|
Homocysteine Desulfhydrase
The enzyme homocysteine desulfhydrase (EC 4.4.1.2) catalyzes the chemical reaction :L-homocysteine + H2O = hydrogen sulfide + NH3 + 2-oxobutanoate (overall reaction) ::(1a) L-homocysteine = hydrogen sulfide + 2-aminobut-2-enoate ::(1b) 2-aminobut-2-enoate = 2-iminobutanoate (spontaneous) ::(1c) 2-iminobutanoate + H2O = 2-oxobutanoate + NH3 (spontaneous) This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the class of carbon-sulfur lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is L-homocysteine hydrogen-sulfide-lyase (deaminating; 2-oxobutanoate-forming). Other names in common use include homocysteine desulfurase, L-homocysteine hydrogen-sulfide-lyase (deaminating). This enzyme participates in nitrogen and sulfur metabolism. It employs one cofactor, pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalysis
Catalysis () is the increase in rate of a chemical reaction due to an added substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed by the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. The rate increase occurs because the catalyst allows the reaction to occur by an alternative mechanism which may be much faster than the noncatalyzed mechanism. However the noncatalyzed mechanism does remain possible, so that the total rate (catalyzed plus noncatalyzed) can only increase in the presence of the catalyst and never decrease. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the chemistry, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. When chemical reactions occur, the atoms are rearranged and the reaction is accompanied by an Gibbs free energy, energy change as new products are generated. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the positions of electrons in the forming and breaking of chemical bonds between atoms, with no change to the Atomic nucleus, nuclei (no change to the elements present), and can often be described by a chemical equation. Nuclear chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that involves the chemical reactions of unstable and radioactive Chemical element, elements where both electronic and nuclear changes can occur. The substance (or substances) initially involved in a chemical reaction are called reagent, reactants or reagents. Chemical reactions are usually characterized by a chemical change, and they yield one or more Product (c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele is credited with having discovered the chemical composition of purified hydrogen sulfide in 1777. Hydrogen sulfide is toxic to humans and most other animals by inhibiting cellular respiration in a manner similar to hydrogen cyanide. When it is inhaled or its salts are ingested in high amounts, damage to organs occurs rapidly with symptoms ranging from breathing difficulties to convulsions and death. Despite this, the human body produces small amounts of this sulfide and its mineral salts, and uses it as a signalling molecule. Hydrogen sulfide is often produced from the microbial breakdown of organic matter in the absence of oxygen, such as in swamps and sewers; this process is commonly known as anaerobic digestio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyase
In biochemistry, a lyase is an enzyme that catalyzes the breaking (an elimination reaction) of various chemical bonds by means other than hydrolysis (a substitution reaction) and oxidation Redox ( , , reduction–oxidation or oxidation–reduction) is a type of chemical reaction in which the oxidation states of the reactants change. Oxidation is the loss of electrons or an increase in the oxidation state, while reduction is ..., often forming a new double bond or a new ring structure. The reverse reaction is also possible (called a Michael reaction). For example, an enzyme that catalyzed this reaction would be a lyase: : ATP → cAMP + PPi Lyases differ from other enzymes in that they require only one substrate for the reaction in one direction, but two substrates for the reverse reaction. Nomenclature Systematic names are formed as "''substrate group-lyase''." Common names include decarboxylase, dehydratase, aldolase, etc. When the product is more importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Metabolism
The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Important processes in the nitrogen cycle include fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. The majority of Earth's atmosphere (78%) is atmospheric nitrogen, making it the largest source of nitrogen. However, atmospheric nitrogen has limited availability for biological use, leading to a scarcity of usable nitrogen in many types of ecosystems. The nitrogen cycle is of particular interest to ecologists because nitrogen availability can affect the rate of key ecosystem processes, including primary production and decomposition. Human activities such as fossil fuel combustion, use of artificial nitrogen fertilizers, and release of nitrogen in wastewater have dramatically altered the global nitr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
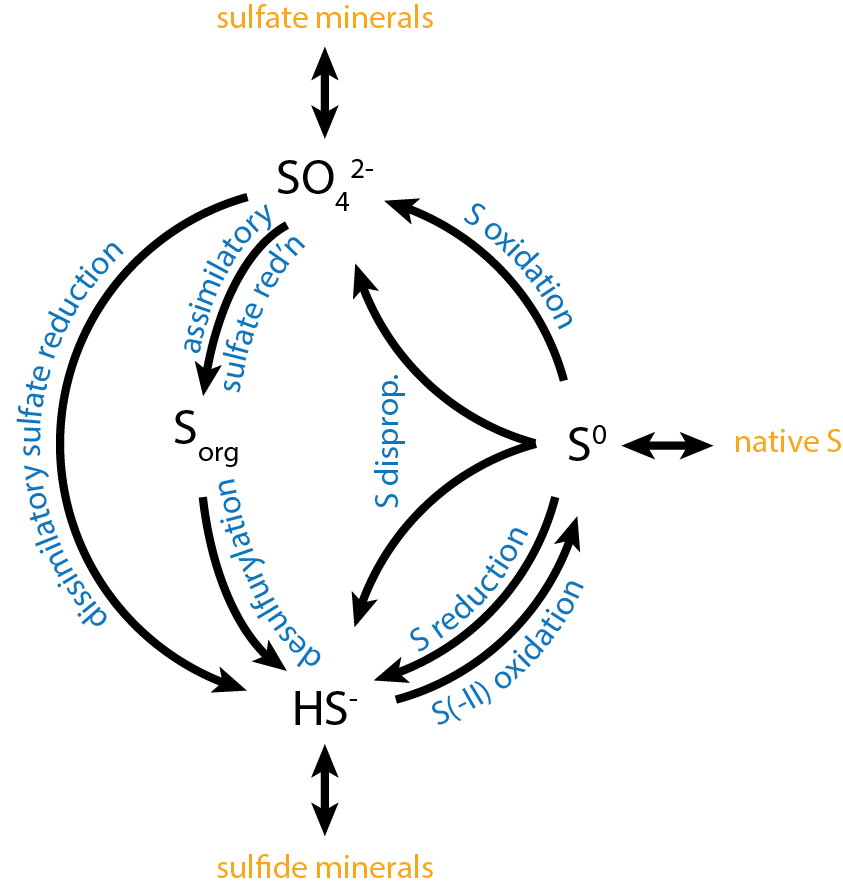
Sulfur Metabolism
Sulfur is metabolized by all organisms, from bacteria and archaea to plants and animals. Sulfur can have an oxidation state from −2 to +6 and is reduced or oxidized by a diverse range of organisms. The element is present in proteins, sulfate esters of polysaccharides, steroids, phenols, and sulfur-containing coenzymes. Oxidation Reduced sulfur compounds are oxidized by most organisms, including higher animals and higher plants. Some organisms can conserve energy (i.e., produce ATP) from the oxidation of sulfur and it can serve as the sole energy source for some lithotrophic bacteria and archaea. Sulfur oxidizers use enzymes such as Sulfide:quinone reductase, sulfur dioxygenase and sulfite oxidase to oxidize sulfur compounds to sulfate. Sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms Reduced sulfur compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide, elemental sulfur, sulfite, thiosulfate, and various polythionates (e.g., tetrathionate), are oxidized by chemotrophic, phototrophic, and mixotrophic bacteria for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofactor (biochemistry)
A cofactor is a non-protein chemical compound or metallic ion that is required for an enzyme's role as a catalyst (a catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction). Cofactors can be considered "helper molecules" that assist in biochemical transformations. The rates at which these happen are characterized in an area of study called enzyme kinetics. Cofactors typically differ from ligands in that they often derive their function by remaining bound. Cofactors can be classified into two types: inorganic ions and complex organic molecules called coenzymes. Coenzymes are mostly derived from vitamins and other organic essential nutrients in small amounts. (Some scientists limit the use of the term "cofactor" for inorganic substances; both types are included here.) Coenzymes are further divided into two types. The first is called a " prosthetic group", which consists of a coenzyme that is tightly (or even covalently and, therefore, permanently) bound to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxal Phosphate
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates. Role as a coenzyme PLP acts as a coenzyme in all transamination reactions, and in certain decarboxylation, deamination, and racemization reactions of amino acids. The aldehyde group of PLP forms a Schiff-base linkage (internal aldimine) with the ε-amino group of a specific lysine group of the aminotransferase enzyme. The α-amino group of the amino acid substrate displaces the ε-amino group of the active-site lysine residue in a process known as transaldimination. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EC 4
EC or ec may refer to: Arts and entertainment * EC Comics, an American publisher of comic books * ''Electric Circus'', a Canadian television program * Eric Clapton Stratocaster, signature model guitars by Fender Businesses and organisations Government * Environment and Climate Change Canada, a Canadian federal government department * European Commission, the executive body of the European Union * European Council, the European Union institution comprising the college of heads of state of government * European Communities, one of the three pillars of the EU * European Community, a significant component of the European Union from 1993 to 2009, renamed European Economic Community Transportation * EuroCity, a train service of the European inter-city rail network * EasyJet Europe (IATA code: EC) * Avialeasing (former IATA code: EC), a cargo airline * East Coast (train operating company), a train operating company in the UK * EC, the aircraft registration prefix for Spain Educatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridoxal Phosphate Enzymes
Pyridoxal (PL) is one form of vitamin B6. Some medically relevant bacteria, such as those in the genera '' Granulicatella'' and '' Abiotrophia'', require pyridoxal for growth. This nutritional requirement can lead to the culture phenomenon of satellite growth. In ''in vitro'' culture, these pyridoxal-dependent bacteria may only grow in areas surrounding colonies of bacteria from other genera ("satellitism") that are capable of producing pyridoxal. Pyridoxal is involved in what is believed to be the most ancient reaction of aerobic metabolism on Earth, about 2.9 billion years ago, a forerunner of the Great Oxidation Event."Protein Domain Structure Uncovers the Origin of Aerobic Metabolism and the Rise of Planetary Oxygen", Gustavo Caetano-Anolles et al., published in Structure; paper available from University of Illinois News Bureau, 2012. See also * Pyridoxal phosphate Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |