|
Hybrid Organization
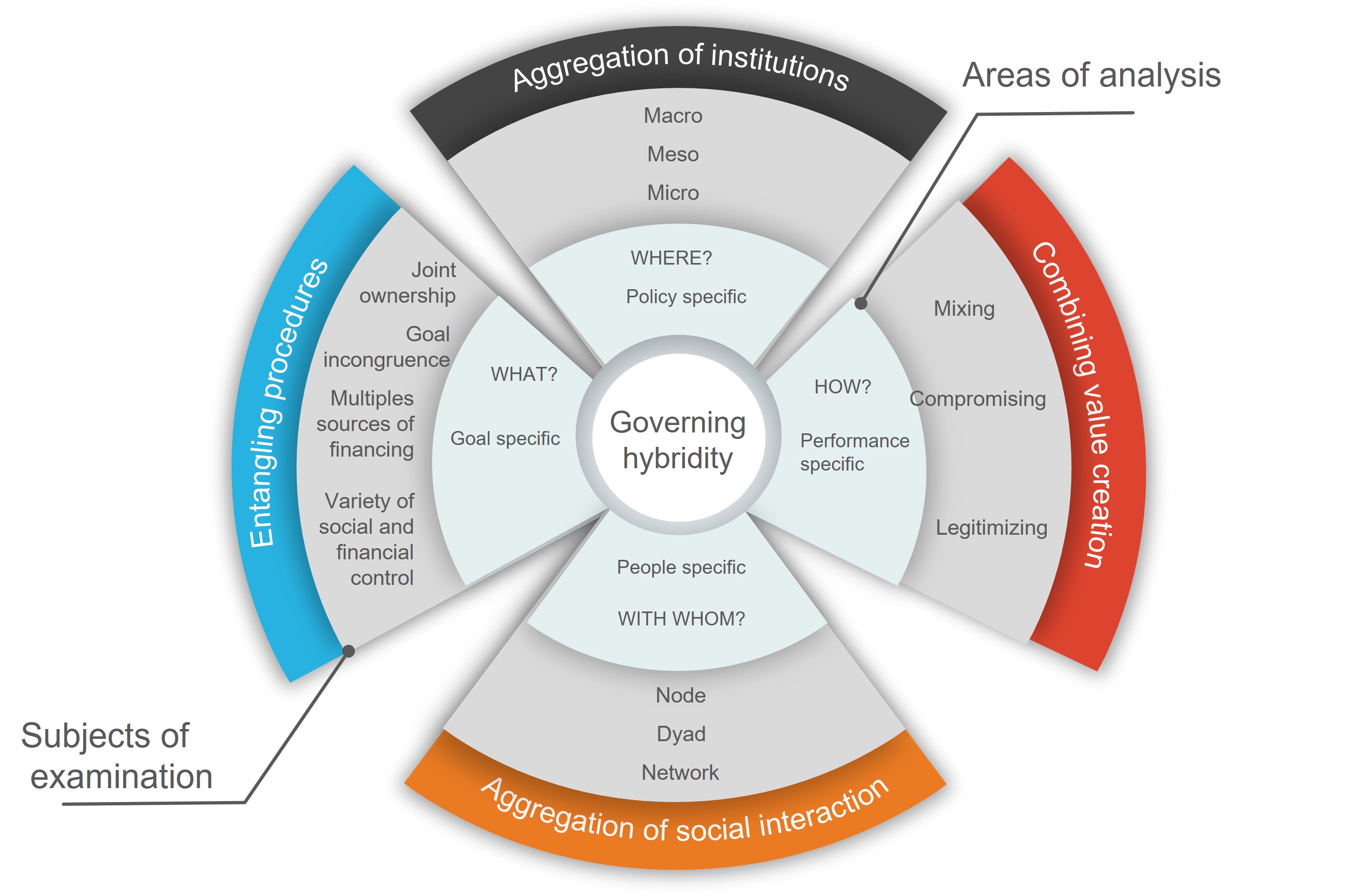
A hybrid organization is an organization that mixes elements, value systems and action logics (e.g. social impact and profit generation) of various sectors of society, i.e. the public sector, the private sector and the voluntary sector. A more general notion of hybridity can be found in Hybrid institutions and governance. According to previous research hybrids between public and private spheres consist of following features: # Shared ownership. # Goal incongruence and different institutional logics in the same organisation. # Variety in the sources of financing. # Differentiated forms of economic and social control. Value creation in hybrids proceeds through three mechanisms: # mixing, # compromising, # legitimizing. Mixing distinct value categories may take several forms. One common feature of these forms is the act of combining existing value categories to contribute novel variants of value. Compromising concern solving grievances among the interacting parties. From the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hospitals
A hospital is a healthcare institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergency department to treat urgent health problems ranging from fire and accident victims to a sudden illness. A district hospital typically is the major health care facility in its region, with many beds for intensive care and additional beds for patients who need long-term care. Specialized hospitals include trauma centers, rehabilitation hospitals, children's hospitals, geriatric hospitals, and hospitals for specific medical needs, such as psychiatric hospitals for psychiatric treatment and other disease-specific categories. Specialized hospitals can help reduce health care costs compared to general hospitals. Hospitals are classified as general, specialty, or government depending on the sources of income received. A teaching hospital cam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David A
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament. The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Damascus in the late 9th/early 8th centuries BCE to commemorate a victory over two enemy kings, contains the phrase (), which is translated as " House of David" by most scholars. The Mesha Stele, erected by King Mesha of Moab in the 9th century BCE, may also refer to the "House of David", although this is disputed. According to Jewish works such as the '' Seder Olam Rabbah'', '' Seder Olam Zutta'', and '' Sefer ha-Qabbalah'' (all written over a thousand years later), David ascended the throne as the king of Judah in 885 BCE. Apart from this, all that is known of David comes from biblical literature, the historicity of which has been extensively challenged,Writing and Rewriting the Story of Solomon in Ancient Israel; by Isaac Kalimi; page 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Profit Motive
In economics, the profit motive is the motivation of firms that operate so as to maximize their profits. Mainstream microeconomic theory posits that the ultimate goal of a business is "to make money" - not in the sense of increasing the firm's stock of means of payment (which is usually kept to a necessary minimum because means of payment incur costs, i.e. interest or foregone yields), but in the sense of "increasing net worth". Stated differently, the reason for a business's existence is to turn a profit. The profit motive is a key tenet of rational choice theory, or the theory that economic agents tend to pursue what is in their own best interests. In accordance with this doctrine, businesses seek to benefit themselves and/or their shareholders by maximizing profits. As it extends beyond economics into ideology, the profit motive has been a major matter of contention. Economics Theoretically, when an economy is fully competitive (i.e. has no market imperfections like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) or corporate social impact is a form of international private business industry self-regulation, self-regulation which aims to contribute to societal goals of a philanthropy, philanthropic, activist, or charitable nature by engaging in, with, or supporting Professional services, professional service volunteering through pro bono programs, community development, administering Grant (money), monetary grants to Nonprofit organization, non-profit organizations for the Common good, public benefit, or to conduct Ethics, ethically oriented business and investment practices. While CSR could have previously been described as an internal organizational policy or a business ethics, corporate ethic strategy, similar to what is now known today as environmental, social, and governance (ESG), that time has passed as various companies have pledged to go beyond that or have been mandated or incentivized by governments to have a better impact on the surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Banking And Finance
Islamic banking, Islamic finance ( ''masrifiyya 'islamia''), or Sharia-compliant finance is banking or Finance, financing activity that complies with Sharia (Islamic law) and its practical application through the development of Islamic economics. Some of the modes of Islamic finance include ''Profit and loss sharing#Mudarabah, mudarabah'' (profit-sharing and loss-bearing), ''wadiah'' (safekeeping), ''musharaka'' (joint venture), ''murabahah'' (cost-plus), and ''ijarah'' (leasing). Sharia prohibits ''riba'', or usury, generally defined as interest paid on all loans of money (although some Muslims dispute whether there is a consensus that interest is equivalent to ''riba''). Investment in businesses that provide goods or services considered contrary to Islamic Value (personal and cultural), principles (e.g. pork or alcohol) is also ''haram'' ("sinful and prohibited"). These prohibitions have been applied historically in varying degrees in Muslim countries/communities to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microfinance
Microfinance consists of financial services targeting individuals and small businesses (SMEs) who lack access to conventional banking and related services. Microfinance includes microcredit, the provision of small loans to poor clients; savings account, savings and checking accounts; microinsurance; and payment systems, among other services. Microfinance product and services in MFI include: # Savings # Microcredit # Microinsurance # Microleasing and # Fund transfer/remittance. Microfinance services are designed to reach excluded customers, usually low income population segments, possibly socially marginalized, or geographically more isolated, and to help them become self-sufficient.Peck Christen, Robert; Rosenberg, Richard; Jayadeva, Veena. ''Financial institutions with a double-bottom line: Implications for the future of microfinance''. CGAP, Occasional Papers series, July 2004, pp. 2–3. ID Ghana is an example of a microfinance institution. Microfinance initially had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Special Interest Groups
A special interest group (SIG) is a community within a larger organization with a shared interest in advancing a specific area of knowledge, learning or technology where members cooperate to effect or to produce solutions within their particular field, and may communicate, meet, and organize conferences. The term was used in 1961 by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), an academic and professional computer society. SIG was later popularized on CompuServe, an early online service provider, where SIGs were a section of the service devoted to particular interests. Technical SIGs The ACM includes many SIGs, some starting as smaller "Special Interest Committees" and formed the first group in 1961. ACM supports further subdivision within SIGs for more impromptu informal discussion groups at conferences which are called Birds of a Feather (BoF). ACM's Special Interest Groups (SIGs) represent major areas of computing, addressing the interests of technical communities that dri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobbying
Lobbying is a form of advocacy, which lawfully attempts to directly influence legislators or government officials, such as regulatory agency, regulatory agencies or judiciary. Lobbying involves direct, face-to-face contact and is carried out by various entities, including individuals acting as Voting, voters, constituents, or private citizens, corporations pursuing their business interests, nonprofits and Non-governmental organization, NGOs through advocacy groups to achieve their missions, and legislators or government officials influencing each other in legislative affairs. Lobbying or certain practices that share commonalities with lobbying are sometimes referred to as government relations, or government affairs and sometimes legislative relations, or legislative affairs. It is also an Industry (economics), industry known by many of the aforementioned names, and has a near-complete overlap with the public affairs industry. Lobbyists may fall into different categories: amateur lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Relations
Public relations (PR) is the practice of managing and disseminating information from an individual or an organization (such as a business, government agency, or a nonprofit organization) to the public in order to influence their perception. Public relations and publicity differ in that PR is controlled internally, whereas publicity is not controlled and contributed by external parties. Public relations may include an organization or individual gaining exposure to their audiences using topics of public interest and news items that do not require direct payment. The exposure is mostly media-based, and this differentiates it from advertising as a form of marketing communications. Public relations often aims to create or obtain coverage for clients for free, also known as earned media, rather than paying for marketing or advertising also known as paid media. However, advertising, especially of the type that focuses on distributing information or core PR messages, is also a part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trade Association
A trade association, also known as an industry trade group, business association, sector association or industry body, is an organization founded and funded by businesses that operate in a specific Industry (economics), industry. Through collaboration between companies within a Business sector, sector, a trade association coordinates public relations activities such as advertising, education, publishing and, especially, lobbying and political action. Associations may offer other services, such as producing conferences, setting industry standards, holding networking or charitable events, or offering classes or educational materials. Many associations are non-profit organizations governed by bylaws and directed by officers who are also members. (FEC: Solicitable Class of Trade Association, Library of Congress). In countries with a social market economy, the role of trade associations is often taken by employers' organizations, which also take a role in social dialogue. Political in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |