|
History Of The Huns
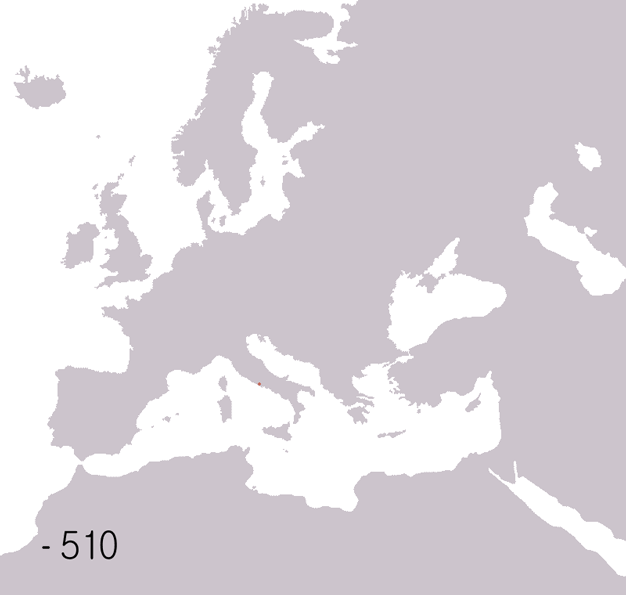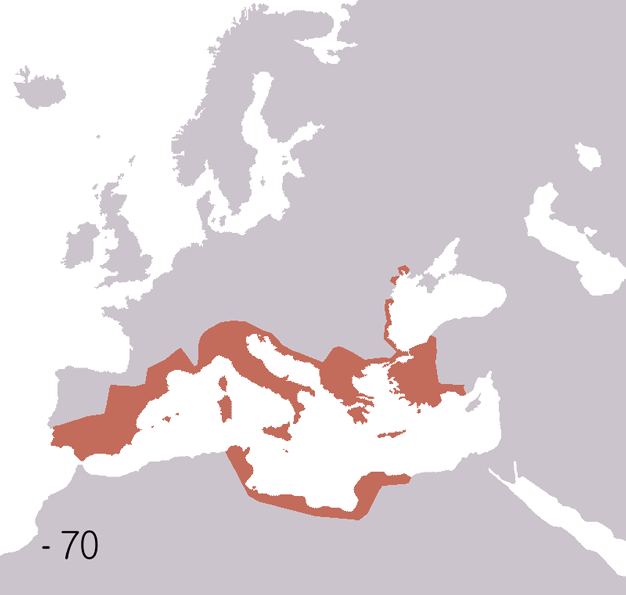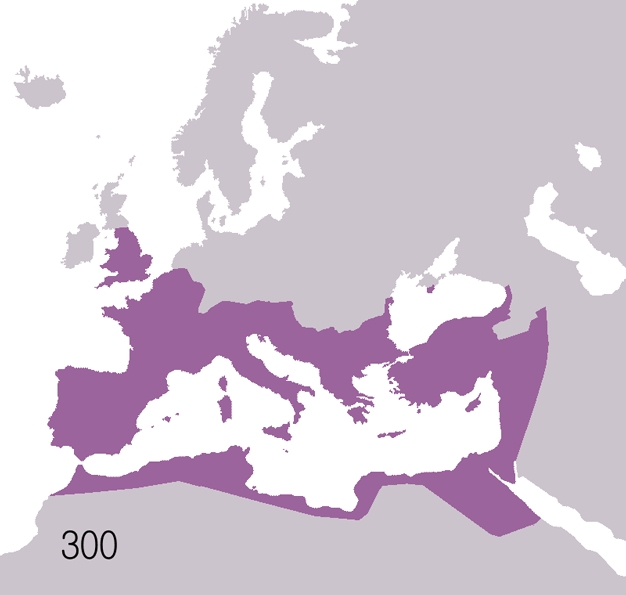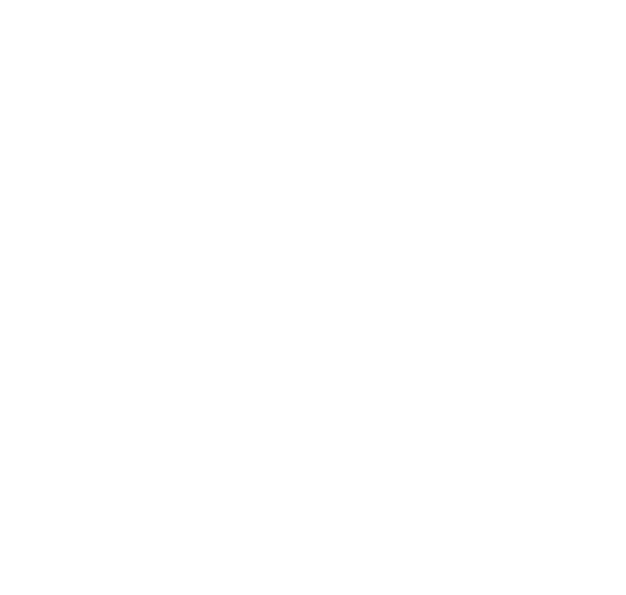
The history of the Huns spans the time from before their first secure recorded appearance in Europe around 370 AD to after the disintegration of their empire around 469. The Huns likely entered Western Asia shortly before 370, from Central Asia: they first conquered the Goths and the Alans, pushing a number of tribes to seek refuge within the Roman Empire. In the following years, the Huns conquered most of the Germanic and Scythian tribes outside of the borders of the Roman Empire. They also launched invasions of both the Asian provinces of Rome and the Sasanian Empire in 375. Under Uldin, the first Hunnic ruler named in contemporary sources, the Huns launched a first unsuccessful large-scale raid into the Eastern Roman Empire in Europe in 408. From the 420s, the Huns were led by the brothers Octar and Ruga, who both cooperated with and threatened the Romans. Upon Ruga's death in 435, his nephews Bleda and Attila became the new rulers of the Huns, and launched a successful raid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Catalaunian Fields
The Battle of the Catalaunian Plains (or Fields), also called the Battle of the Campus Mauriacus, Battle of Châlons, Battle of Troyes or the Battle of Maurica, took place on June 20, 451 AD, between a victorious coalition, led by the Roman general Flavius Aetius and the Visigothic king Theodoric I, against the Huns and their vassals, commanded by their king, Attila. It proved to be one of the last major military operations of the Western Roman Empire, although Germanic ''foederati'' composed the majority of the coalition army. The exact strategic significance is disputed. Historians generally agree that the siege of Aurelianum was the decisive moment in the campaign and stopped the Huns' attempt to advance any further into Roman territory or establish vassals in Roman Gaul. However, the Huns looted and pillaged much of Gaul and crippled the military capacity of the Romans and Visigoths. Attila died only two years later, in 453. After the Battle of Nedao in 454, the coalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Northeast Asian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Northeast Asian (ANA), also known as Amur ancestry, is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 7th–4th millennia before present, in far eastern Siberia, Mongolia and the Baikal regions. They are inferred to have diverged from Ancient East Asians about 24kya ago, and are represented by several ancient human specimens found in archaeological excavations east of the Altai Mountains. They are a sub-group of the Ancient Northern East Asians (ANEA). ANA ancestry is represented by hunter-gatherer remains from the Amur region, as well as remains found in present-day Mongolia. Origins The Paleolithic origins of Ancient Northern East Asians (ANEA) are not well clarified, mainly due to the lack of archaeological specimens. So far, the oldest populations for which genomic data have been obtained are the "Basal East Asian" Tianyuan man ( BP), as well as the Amur33K (c. 33,000 BP) s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xianbei
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multilingual, multi-ethnic confederation consisting of mainly Proto-Mongols (who spoke either pre-Proto-Mongolic,, quote: "The Xianbei confederation appears to have contained speakers of Pre-Proto-Mongolic, perhaps the largest constituent linguistic group, as well as former Xiongnu subjects, who spoke other languages, Turkic almost certainly being one of them."Pulleyblank, Edwin G. (1983). "The Chinese and Their Neighbors in Prehistoric and Early Historic China," in The Origins of Chinese Civilization, University of California Pressp. 452of pp. 411–466. or Para-Mongolic languages), and, to a minor degree, Tungusic and Turkic peoples. They originated from the Donghu people who splintered into the Wuhuan and Xianbei when they were defeated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Steppe
The Eurasian Steppe, also called the Great Steppe or The Steppes, is the vast steppe ecoregion of Eurasia in the temperate grasslands, savannas and shrublands biome. It stretches through Manchuria, Mongolia, Xinjiang, Kazakhstan, Siberia, European Russia, Ukraine, Moldova, Romania, Bulgaria, Hungary and Slovakia. Since the Paleolithic, Paleolithic age, the Steppe Route has been the main overland route between Eastern Europe, North Asia, Central Asia and East Asia economically, politically, and culturally. The Steppe route is a predecessor not only of the Silk Road, which developed during Classical antiquity, antiquity and the Middle Ages, but also of the Eurasian Land Bridge in the modern era. It has been home to nomadic empires and many large tribal confederations and ancient states throughout history, such as the Xiongnu, Scythia, Cimmerians, Cimmeria, Sarmatians, Sarmatia, Hunnic Empire, Sogdia, Xianbei, Mongol Empire, Magyar tribes, and Göktürk Khaganate. Geography Divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Tribal Confederations
The Turkic term ''oğuz'' or ''oğur'' (in z- and r-Turkic, respectively) is a historical term for "military division, clan, or tribe" among the Turkic peoples. With the Mongol invasions of 1206–21, the Turkic khaganates were replaced by Mongol or hybrid Turco-Mongol confederations, where the corresponding military division came to be known as '' orda''. Background The 8th-century Kul Tigin stela has the earliest instance of the term in Old Turkic epigraphy: ''Toquz Oghuz'', the "nine tribes". Later the word appears often for two largely separate groups of the Turkic migration in the early medieval period, namely: * Onogur ("ten tribes") * Utigurs * Kutrigurs * Uyghur * Saragurs The stem ''uq-, oq-'' "kin, tribe" is from a Proto-Turkic ''*uk''. The Old Turkic word has often been connected with ''oq'' "arrow"; Pohl (2002) in explanation of this connection adduces the Chinese ''T'ang-shu'' chronicle, which reports: "the khan divided his realm into ten tribes. To the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Of The Western Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast territory was divided among several successor polities. The Roman Empire lost the strengths that had allowed it to exercise effective control over its Western provinces; modern historians posit factors including the effectiveness and numbers of the army, the health and numbers of the Roman population, the strength of the economy, the competence of the emperors, the internal struggles for power, the religious changes of the period, and the efficiency of the civil administration. Increasing pressure from invading peoples outside Roman culture also contributed greatly to the collapse. Climatic changes and both endemic and epidemic disease drove many of these immediate factors. The reasons for the collapse are major subjects of the hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sciri
The Sciri, or Scirians, were a Germanic people. They are believed to have spoken an East Germanic language. Their name probably means "the pure ones". The Sciri were mentioned already in the late 3rd century BC as participants in a raid on the city of Olbia (Pontic), Olbia near modern-day Odesa. In the late 4th century they lived somewhere north of the Black Sea and Lower Danube in the vicinity of the Goths. By the early 5th century, the Sciri had been subdued by the Huns, whom they fought under at the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains in 451 AD. After the death of Attila, the Sciri broke free from Hunnic rule at the Battle of Nedao in 454 AD. They subsequently were recorded holding their own kingdom north of the Middle Danube, under the leadership of Edeko and his son Onoulphus. After the destruction of this kingdom by the Ostrogoths in the late 460s AD, Odoacer, another son of Edeko, attained high status within the Roman army in Italy, ruling Sciri, Rugii and other non-Roman pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogoths
The Ostrogoths () were a Roman-era Germanic peoples, Germanic people. In the 5th century, they followed the Visigoths in creating one of the two great Goths, Gothic kingdoms within the Western Roman Empire, drawing upon the large Gothic populations who had settled in the Balkans in the 4th century. While the Visigoths had formed under the leadership of Alaric I, the new Ostrogothic political entity which came to rule Italy was formed in the Balkans under Theodoric the Great. Theoderic's family, the Amal dynasty, accumulated royal power in Roman Pannonia after the death of Attila, and collapse of his Hunnic empire. Byzantine Empire, Byzantine Zeno (emperor), Emperor Zeno played these Pannonian Goths off against the Thracian Goths to their south. However, instead the two groups united after the death of the Thracian leader Theoderic Strabo and his son Recitach. Zeno then backed Theodoric to invade Italy and replace Odoacer there, whom he had previously supported as its king. In 493, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gepids
The Gepids (; ) were an East Germanic tribes, East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary, and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava, and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion and language of the Goths and Vandals. They are first mentioned by Roman sources in the third century. In the fourth century, they were among the peoples incorporated into the Huns, Hunnic Empire, within which they formed an important part. After the death of Attila, the Gepids under their leader Ardaric, led an alliance of other peoples who had been in the empire, and defeated the sons of Attila and their remaining allies at the Battle of Nedao in 454. The Gepids and their allies subsequently founded kingdoms on the Middle Danube, bordering on the Roman Empire. The Gepid Kingdom was one of the most important and long-lasting of these, centered on Sirmium, and sometimes referred to as Gepidia. It covered a large part of the Roman Dacia, former Roman province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |