|
Hudud Laws
''Hudud'' is an Arabic word meaning "borders, boundaries, limits". The word is applied in classical Islamic literature to punishments (ranging from public lashing, public stoning to death, amputation of hands, crucifixion, depending on the crime), for a limited number of crimes (murder, adultery, slander, theft, etc.), for which punishments have been determined (or traditionally thought to have been determined) in the verses of Quran. In classical Islamic literature, punishments are mainly of three types; Qisas-diya, Hudud, and Ta'zeer. Hudud covers the punishments given to people who exceed the limits associated with the Quran and deemed to be set by Allah (Hududullah is a phrase repeated several times in the Quran without labeling any type of crime), and in this respect it differs from Ta'zeer (). These punishments were applied in pre-modern Islam, Wael Hallaq (2009), ''An introduction to Islamic law'', p.173. Cambridge University Press. . and their use in some modern state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns language codes to 32 varieties of Arabic, including its standard form of Literary Arabic, known as Modern Standard Arabic, which is derived from Classical Arabic. This distinction exists primarily among Western linguists; Arabic speakers themselves generally do not distinguish between Modern Standard Arabic and Classical Arabic, but rather refer to both as ( "the eloquent Arabic") or simply ' (). Arabic is the List of languages by the number of countries in which they are recognized as an official language, third most widespread official language after English and French, one of six official languages of the United Nations, and the Sacred language, liturgical language of Islam. Arabic is widely taught in schools and universities around the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hadith
Hadith is the Arabic word for a 'report' or an 'account f an event and refers to the Islamic oral tradition of anecdotes containing the purported words, actions, and the silent approvals of the Islamic prophet Muhammad or his immediate circle ( companions in Sunni Islam, Ahl al-Bayt in Shiite Islam). Each hadith is associated with a chain of narrators ()—a lineage of people who reportedly heard and repeated the hadith from which the source of the hadith can be traced. The authentication of hadith became a significant discipline, focusing on the ''isnad'' (chain of narrators) and '' matn'' (main text of the report). This process aimed to address contradictions and questionable statements within certain narrations. Beginning one or two centuries after Muhammad's death, Islamic scholars, known as muhaddiths, compiled hadith into distinct collections that survive in the historical works of writers from the second and third centuries of the Muslim era ( 700−1000 CE). For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
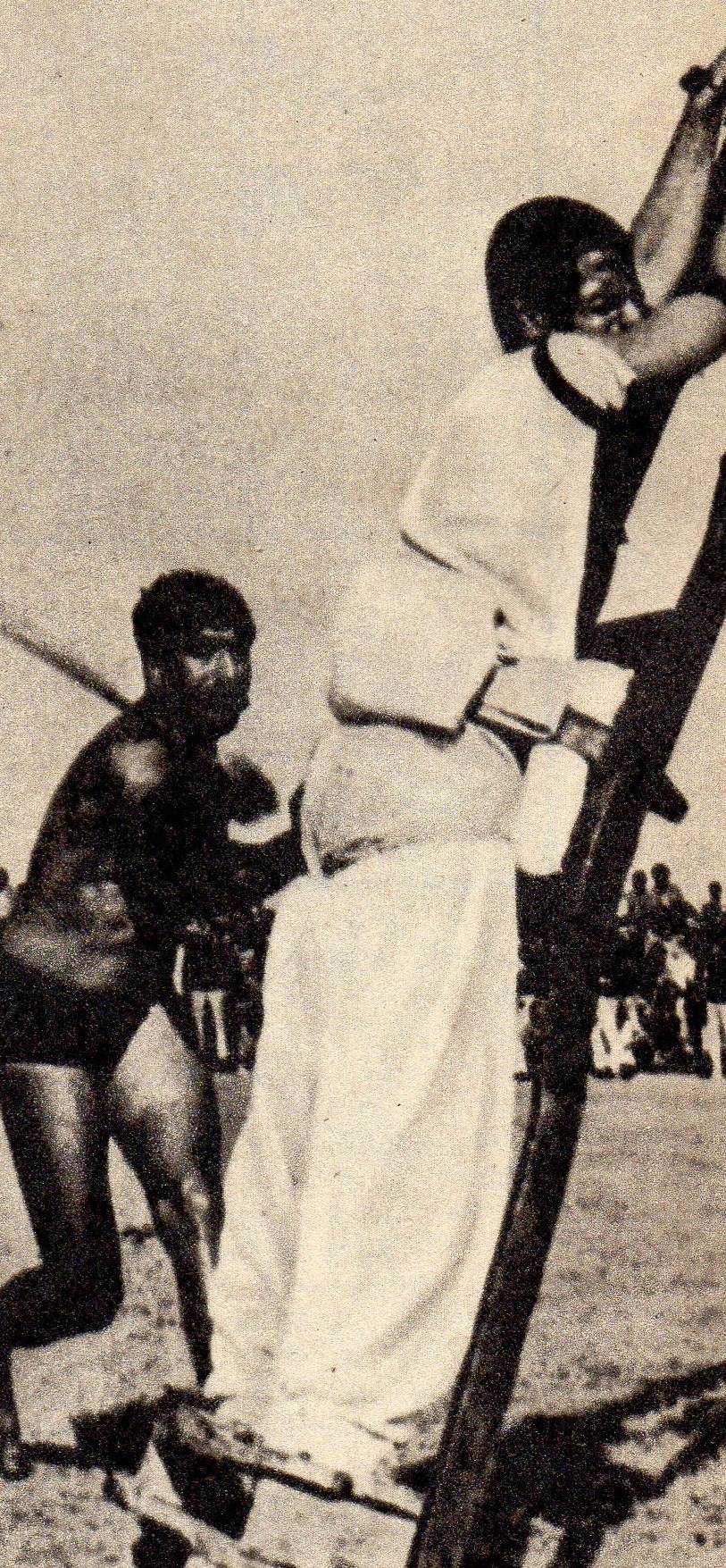
Amputation
Amputation is the removal of a Limb (anatomy), limb or other body part by Physical trauma, trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as cancer, malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a Preventive healthcare, preventive surgery for such problems. A special case is that of congenital amputation, a congenital disorder, where fetus, fetal limbs have been cut off by constrictive bands. In some countries, judicial amputation is currently used punishment, to punish people who commit crimes. Amputation has also been used as a tactic in war and acts of terrorism; it may also occur as a war injury. In some cultures and religions, minor amputations or mutilations are considered a ritual accomplishment. When done by a person, the person executing the amputation is an amputator. The oldest evidence of this practice comes from a skeleton found buried in Liang Tebo c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tazir
In Islamic Law, ''tazir'' (''ta'zeer'' or ''ta'zir'', ) lit. scolding; refers to punishment for offenses at the discretion of the judge (Qadi) or ruler of the state.Tazir Oxford Islamic Studies, Oxford University Press It is one of three major types of punishments or sanctions under Islamic law, — '' hadd'', '' qisas / '' and ''ta'zir''. Contrary to the lightness of naming, tazir are discretionary p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Diya (Islam)
''Diya'' (; : ''diyāt'', ) in Islamic law, is the financial compensation paid to the victim or heirs of a victim in the cases of murder, bodily harm or property damage by mistake. It is an alternative punishment to '' qisas'' (equal retaliation). In Arabic, the word means both blood money and ransom, and it is spelled sometimes as ''diyah'' or ''diyeh''. It only applies when murder is committed by mistake and secondly victim's family has the free consent to compromise with the guilty party; otherwise '' qisas'' applies. ''Diya'' compensation rates have historically varied based on the gender and religion of the victim.Anver M. Emon (2012), ''Religious Pluralism and Islamic Law: Dhimmis and Others in the Empire of Law'', Oxford University Press, , pp. 234-235 In the modern era, diya plays a role in the legal system of Iran, Pakistan, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. In Iran, the diya for recognized religious minorities ( Zoroastrians, Jews, and Christians, with the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Qisas
''Qisas'' or ''Qiṣāṣ'' () is an Islamic term interpreted to mean "retaliation in kind",Mohamed S. El-Awa (1993), Punishment In Islamic Law, American Trust Publications, "eye for an eye", or retributive justice. ''Qisas'' and ''diyya'' applied as an alternative in cases where retaliation conditions not met are two of several forms of punishment in classical/traditional Islamic criminal jurisprudence, the others being '' Hudud'' and '' Ta'zir''. In ancient societies, the principle of retaliation meant that the person who committed a crime or the tribe to which he belonged was punished in a manner, equivalent to the crime committed. So, an eye for an eye, a tooth for a tooth, an ear for an ear, and a life for a life. Since there was no principle of individual responsibility in ancient societies, someone else, such as the closest relative, could be punished instead of the criminal. Most of the time, it was ignored whether the act was intentional or not, and a price of life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Islamic Revival
Islamic revival ('' '', lit., "regeneration, renewal"; also ', "Islamic awakening") refers to a revival of the Islamic religion, usually centered around enforcing sharia. A leader of a revival is known in Islam as a '' mujaddid''. Within the Islamic tradition, ''tajdid'' is an important religious concept, called for periodically throughout Islamic history and according to a sahih hadith occurring every century. They manifest in renewed commitment to the fundamentals of Islam, the teachings of the Quran and hadith (aka traditions) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, the divine law of sharia, and reconstruction of society in accordance with them. In academic literature, "Islamic revival" is an umbrella term for revivalist movements in Islam, movements which may be "intolerant and exclusivist", or "pluralistic"; "favorable to science", or against it; "primarily devotional", or "primarily political"; democratic, or authoritarian; pacific, or violent. The Islamic revival of the late 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula (, , or , , ) or Arabia, is a peninsula in West Asia, situated north-east of Africa on the Arabian plate. At , comparable in size to India, the Arabian Peninsula is the largest peninsula in the world. Geographically, the Arabian Peninsula comprises Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Yemen, as well as southern Iraq and Jordan. The largest of these is Saudi Arabia. In the Roman era, the Sinai Peninsula was also considered a part of Arabia. The Arabian Peninsula formed as a result of the rifting of the Red Sea between 56 and 23 million years ago, and is bordered by the Red Sea to the west and south-west, the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman to the north-east, the Levant and Mesopotamia to the north and the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean to the south-east. The peninsula plays a critical geopolitical role in the Arab world and globally due to its vast reserves of petroleum, oil and natural gas. Before the mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zina
''Zināʾ'' () or ''zinā'' ( or ) is an Islamic legal term referring to unlawful sexual intercourse. According to traditional jurisprudence, ''zina'' can include adultery, fornication, prostitution, sodomy, incest, and bestiality. ''Zina'' must be proved by testimony of four Muslim eyewitnesses to the actual act of penetration, confession repeated four times and not retracted later. The offenders must have acted of their own free will. Rapists could be prosecuted under different legal categories which used normal evidentiary rules.A. Quraishi (1999), Her honour: an Islamic critique of the rape provisions in Pakistan's ordinance on ''zina'', ''Islamic studies'', Vol. 38, No. 3, pp. 403–431 Accusing ''zina'' without presenting the required eyewitnesses is called ''qadhf'' (), which is itself a '' hudud'' offense. There are very few recorded examples of the stoning penalty for ''zinā'' being implemented legally. Before legal reform was introduced in several countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oneworld Publications
Oneworld Publications is a British independent publishing firm founded in 1986 by Novin Doostdar and Juliet Mabey originally to publish accessible non-fiction by experts and academics for the general market. Based in London, it later added a literary fiction list (in 2009) and both a children's list (Rock the Boat, 2015) and an upmarket crime list (Point Blank, 2016), and now publishes across a wide range of subjects, including history, politics, current affairs, popular science, religion, philosophy, and psychology, as well as literary fiction, crime fiction and suspense, and children's titles. History Oneworld Publications was founded in 1986 by Novin Doostdar and Juliet Mabey, who had met as students in the 1970s and subsequently married;Alison Flood"Oneworld: the tiny publisher behind the last two Man Booker winners" ''The Guardian'', 15 November 2016. the company's name reflects their international approach to publishing with global values, initially producing non-fiction " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ) is the term for Islamic jurisprudence.Fiqh Encyclopædia Britannica ''Fiqh'' is often described as the style of human understanding, research and practices of the sharia; that is, human understanding of the divine Islamic law as revealed in the Quran and the sunnah (the teachings and practices of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions). Fiqh expands and develops Shariah through interpretation (''ijtihad'') of the Quran and ''Sunnah'' by Islamic jurists (''ulama'') and is implemented by the rulings (''fatwa'') of jurists on questions presented to them. Thus, whereas ''sharia'' is considered immutable and infallible by Muslims, ''fiqh'' is considered fallible and changeable. ''Fiqh'' deals with the observance of rituals, morals and social legislation in Islam as well as econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |