|
Humidifying
A humidifier is a household appliance or device designed to increase the moisture level in the air within a room or an enclosed space. It achieves this by emitting water droplets or steam into the surrounding air, thereby raising the humidity. In the home, point-of-use humidifiers are commonly used to humidify a single room, while whole-house or furnace humidifiers, which connect to a home's HVAC system, provide humidity to the entire house. Medical ventilators often include humidifiers for increased patient comfort. Large humidifiers are used in commercial, institutional, or industrial contexts, often as part of a larger HVAC system. Overview Humidification calculation : Humidity per hour: X = ''Air changes per hour (ACPH) * M³ * density of air * humidity ratio'' :: Humidity per day: X * 24 * The air changes per hour (ACPH) ranges wildly based on: ** Ventilation: Values may be obtained from the HVAC maintainer that routinely (typically every third year or so) tests the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
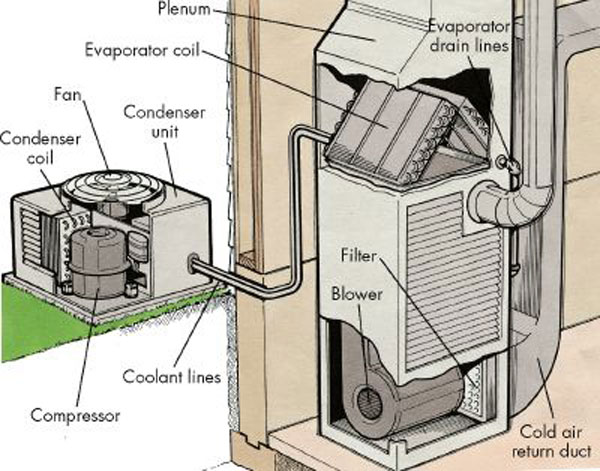
HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Appliance
A home appliance, also referred to as a domestic appliance, an electric appliance or a household appliance, is a machine which assists in household functions such as cooking, cleaning and food preservation. The domestic application attached to home appliance is tied to the definition of appliance as "an instrument or device designed for a particular use or function". ''Collins English Dictionary'' defines "home appliance" as: "devices or machines, usually electrical, that are in your home and which you use to do jobs such as cleaning or cooking". The broad usage allows for nearly any device intended for domestic use to be a home appliance, including consumer electronics as well as stoves, refrigerators, toasters and air conditioners. The development of self-contained electric and gas-powered appliances, an American innovation, emerged in the early 20th century. This evolution is linked to the decline of full-time domestic servants and desire to reduce household chores, allowing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert Climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk'') is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert climates are dry and hold little moisture, quickly evaporating the already little rainfall they receive. Covering 14.2% of Earth's land area, hot deserts are the second-most common type of climate on Earth after the Polar climate. There are two variations of a desert climate according to the Köppen climate classification: a hot desert climate (''BWh''), and a cold desert climate (''BWk''). To delineate "hot desert climates" from "cold desert climates", a mean annual temperature of is used as an isotherm so that a location with a ''BW'' type climate with the appropriate temperature above this isotherm is classified as "hot arid subtype" (''BWh''), and a location with the appropriate temperature below the isotherm is classified as "cold a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric current, current electricity, where an electric charge flows through an electrical conductor. A static electric charge can be created whenever two surfaces contact and/or slide against each other and then separate. The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because they can feel, hear, and even see sparks if the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to an electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shockmore specifically, an electrostatic dischargeis caused by the neutralization of a charge. Causes Materials are made of atoms that are normally electrically neutral because they contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perspiration
Perspiration, also known as sweat, is the fluid secreted by sweat glands in the skin of mammals. Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and Apocrine sweat gland, apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distributed over much of the body and are responsible for secreting the watery, brackish sweat most often triggered by excessive body temperature. Apocrine sweat glands are restricted to the armpits and a few other areas of the body and produce an odorless, oily, opaque secretion which then gains its characteristic odor from bacterial decomposition. In humans, sweating is primarily a means of thermoregulation, which is achieved by the water-rich secretion of the eccrine glands. Maximum sweat rates of an adult can be up to per hour or per day, but is less in children prior to puberty. Evaporation of sweat from the skin surface has a cooling effect due to evaporative cooling. Hence, in Temperature, hot weather, or when the individual's muscles hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humidex
The humidex (short for humidity index) is an index number used by Canadian meteorologists to describe how hot the weather feels to the average person, by combining the effect of heat and humidity. The term ''humidex'' was coined in 1965. The humidex is a nominally dimensionless quantity (though generally recognized by the public as equivalent to the degree Celsius) based on the dew point. ''Range of humidex: Scale of comfort'': * 20 to 29: Little to no discomfort * 30 to 39: Some discomfort * 40 to 45: Great discomfort; avoid exertion * Above 45: Dangerous; heat stroke quite possible History The current formula for determining the humidex was developed by J. M. Masterton and F. A. Richardson of Canada's Atmospheric Environment Service in 1979. Humidex differs from the heat index used in the United States in being derived from the dew point rather than the relative humidity, though both dew point and relative humidity (when used in conjunction with air temperature) are direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shade (shadow), shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the Shade (shadow), shade. For example, when the temperature is with 70% relative humidity, the heat index is (see table below). The heat index is meant to describe experienced temperatures in the shade, but it does not take into account heating from direct sunlight, physical activity or cooling from wind. The human body normally cools itself by evaporation of perspiration, sweat. High relative humidity reduces evaporation and cooling, increasing discomfort and potential Hyperthermia, heat stress. Different individuals perceive heat differently due to body shape, metabolism, level of hydration, pregnancy, or other physical conditions. Measurement of perceived temperature has been based on reports of how hot subjects feel under controlled conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Temperature
Apparent temperature, also known as "feels like", is the temperature equivalent perceived by humans, caused by the combined effects of air temperature, relative humidity and wind speed. The measure is most commonly applied to the perceived outdoor temperature. Apparent temperature was invented by Robert G. Steadman who published a paper about it in 1984. It also applies, however, to indoor temperatures, especially saunas, and when houses and workplaces are not sufficiently heated or cooled. * The heat index and humidex measure the effect of humidity on the perception of temperatures above . In humid conditions, the air feels much hotter, because less perspiration evaporates from the skin. * The wind chill factor measures the effect of wind speed on cooling of the human body below . As airflow increases over the skin, more heat will be removed. Standard models and conditions are used. * The wet-bulb globe temperature (WBGT) combines the Effect of radiation on perceived temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Eye Syndrome
Dry eye syndrome, also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is the condition of having dry eyes. Symptoms include dryness in the eye, irritation, redness, discharge, blurred vision, and easily fatigued eyes. Symptoms range from mild and occasional to severe and continuous. Dry eye syndrome can lead to blurred vision, instability of the tear film, increased risk of damage to the ocular surface such as scarring of the cornea, and changes in the eye including the neurosensory system. Dry eye occurs when either the eye does not produce enough tears or when the tears evaporate too quickly. This can be caused by age, contact lens use, meibomian gland dysfunction, pregnancy, Sjögren syndrome, vitamin A deficiency, omega-3 fatty acid deficiency, LASIK surgery, and certain medications such as antihistamines, some blood pressure medication, hormone replacement therapy, and antidepressants. Chronic conjunctivitis such as from tobacco smoke exposure or infection may also lead to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that consists of qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity", and recommends evaluating dyspnea by assessing the intensity of its distinct sensations, the degree of distress and discomfort involved, and its burden or impact on the patient's activities of daily living. Distinct sensations include effort/work to breathe, chest tightness or pain, and "air hunger" (the feeling of not enough oxygen). The tripod position is often assumed to be a sign. Dyspnea is a normal symptom of heavy physical exertion but becomes pathological if it occurs in unexpected situations, when resting or during light exertion. In 85% of cases it is due to asthma, pneumonia, reflux/LPR, cardiac ischemia, COVID-19, interstitial lung disease, congestive hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cough
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and Microorganism, microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three phases: an inhalation, a forced exhalation against a closed glottis, and a violent release of air from the lungs following opening of the glottis, usually accompanied by a distinctive sound. Coughing into one's elbow or toward the ground—rather than forward at breathing height—can reduce the spread of infectious droplets in the air. Frequent coughing usually indicates the presence of a disease. Many viruses and bacteria benefit, from an evolutionary perspective, by causing the Host (biology), host to cough, which helps to spread the disease to new hosts. Irregular coughing is usually caused by a respiratory tract infection but can also be triggered by choking, smoking, air pollution, asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |