|
Hook Flash
On analog telephone lines with special services, a flash or register-recall signal is used to control functions on the public telephone exchange, Business telephone system, PBX or analog telephone adapter, VoIP ATA. The term "register-recall" in Europe refers to sending a discrete signal to alert the "register" — the logical system controlling a telephone exchange, that it should accept commands from the end user in the middle of a call. The register was normally disconnected from the circuit once a call was setup. In contemporary telephone systems, the functions of the register are carried out by software and computer hardware, but in previous generations of electromechanical exchanges, using technology such as crossbar switch, crossbar or reed relay, the register was often a system of analog electronics or even relay logic. The term "flash" or "hook flash" is commonly used in North America, while in Europe a similar signal is referred to as a register-recall or more comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone
A telephone, colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that enables two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into electronic signals that are transmitted via Electrical cable, cables and other communication channels to another telephone which reproduces the sound to the receiving user. The term is derived from and (, ''voice''), together meaning ''distant voice''. In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell was the first to be granted a United States patent for a device that produced clearly intelligible replication of the human voice at a second device. This instrument was further developed by many others, and became rapidly indispensable in business, government, and in households. The essential elements of a telephone are a microphone (''transmitter'') to speak into and an earphone (''receiver'') which reproduces the voice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conference Call
A conference call (sometimes called an audio teleconference or ATC) is a telephone call in which several people share a telephone line at the same time. The conference call may be designed to allow the called party to participate during the call or set up so that the called party merely listens into the call and cannot speak. The more limited three-way calling is available (usually at an extra charge) on home or office phone lines. For a three-way call, the first called party is dialed. Then the hook flash button (or recall button) is pressed and the other called party's phone number is dialed. While it is ringing, flash/recall is pressed again to connect the three people together. This option allows callers to add a second outgoing call to an already connected call. Features Conference calls can be designed so that the calling party calls the other participants and adds them to the call; however, participants are usually able to call into the conference call themselves by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Called Party
The called party (in some contexts called the "B-Number") is a person who (or device that) answers a telephone call. The person who (or device that) initiates a telephone call is the calling party. In some situations, the called party may number more than one. Such an instance is known as a conference call. In some systems, only one called party is contacted at each event. To initiate a conference call the calling party contacts the first called party, then this person contacts the second called party, but audio is transferred to both called parties. While a calling party will typically pay the fee for making a call, in a collect call (also known as a reverse charge call), it is instead the called party that pays the fee for the call. The called party also pays if the number dialed is a toll-free telephone number. In some countries such as Canada, the United States and China, users of mobile phone A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calling Party
The calling party (in some contexts called the "A-Number") is a person who (or device that) initiates a telephone call. The person who, or device that, receives a telephone call is the called party (or callee or B-party). In some countries, it is common etiquette for a call originator to identify himself first instead of the receiver, when the connection is established. Modems and fax machine Fax (short for facsimile), sometimes called telecopying or telefax (short for telefacsimile), is the telephonic transmission of scanned printed material (both text and images), normally to a telephone number connected to a printer or other out ...s use different tones when originating or answering a connection, which may be a source of problems for the user. References Telephony Teletraffic {{telephony-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
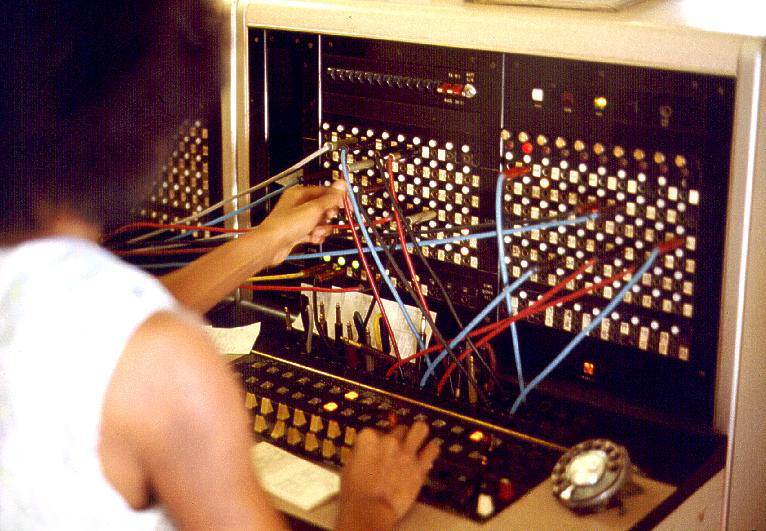
Telephone Switchboard
A telephone switchboard is a device used to connect circuits of telephones to establish telephone calls between users or other switchboards. The switchboard is an essential component of a manual telephone exchange, and is operated by switchboard operators who use electrical cords or switches to establish the connections. The switchboard saw the peak of its use in the 20th century before wider adoption of the electromechanical automatic telephone exchange. The automatic exchange, invented by Almon Strowger in 1888, has replaced most switchboards in central telephone exchanges around the world. Nevertheless, many manual branch exchanges remained operational into the second half of the 20th century in many enterprises. Some establishments, such as the White House, still operate a switchboard. Electronic devices and computer technology have given exchange operators more features. For example, a private branch exchange (PBX) in a business usually has an attendant console, or an auto- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cord Circuit
In telecommunications, a cord circuit is a switchboard circuit in which a plug-terminated cord is used to establish connections manually between user lines or between trunks and user lines. A number of cord circuits are furnished as part of the switchboard position equipment. The cords may be referred to as front cord and rear cord or trunk cord and station cord. In modern cordless switchboards, the cord-circuit function is switch operated and may be programmable. In early and middle 20th century telephone exchange A telephone exchange, telephone switch, or central office is a central component of a telecommunications system in the public switched telephone network (PSTN) or in large enterprises. It facilitates the establishment of communication circuits ...s this task was done by a supervisory relay set known variously as junctor circuit or district junctor. Later designs made it a function of the trunk circuit or absorbed it into software. See also * Switched loop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Hook
A telephone hook or switchhook is an electrical switch which indicates when the phone is hung up, often with a lever or magnetic button inside the cradle or base where a telephone handset resides. It takes its name from old wooden wall telephones and candlestick telephones, where the mouthpiece was mounted on the telephone box and, due to sidetone considerations, the receiver was separate, on a cable. When the telephone was not in use, the receiver was hung on a spring-loaded hook; its weight would cause the hook to swing down and open an electrical contact, disconnecting something, but not the telephone from the line or the phone could not ring. When the handset is on the cradle, the telephone is said to be "on-hook", or ready for a call. When the handset is off the cradle, the telephone is said to be "off-hook", or unable to receive any (further) calls. Pushing the switchhook quickly is termed a "hook flash". Purpose Telephone switchhook separates calling and transmitting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Telephone Adapter
An analog telephone adapter (ATA) or FXS gateway is a device for connecting traditional analog telephones, fax machines, and similar customer-premises devices to a digital telephone system or a voice over IP telephone network. An ATA is often built into a small enclosure with an internal or external power adapter, an Ethernet port, and one or more foreign exchange station (FXS) telephone ports. Such devices may also have a foreign exchange office (FXO) interface for providing alternative access to traditional landline telephone service. The ATA provides dial tone, ringing generator, DC power, caller ID data and other standard telephone line signaling (known collectively as BORSCHT) to the telephone connected to a modular jack. The digital interface of the ATA typically consists of an Ethernet port to connect to an Internet Protocol (IP) network, but may also be a USB port for connecting the device to a personal computer. Using such an ATA, it is possible to connect a conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centrex
Centrex is a portmanteau of central exchange, a kind of telephone exchange. It provides functions similar to a PBX, but is provisioned with equipment owned by, and located at, the telephone company premises. Centrex service was first installed in the early 1960s in New York's financial district by New York Telephone. As of 2003, it was estimated that there were 20 million Centrex lines installed worldwide by 20 telephone companies, with the most installations in the United States (15 million), Canada (2 million), and the United Kingdom (1 million). This accounted for approximately 5% of all installed business telephone lines, worldwide. In terms of user-visible features, Centrex and PBX are similar. Features include: * Direct inward dialing (DID) * Automatic routing of calls to obtain lowest cost * Call pick-up groups * Call forwarding * Conference calling * Automatic call distribution An automated call distribution system, commonly known as automatic call distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dual-tone Multi-frequency Signaling
Dual-tone multi-frequency (DTMF) signaling is a telecommunication signaling system using the voice-frequency band over telephone lines between telephone equipment and other communications devices and Automatic telephone exchange, switching centers. DTMF was first developed in the Bell System in the United States, and became known under the trademark Touch-Tone for use in push-button telephones, starting in 1963. The DTMF frequencies are standardized in ITU-T Recommendation Q.23. The signaling system is also known as ''MF4'' in the United Kingdom, as ''MFV'' in Germany, and ''Digitone'' in Canada. Touch-tone dialing with a telephone keypad gradually replaced the use of rotary dials and has become the industry standard in telephony to control equipment and signal user intent. The signaling on trunks in the telephone network uses a different type of multi-frequency signaling. Multifrequency signaling Before the development of DTMF, telephone numbers were dialed with rotary dials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
On- And Off-hook
In telephony, on-hook and off-hook are two states of a communication circuit. On subscriber telephones the states are produced by placing the handset onto or off the hookswitch. Placing the circuit into the off-hook state is also called ''seizing the line''. ''Off-hook'' originally referred to the condition that prevailed when telephones had a separate earpiece (''receiver''), which hung from its switchhook until the user initiated a telephone call by removing it. When off hook the weight of the receiver no longer depresses the spring-loaded switchhook, thereby connecting the instrument to the telephone line. Off-hook The term off-hook has the following meanings: * The condition that exists when a telephone or other user instrument is in use, i.e., during dialing or communicating. * A general description of one of two possible signaling states at an interface between telecommunications systems, such as tone or no tone and ground connection versus battery connection. Note that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
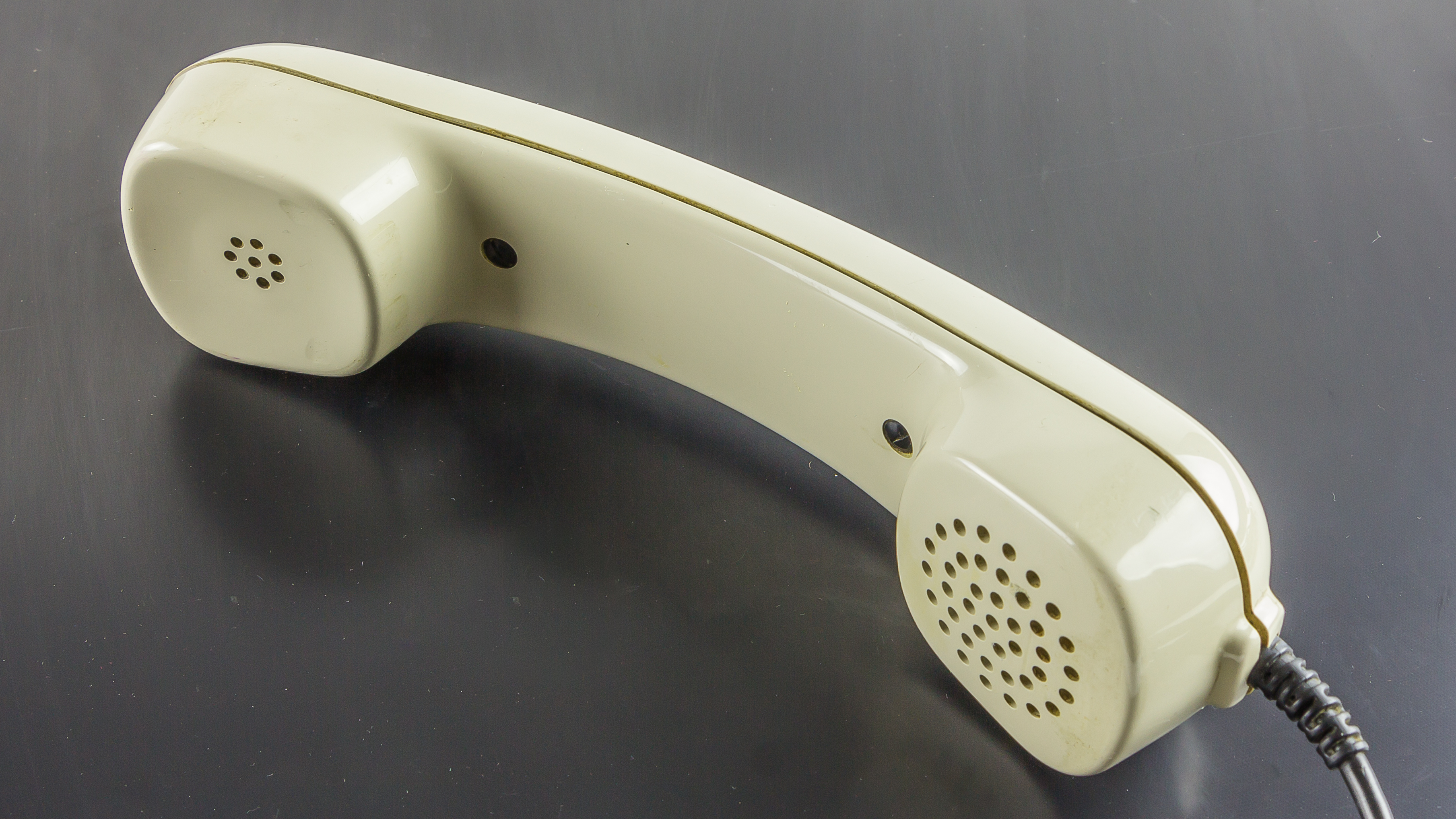
Handset
A handset is a component of a telephone that a user holds to the ear and mouth to receive audio through the receiver and speak to the remote party using the built-in transmitter. In earlier telephones, the transmitter was mounted directly on the telephone itself, which was attached to a wall at a convenient height or placed on a desk or table. Until the advent of the cordless telephone, the handset was usually wired to the base unit, typically by a flexible tinsel wire cord. The handset of a cordless telephone contains a radio transceiver which relays communication via a base station that is wired to the telephone line. A mobile phone does not require a base station and communicates directly with a cell site in designated frequency bands. Handset symbol A graphic symbol that designates a handset is used on cordless and mobile phones to specify placing or ending a telephone call. Usually a button with green upright (off-hook) handset icon is used for starting a call, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |