|
Humanzee
The humanzee (sometimes chuman, manpanzee or chumanzee) is a hypothetical hybrid of chimpanzee and human, thus a form of human–animal hybrid. Serious attempts to create such a hybrid were made by Soviet biologist Ilya Ivanovich Ivanov in the 1920s, and possibly by researchers in China in the 1960s, though neither succeeded. Etymology The portmanteau ''humanzee'' for a human–chimpanzee hybrid appears to have entered usage in the 1980s. Possibility The possibility of hybrids between humans and other apes has been entertained since at least the medieval period; Saint Peter Damian (11th century) claimed to have been told of the offspring of a human woman who had mated with a non-human ape, and so did Antonio Zucchelli, an Italian Franciscan capuchin friar who was a missionary in Africa from 1698 to 1702, and Sir Edward Coke in "The Institutes of the Lawes of England". Chimpanzees and humans are closely related. Genetic animal hybrids with different chromosome numbers decreas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hybrid (biology)
In biology, a hybrid is the offspring resulting from combining the qualities of two organisms of different varieties, subspecies, species or genera through sexual reproduction. Generally, it means that each cell has genetic material from two different organisms, whereas an individual where some cells are derived from a different organism is called a chimera. Hybrids are not always intermediates between their parents such as in blending inheritance (a now discredited theory in modern genetics by particulate inheritance), but can show hybrid vigor, sometimes growing larger or taller than either parent. The concept of a hybrid is interpreted differently in animal and plant breeding, where there is interest in the individual parentage. In genetics, attention is focused on the numbers of chromosomes. In taxonomy, a key question is how closely related the parent species are. Species are reproductively isolated by strong barriers to hybridization, which include genetic and morph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Genetic Hybrids
This is a list of genetic hybrids which is limited to well documented cases of animals of differing species able to create hybrid offspring which may or may not be infertile. Hybrids should not be confused with Chimera (genetics), genetic chimeras, such as that between Domestic sheep, sheep and goat known as the Sheep–goat chimera, geep. Wider interspecific hybrids can be made via in vitro fertilization or somatic hybridization; however, the resulting cells are not able to develop into a full organism. Nomenclature The naming of hybrid animals depends on the sex and species of the parents. The father giving the first half of his species' name and the mother the second half of hers. (e.g. a pizzly bear has a polar bear father and grizzly bear mother whereas a grolar bear's parents would be reversed.) Animals Phylum Chordata Chordate * Class Chondrichthyes ** Order Carcharhiniformes *** Family Requiem shark, Carcharhinidae **** Genus ''Carcharhinus'' ***** A group of abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–animal Hybrid
A human–animal hybrid and animal–human hybrid is an organism that incorporates elements from both humans and non-human animals. Technically, in a ''human–animal Hybrid (biology), hybrid'', each cell has both human and non-human genetic material. It is in contrast to an individual where some cells are human and some are derived from a different organism, called a ''human-animal chimera''. (A ''human chimera'', on the other hand, consists only of human cells, from different zygotes.) Examples of human–animal hybrids mainly include Humanized mouse, humanized mice that have been genetically modified mice, genetically modified by xenotransplantation of human genes. Humanized mice are commonly used as small animal models in biological and medical research for human therapeutics. Human–animal hybrids are the subject of legal, moral, and technological debate in the context of recent advances in genetic engineering. Human–animal hybrids have existed throughout Culture, soci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilya Ivanov
Ilya Ivanovich Ivanov (, – March 20, 1932) was a Russian and Soviet biologist who specialized in the field of artificial insemination and the interspecific hybridization of animals. He is famous for his controversial attempts to create a human–ape hybrid by inseminating three female chimpanzees with human sperm. Biography Ilya Ivanovich Ivanov was born in the town of Shchigry, Russia. He graduated from Kharkiv University in 1896 and became a professor in 1907. He worked as a researcher in the Askania-Nova natural reserve, also for the State Experimental Veterinary Institute (1917–1921, 1924–1930), for the Central Experimental Station for Researching Reproduction of Domestic Animals (1921-1924), and for the Moscow Higher Zootechnic Institute (1928–1930). Around the start of the 20th century, Ilya Ivanov perfected artificial insemination and its practical usage for horse breeding. He proved that this technology allows one stallion to fertilize up to 500 mares (instea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorilla
Gorillas are primarily herbivorous, terrestrial great apes that inhabit the tropical forests of equatorial Africa. The genus ''Gorilla'' is divided into two species: the eastern gorilla and the western gorilla, and either four or five subspecies. The DNA of gorillas is highly similar to that of humans, from 96 to 99% depending on what is included, and they are the next closest living relatives to humans after the chimpanzees. Gorillas are the largest living primates, reaching heights between , weights between , and arm spans up to , depending on species and sex. They tend to live in troops, with the leader being called a silverback. The eastern gorilla is distinguished from the western by darker fur colour and some other minor morphological differences. Gorillas tend to live 35–40 years in the wild. Gorillas' natural habitats cover tropical or subtropical forest in Sub-Saharan Africa. Although their range covers a small percentage of Sub-Saharan Africa, gorillas c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ResearchGate
ResearchGate is a European commercial social networking site for scientists and researchers to share papers, ask and answer questions, and find collaborators. According to a 2014 study by ''Nature'' and a 2016 article in ''Times Higher Education'', it is the largest academic social network in terms of active users, although other services have more registered users, and a 2015–2016 survey suggests that almost as many academics have Google Scholar profiles. While reading articles does not require registration, people who wish to become site members need to have an email address at a recognized institution or to be manually confirmed as a published researcher in order to sign up for an account. Articles are free to read by visitors, however additional features (such as job postings or advertisements) are accessible only as a paid subscription. Members of the site each have a user profile and can upload research output including papers, data, chapters, negative results, patents, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Ape
The Hominidae (), whose members are known as the great apes or hominids (), are a taxonomic family of primates that includes eight extant species in four genera: '' Pongo'' (the Bornean, Sumatran and Tapanuli orangutan); '' Gorilla'' (the eastern and western gorilla); '' Pan'' (the chimpanzee and the bonobo); and ''Homo'', of which only modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') remain. Numerous revisions in classifying the great apes have caused the use of the term ''hominid'' to change over time. The original meaning of "hominid" referred only to humans (''Homo'') and their closest extinct relatives. However, by the 1990s humans and other apes were considered to be "hominids". The earlier restrictive meaning has now been largely assumed by the term ''hominin'', which comprises all members of the human clade after the split from the chimpanzees (''Pan''). The current meaning of "hominid" includes all the great apes including humans. Usage still varies, however, and some scientis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
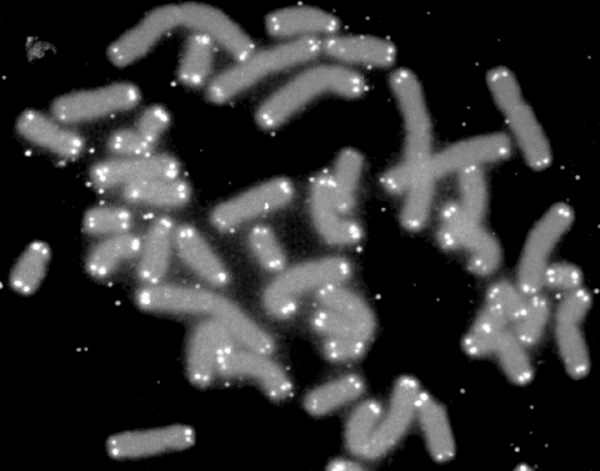
Centromere
The centromere links a pair of sister chromatids together during cell division. This constricted region of chromosome connects the sister chromatids, creating a short arm (p) and a long arm (q) on the chromatids. During mitosis, spindle fibers attach to the centromere via the kinetochore. The physical role of the centromere is to act as the site of assembly of the kinetochores – a highly complex multiprotein structure that is responsible for the actual events of chromosome segregation – i.e. binding microtubules and signaling to the cell cycle machinery when all chromosomes have adopted correct attachments to the spindle, so that it is safe for cell division to proceed to completion and for cells to enter anaphase. There are, broadly speaking, two types of centromeres. "Point centromeres" bind to specific proteins that recognize particular DNA sequences with high efficiency. Any piece of DNA with the point centromere DNA sequence on it will typically form a centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes (see #Sequences, Sequences). Telomeres are a widespread genetic feature most commonly found in eukaryotes. In most, if not all species possessing them, they protect the terminal regions of DNA, chromosomal DNA from progressive degradation and ensure the integrity of linear chromosomes by preventing DNA repair systems from mistaking the very ends of the DNA strand for a double-strand break. Discovery The existence of a special structure at the ends of chromosomes was independently proposed in 1938 by Hermann Joseph Muller, studying the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'', and in 1939 by Barbara McClintock, working with maize. Muller observed that the ends of irradiated fruit fly chromosomes did not present alterations such as deletions or inversions. He hypothesized the presence of a protective cap, which he coined "telomeres", from the Greek ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey, and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two possible first-generation hybrids between them, the mule is easier to obtain and more common than the hinny, which is the offspring of a male horse (a stallion) and a female donkey (a jenny). Mules vary widely in size, and may be of any color seen in horses or donkeys. They are more patient, hardier and longer-lived than horses, and are perceived as less obstinate and more intelligent than donkeys. Terminology A female mule is often called a "molly" or "Molly mule," though the correct term is "mare mule." A male mule is called a "john" or "John mule," though the correct term is "horse mule." A young male mule is called a "mule colt," and a young female is called a "mule filly." The donkey used to produce mules is called a "mule ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equus (genus)
''Equus'' () is a genus of mammals in the perissodactyl family (biology), family Equidae, which includes wild horse, horses, Asinus, asses, and zebras. Within the Equidae, ''Equus'' is the only recognized Extant taxon, extant genus, comprising seven living species. Like Equidae more broadly, ''Equus'' has numerous extinct species known only from fossils. The genus originated in North America and dispersed into the Old World and South America during the Early and Middle Pleistocene. Equinae, Equines are odd-toed ungulates with slender legs, long heads, relatively long necks, manes (erect in most subspecies), and long tails. All species are herbivorous, and mostly grazers, with simpler digestive systems than Ruminantia, ruminants but able to subsist on lower-quality vegetation. While the domestic horse and donkey (along with their feral horse, feral descendants) exist worldwide, wild equine populations are limited to Africa and Asia. Wild equine social systems are in two forms; a H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Humans
''Homo'' () is a genus of great ape (family Hominidae) that emerged from the genus ''Australopithecus'' and encompasses only a single extant species, ''Homo sapiens'' (modern humans), along with a number of extinct species (collectively called archaic humans) classified as either ancestral or closely related to modern humans; these include '' Homo erectus'' and '' Homo neanderthalensis''. The oldest member of the genus is '' Homo habilis'', with records of just over 2 million years ago. ''Homo'', together with the genus '' Paranthropus'', is probably most closely related to the species '' Australopithecus africanus'' within ''Australopithecus''.'''' The closest living relatives of ''Homo'' are of the genus '' Pan'' ( chimpanzees and bonobos), with the ancestors of ''Pan'' and ''Homo'' estimated to have diverged around 5.7–11 million years ago during the Late Miocene. ''H. erectus'' appeared about 2 million years ago and spread throughout Africa (debatab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |