networks and hydrogen purification. Principle A mass analysis is done by representing the purity and flowrate for each stream from the hydrogen consumers (sinks), such as hydrotreaters, hydrocrackers, isomerization units and lubricant plants and the hydrogen producers (sources), such as hydrogen plants and naphtha reformers, streams from hydrogen purifiers, membrane reactors, pressure swing adsorption and continuous distillation and off-gas streams from low- or high-pressure separators. The source-demand diagram shows bottlenecks, surplus or shortages. The hydrogen pinch is the purity at which the hydrogen network has neither hydrogen surplus n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Separation
Gas separation can refer to any of a number of techniques used to separate gases, either to give multiple products or to purify a single product. Swing adsorption techniques Pressure swing adsorption Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) pressurizes and depressurizes a multicomponent gas around an adsorbent medium to selectively adsorb some components of a gas while leaving other components free-flowing. Vacuum swing adsorption Vacuum swing adsorption (VSA) uses the same principle as PSA but swings between vacuum pressures and atmospheric pressure Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013. .... PSA and VSA techniques may be combined and are called "vacuum pressure swing adsorption" (VPSA) in this case. Temperature swing adsorption Temperature swing adsorption (TSA) is similar t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |