|
Holosteans
Holostei is a group of ray-finned bony fish. It is divided into two major clades, the Halecomorphi, represented by the single living genus, '' Amia'' with two species, the bowfins (''Amia calva'' and ''Amia ocellicauda''), as well as the Ginglymodi, the sole living representatives being the gars (Lepisosteidae), represented by seven living species in two genera (''Atractosteus'', ''Lepisosteus''). The earliest members of the clade, which are putative " semionotiforms" such as ''Acentrophorus'' and '' Archaeolepidotus'', are known from the Middle to Late Permian and are among the earliest known neopterygians. Holostei was thought to be regarded as paraphyletic. However, a recent study provided evidence that the Holostei are the closest living relatives of the Teleostei, both within the Neopterygii. This was found from the morphology of the Holostei, for example presence of a paired vomer. Holosteans are closer to teleosts than are the chondrosteans, the other group intermediate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neopterygii
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant fishes, and over half of all living vertebrate species. While living holosteans include only freshwater taxa, teleosts are diverse in both freshwater and marine environments. Many new species of teleosts are scientifically described each year. The potentially oldest known neopterygian is the putative " semionotiform" '' Acentrophorus varians'' from the Middle Permian of Russia; however, one study incorporating morphological data from fossils and molecular data from nuclear and mitochondrial DNA, places this divergence date at least 284 mya (million years ago), during the Artinskian stage of the Early Permian. Another study suggests an even earlier split (360 myr ago, near the Devonian-Carboniferous boundary). Evolution a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinopterygii
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class (biology), class of Osteichthyes, bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fish fin, fins made of webbings of skin supported by radially extended thin bony spine (zoology), spines called ''lepidotrichia'', as opposed to the bulkier, fleshy lobed fins of the sister taxon, sister clade Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). Resembling folding fans, the actinopterygian fins can easily change shape and wetted area, providing superior thrust-to-weight ratios per movement compared to sarcopterygian and chondrichthyian fins. The fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the articulation (anatomy), articulation between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). The vast majority of actinopterygians are teleosts. By species count, they domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amia (fish)
''Amia'', commonly called bowfin, is a genus of Actinopterygii, ray-finned fish related to gars in the infraclass Holostei. They are regarded as taxonomy (biology), taxonomic relict species, relicts, being the sole surviving species of the order (biology), order Amiiformes and clade Halecomorphi, which dates from the Triassic to the Eocene, persisting to the present. There are two living species in ''Amia'', ''Amia calva'' and ''Amia ocellicauda'', and a number of extinct species which have been described from the fossil record. Etymology The genus name ''Amia'' derives from the Ancient Greek and Latin name for an unknown fish (most likely the Atlantic bonito) referred to by ancient and medieval authors including Pliny the Elder, Isidore of Seville, and Thomas of Cantimpré. Evolution and phylogeny ''Amia'' is thought to have diverged from its Sister group, sister genus, ''Cyclurus'', during the Late Cretaceous. These two genera, their sister amiine ''Pseudoamiatus'', and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
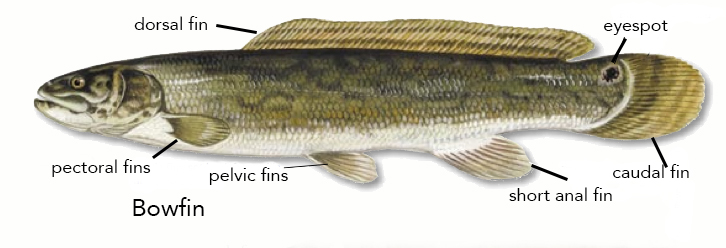
Bowfin
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "living fossil" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with '' Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halecomorphi
Halecomorphi is a taxon of Actinopterygii, ray-finned bony fish in the clade Neopterygii. The only extant Halecomorph species are the bowfin (''Amia calva'') and eyespot bowfin (''Amia ocellicauda''), but the group contains many extinct species in several family (biology), families (including Amiidae, Caturidae, Liodesmidae, Sinamiidae) in the order (biology), order Amiiformes, as well as the extinct orders Ionoscopiformes, Panxianichthyiformes, and Parasemionotiformes. The fossil record of halecomorphs goes back at least to the Early Triassic epoch (geology), epoch. The Halecomorphi exhibit a combination of plesiomorphy, ancestral features, such as most heavily mineralized fish scale, scales, but also by more derived or "modern" features, particularly in the structure of the skull (e.g. position and shape of preopercles). Unique derived traits (synapomorphies) of the Halecomorphi include: *Unique jaw articulation in which the Quadrate bone, quadrate and Symplectic bone, sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bowfin
The ruddy bowfin (''Amia calva'') is a ray-finned fish native to North America. Common names include mudfish, mud pike, dogfish, grindle, grinnel, swamp trout, and choupique. It is regarded as a relict, being one of only two surviving species of the Halecomorphi, a group of fish that first appeared during the Early Triassic, around 250 million years ago. The bowfin is often considered a "living fossil" because they have retained some morphological characteristics of their early ancestors. It is one of two species in the genus ''Amia,'' along with '' Amia ocellicauda'', the eyespot bowfin. The closest living relatives of bowfins are gars, with the two groups being united in the clade Holostei. Bowfins are demersal freshwater piscivores, commonly found throughout much of the eastern United States, and in southern Ontario and Quebec. Fossil deposits indicate Amiiformes were once widespread in both freshwater and marine environments across North and South America, Europe, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chondrostei
Chondrostei is a subclass of non- neopterygian ray-finned fish. While the term originally referred to the paraphyletic grouping of all non-neopterygian ray-finned fish, it was redefined by Patterson in 1982 to be a clade comprising the Acipenseriformes (which includes sturgeon and paddlefish) and their extinct relatives. Taxa commonly suggested to represent relatives of the Acipenseriformes include the Triassic marine fish '' Birgeria'' and the Saurichthyiformes, but their relationship with the Acipenseriformes has been strongly challenged on cladistic grounds. Coccolepididae, a group of small weakly ossified Jurassic and Cretaceous fish found in both marine and freshwater environments, have also been suggested to be close relatives of the Acipenseriformes. However, this has never been subject to cladistic analysis. Near & Thacker (2024) also recovered the ptycholepiform '' Boreosomus'' as a stem-acipenseriform. The following taxa are known: * Subclass Chondrostei ** Genus � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
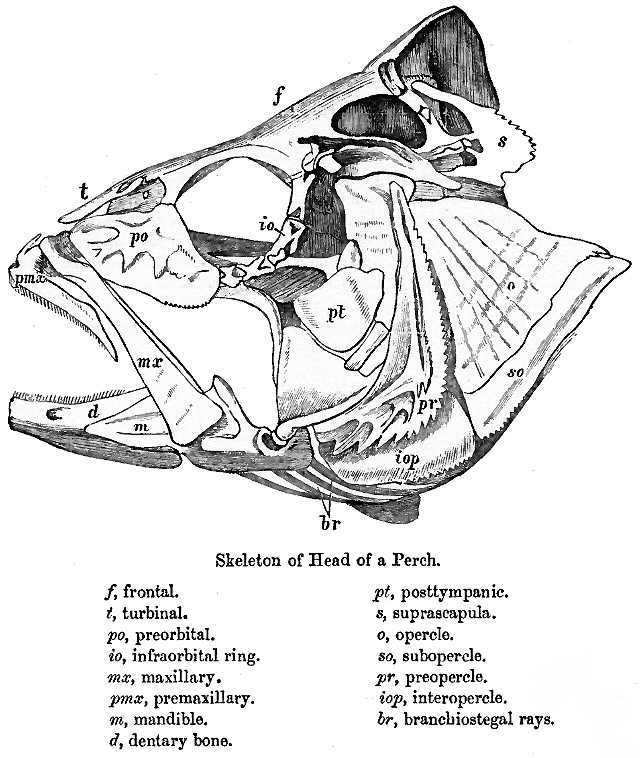
Vomer
The vomer (; ) is one of the unpaired facial bones of the skull. It is located in the midsagittal line, and articulates with the sphenoid, the ethmoid, the left and right palatine bones, and the left and right maxillary bones. The vomer forms the inferior part of the nasal septum in humans, with the superior part formed by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone. The name is derived from the Latin word for a ploughshare and the shape of the bone. In humans The vomer is situated in the median plane, but its anterior portion is frequently bent to one side. It is thin, somewhat quadrilateral in shape, and forms the hinder and lower part of the nasal septum; it has two surfaces and four borders. The surfaces are marked by small furrows for blood vessels, and on each is the nasopalatine groove, which runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the nasopalatine nerve and vessels. Borders The ''superior border'', the thickest, presents a deep furrow, bounded on eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teleostei
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of fish. The Teleostei, which is variously considered a Division (zoology), division or an infraclass in different taxonomic systems, include over 26,000 species that are arranged in about 40 order (biology), orders and 448 family (biology), families. Teleosts range from giant oarfish measuring or more, and ocean sunfish weighing over , to the minute male anglerfish ''Photocorynus spiniceps'', just long. Including not only torpedo-shaped fish built for speed, teleosts can be flattened vertically or horizontally, be elongated cylinders or take specialised shapes as in anglerfish and seahorses. The difference between teleosts and other bony fish lies mainly in their jaw bones; teleosts have a movable premaxilla and corresponding modifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraphyly
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In contrast, a monophyletic grouping (a clade) includes a common ancestor and ''all'' of its descendants. The terms are commonly used in phylogenetics (a subfield of biology) and in the tree model of historical linguistics. Paraphyletic groups are identified by a combination of synapomorphies and symplesiomorphies. If many subgroups are missing from the named group, it is said to be polyparaphyletic. The term received currency during the debates of the 1960s and 1970s accompanying the rise of cladistics, having been coined by zoologist Willi Hennig to apply to well-known taxa like Reptilia (reptiles), which is paraphyletic with respect to birds. Reptilia contains the last common ancestor of reptiles and all descendants of that ancest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atractosteus
''Atractosteus'' (from Greek ''atraktos'' (ἀτρακτὀς), 'spindle' and ''osteon'' (ὀστέον), 'bone') is a genus of gars in the family Lepisosteidae, with three extant species. It is one of two surviving gar genera alongside ''Lepisosteus''. The three surviving species are all widely separated from one another, with ''A. spatula'' being found in the south-central United States, ''A. tropicus'' in southern Mexico and Central America, and ''A. tristoechus'' in Cuba. Although generally inhabiting fresh water, they are tolerant of marine conditions. Evolution The genus first appeared during the Santonian stage of the Late Cretaceous, having diverged from ''Lepisosteus'' earlier in the Cretaceous. It quickly achieved a widespread distribution throughout the rest of the Cretaceous, being known from North America, South America and Europe. ''Atractosteus'' survived the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, with one articulated foss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |