|
History Of Rocketry
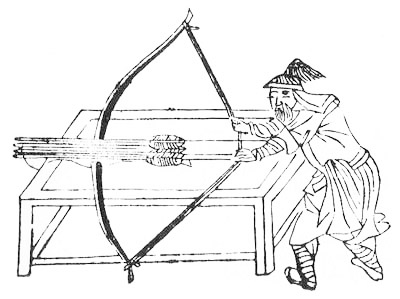
The first rockets were used as propulsion systems for arrows, and may have appeared as early as the 10th century in Song dynasty China. However, more solid documentary evidence does not appear until the 13th century. The technology probably spread across Eurasia in the wake of the Mongol invasions of the mid-13th century. Usage of rockets as weapons before modern rocketry is attested to in China, Korea, India, and Europe. One of the first recorded rocket launchers is the "wasp nest" fire arrow launcher produced by the Ming dynasty in 1380. In Europe, rockets were also used in the same year at the Battle of Chioggia. The Joseon kingdom of Korea used a type of mobile multiple rocket launcher known as the "Munjong Hwacha" by 1451. Iron-cased rockets were used by Kingdom of Mysore (Mysorean rockets) and by Marathas during the mid 18th century, and were later modified and used by the British. The later models and improvements were known as the Congreve rocket and used in the Napoleoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mysorean Rockets
Mysorean rockets were an Indian military weapon. The iron-cased rockets were successfully deployed for military use. They were the first successful iron-cased rockets, developed in the late 18th century in the Kingdom of Mysore (part of present-day India) under the rule of King Hyder Ali. The Mysorean army, under King Hyder Ali and his son King Tipu Sultan, used the rockets effectively against the British East India Company during the 1780s and 1790s. According to James Forbes, Marathas also used iron-encased rockets in their battles. Their conflicts with the company exposed the British to this technology further, which was then used to advance European rocketry with the development of the Congreve rocket in 1805. Technology and deployment There was a regular rocket corps in the Mysore Army, beginning with about 1,200 men in King Hyder Ali's time. During the Second Anglo-Mysore War, Colonel William Baillie's ammunition stores are thought to have been detonated by a stra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium nitrate (saltpeter). The sulfur and charcoal act as fuels while the saltpeter is an oxidizer. Gunpowder has been widely used as a propellant in firearms, artillery, rocketry, and pyrotechnics, including use as a blasting agent for explosives in quarrying, mining, building Pipeline transport, pipelines, tunnels, and road#Construction, roads. Gunpowder is classified as a Explosive#Low, low explosive because of its relatively slow decomposition rate, low ignition temperature and consequently low brisance, brisance (breaking/shattering). Low explosives deflagration, deflagrate (i.e., burn at subsonic speeds), whereas high explosives detonation, detonate, producing a supersonic shockwave. Ignition of gunpowder packed behind a projectile generates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
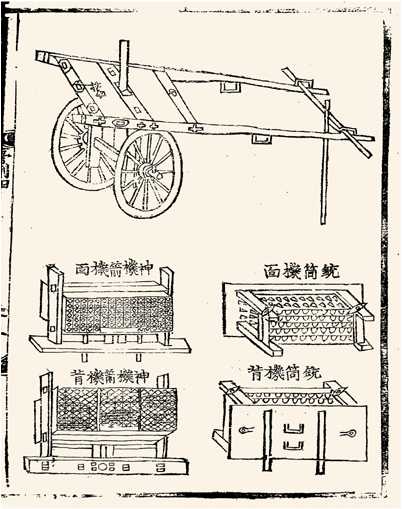
Hwacha
The ''hwacha'' or ''hwach'a'' () was a multiple rocket launcher and an organ gun of similar design which were developed in fifteenth century Korea. It resembled a wooden cart with a launch pad attached, and it had up to 200 tiny Sin'gijŏn, singijeon arrows propelled by rockets. The former variant fired one or two hundred rocket-powered arrows, while the latter fired several dozen iron-headed arrows or bolts out of gun barrels. The term was used to refer to other war wagons or other cart-based artillery in later periods, such as that developed by Byeon Yijung in the 1590s. These weapons were notably deployed in the defense of the Korean Peninsula against the Japanese when they Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98), invaded in the 1590s. Some List of historians by area of study#History of Korea, East Asian historians believe this technological breakthrough, alongside the turtle ship in the mid-16th century, had a distinctive effect during the war. Hwachas appear in Korean museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wubei Zhi
The ''Wubei Zhi'' (; ''Treatise on Armament Technology'' or ''Records of Armaments and Military Provisions''), also commonly known by its Japanese translated name Bubishi, is a military book in Chinese history. It was compiled in 1621 by (茅元儀 ''Máo Yuányí''; 1594–1640?), an officer of waterborne troops in the Ming dynasty. The ''Wubei Zhi'' contains 240 volumes, 10,405 pages, and more than 200,000 Chinese characters. Structure ''Wubei Zhi'' consists of five sections, "Bing Jue Ping", "Zhan Lue Kao", "Zhen Lian Zhi", "Jun Zi Sheng", and "Zhan Du Zai". *"Bing Jue Ping" (Commentary on Military Formulae) Containing 18 chapters, this section includes military theories from significant figures including, but not limited to, Sun Tzu. Some of these theories date back to the last years of the Eastern Zhou dynasty, more than 1,800 years before the editor. *"Zhan Lue Kao" (Consideration of Tactics) This section consists of 31 chapters, and describes more than 600 specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Huolongjing
The ''Huolongjing'' (; Wade-Giles: ''Huo Lung Ching''; rendered in English as ''Fire Drake Manual'' or ''Fire Dragon Manual''), also known as ''Huoqitu'' (“Firearm Illustrations”), is a Chinese military treatise compiled and edited by Jiao Yu and Liu Bowen of the early Ming dynasty (1368–1683) during the 14th century. The ''Huolongjing'' is primarily based on the text known as ''Huolong Shenqi Tufa'' (''Illustrations of Divine Fire Dragon Engines''), which no longer exists. History The ''Huolongjings intended function was to serve as a guide to "fire weapons" involving gunpowder during the 1280s to 1350s. Its predecessor, the ''Huolong Shenqi Tufa'' (Fire-Drake Illustrated Technology of Magically (Efficacious) Weapons), has since been lost. The ''Huolongjing'' was one of three early Ming military treatises that were mentioned by Jiao Xu, but only the ''Huolongjing'' remains. Although the earliest edition of the ''Huolongjing'' was written by Jiao Yu, a Ming general, some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aeolipile
An aeolipile, aeolipyle, or eolipile, from the Greek "Αἰόλου πύλη," , also known as a Hero's (or Heron's) engine, is a simple, bladeless radial turbine, radial steam turbine which spins when the central water container is heated. Torque is produced by steam jets exiting the turbine. The Greeks in Egypt, Greek-Egyptian mathematician and engineer Hero of Alexandria described the device in the 1st century AD, and many sources give him the credit for its invention. However, Vitruvius was the first to describe this appliance in his ''De architectura'' (). The aeolipile is considered to be the first recorded steam engine or reaction steam turbine, but it is neither a practical source of power nor a direct predecessor of the type of steam engine invented during the Industrial Revolution. The name – derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek word Αἴολος and Latin word ''pila'' – translates to "the ball of Aeolus", Aeolus being the Greek mythology, Greek god of the air a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hero Of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria (; , , also known as Heron of Alexandria ; probably 1st or 2nd century AD) was a Greek mathematician and engineer who was active in Alexandria in Egypt during the Roman era. He has been described as the greatest experimentalist of antiquity and a representative of the Hellenistic scientific tradition. Hero published a well-recognized description of a steam-powered device called an '' aeolipile'', also known as "Hero's engine". Among his most famous inventions was a windwheel, constituting the earliest instance of wind harnessing on land. In his work ''Mechanics'', he described pantographs. Some of his ideas were derived from the works of Ctesibius. In mathematics, he wrote a commentary on Euclid's ''Elements'' and a work on applied geometry known as the ''Metrica''. He is mostly remembered for Heron's formula; a way to calculate the area of a triangle using only the lengths of its sides. Much of Hero's original writings and designs have been lost, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pythagoreanism
Pythagoreanism originated in the 6th century BC, based on and around the teachings and beliefs held by Pythagoras and his followers, the Pythagoreans. Pythagoras established the first Pythagorean community in the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek colony of Crotone, Kroton, in modern Calabria (Italy) circa 530 BC. Early Pythagorean communities spread throughout Magna Graecia. Already during Pythagoras' life it is likely that the distinction between the ''akousmatikoi'' ("those who listen"), who is conventionally regarded as more concerned with religious, and ritual elements, and associated with the oral tradition, and the ''mathematikoi'' ("those who learn") existed. The ancient biographers of Pythagoras, Iamblichus () and his master Porphyry (philosopher), Porphyry ( ) seem to make the distinction of the two as that of 'beginner' and 'advanced'. As the Pythagorean cenobites practiced an esoteric path, like the Greco-Roman mysteries, mystery schools of antiquity, the adherents, ''akou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Greek People
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Albania, Anatolia, parts of Italy and Egypt, and to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Eastern Mediterranean and Black Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with many Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th century and the Eastern Mediterranean areas of ancient Gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Archytas
Archytas (; ; 435/410–360/350 BC) was an Ancient Greek mathematician, music theorist, statesman, and strategist from the ancient city of Taras (Tarentum) in Southern Italy. He was a scientist and philosopher affiliated with the Pythagorean school and famous for being the reputed founder of mathematical mechanics and a friend of Plato. As a Pythagorean, Archytas believed that arithmetic (logistic), rather than geometry, provided the basis for satisfactory proofs, and developed the most famous argument for the infinity of the universe in antiquity. Life Archytas was born in Tarentum, a Greek city in the Italian Peninsula that was part of Magna Graecia, and was the son of Hestiaeus. He was presumably taught by Philolaus, and taught mathematics to Eudoxus of Cnidus and to Eudoxus' student, Menaechmus. Politically and militarily, Archytas appears to have been the dominant figure in Tarentum in his generation, somewhat comparable to Pericles in Athens a half-century earlier. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Napoleonic Wars
{{Infobox military conflict , conflict = Napoleonic Wars , partof = the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars , image = Napoleonic Wars (revision).jpg , caption = Left to right, top to bottom:Battles of Battle of Austerlitz, Austerlitz, Fall of Berlin (1806), Berlin, Battle of Friedland, Friedland, Battle of Aspern-Essling, Aspern-Essling, French occupation of Moscow, Moscow, Battle of Leipzig, Leipzig and Battle of Paris (1814), Paris , date = {{start and end dates, 1803, 5, 18, 1815, 11, 20, df=yes({{Age in years, months, weeks and days, month1=05, day1=18, year1=1803, month2=11, day2=20, year2=1815) , place = Atlantic Ocean, Caucasus, Europe, French Guiana, Mediterranean Sea, North Sea, West Indies, Ottoman Egypt, Egypt, East Indies. , result = Coalition victory , combatant1 = Coalition forces of the Napoleonic Wars, Coalition forces:{{flagcountry, United Kingdom of Great Britain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |