|
Hirsute
Hirsutism is excessive body hair on parts of the body where hair is normally absent or minimal. The word is from early 17th century: from Latin ''hirsutus'' meaning "hairy". It usually refers to a male pattern of hair growth in a female that may be a sign of a more serious medical condition, especially if it develops well after puberty. Cultural stigma against hirsutism can cause much psychological distress and social difficulty. Discrimination based on facial hirsutism often leads to the avoidance of social situations and to symptoms of anxiety and depression. Hirsutism is usually the result of an underlying endocrine imbalance, which may be adrenal, ovarian, or central. It can be caused by increased levels of androgen hormones. The amount and location of the hair is measured by a Ferriman–Gallwey score. It is different from hypertrichosis, which is excessive hair growth anywhere on the body. Treatments may include certain birth control pills, antiandrogens, or in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
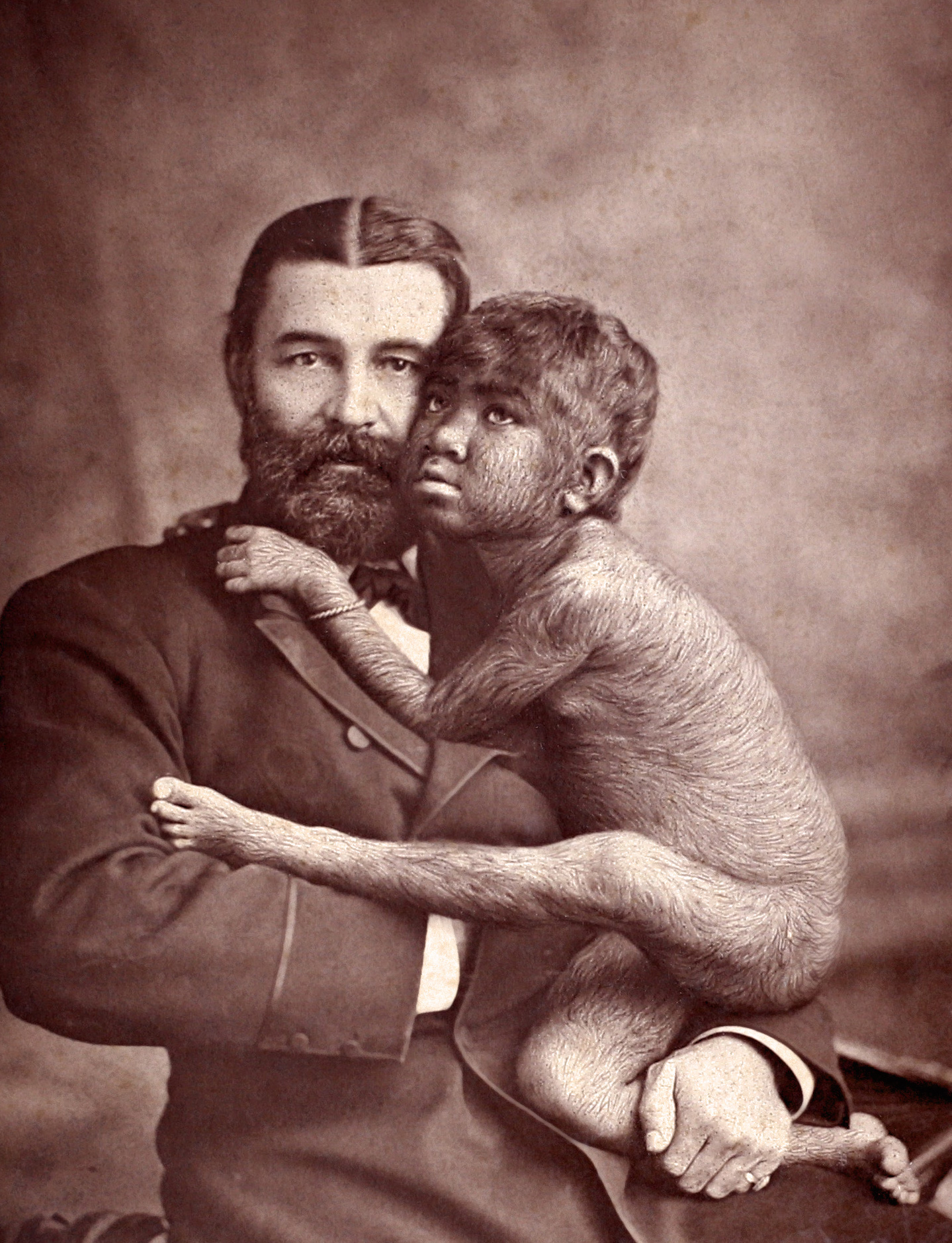
Hypertrichosis
Hypertrichosis (sometimes known as werewolf syndrome) is an abnormal amount of hair growth over the body. The two distinct types of hypertrichosis are generalized hypertrichosis, which occurs over the entire body, and localized hypertrichosis, which is restricted to a certain area. Hypertrichosis can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired later in life. The excess growth of hair occurs in areas of the skin with the exception of androgen-dependent hair of the pubic area, face, and axillary regions. Several circus sideshow performers in the 19th and early 20th centuries, such as Julia Pastrana, had hypertrichosis. Many of them worked as freaks and were promoted as having distinct human and animal traits. Classification Two methods of classification are used for hypertrichosis. One divides them into either generalized versus localized hypertrichosis, while the other divides them into congenital versus acquired. Congenital Congenital forms of hypertrichosis are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Hair
Body hair or androgenic hair is terminal hair that develops on the human body during and after puberty. It is different from head hair and also from less visible vellus hair, which is much finer and lighter in color. Growth of androgenic hair is related to the level of androgens (male hormones) and the density of androgen receptors in the dermal papillae. Both must reach a threshold for the proliferation of hair follicle cells. From childhood onward, regardless of sex, vellus hair covers almost the entire area of the human body. Exceptions include the lips, the backs of the ears, palms of hands, soles of the feet, certain external genital areas, the navel, and scar tissue. Density of hair – i.e. the number of hair follicles per unit area of skin – varies from person to person. In many cases, areas on the human body that contain vellus hair will begin to produce darker and thicker body hair during puberty, such as the first growth of beard hair on a male and female adole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac within the ovary. They usually cause no symptoms, but occasionally they may produce bloating, lower abdominal pain, or lower back pain. The majority of cysts are harmless. If the cyst either #Cyst rupture, breaks open or causes ovarian torsion, twisting of the ovary, it may cause severe pain. This may result in vomiting or Lightheadedness, feeling faint, and even cause headaches. Most ovarian cysts are related to ovulation, being either follicular cyst of ovary, follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts. Other types include Endometrioma, cysts due to endometriosis, dermoid cysts, and cystadenomas. Many small cysts occur in both ovaries in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Pelvic inflammatory disease may also result in cysts. Rarely, cysts may be a form of ovarian cancer. Diagnosis is undertaken by pelvic examination with a pelvic ultrasound or other testing used to gather further details. Often, cysts are simply observed over time. If they c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
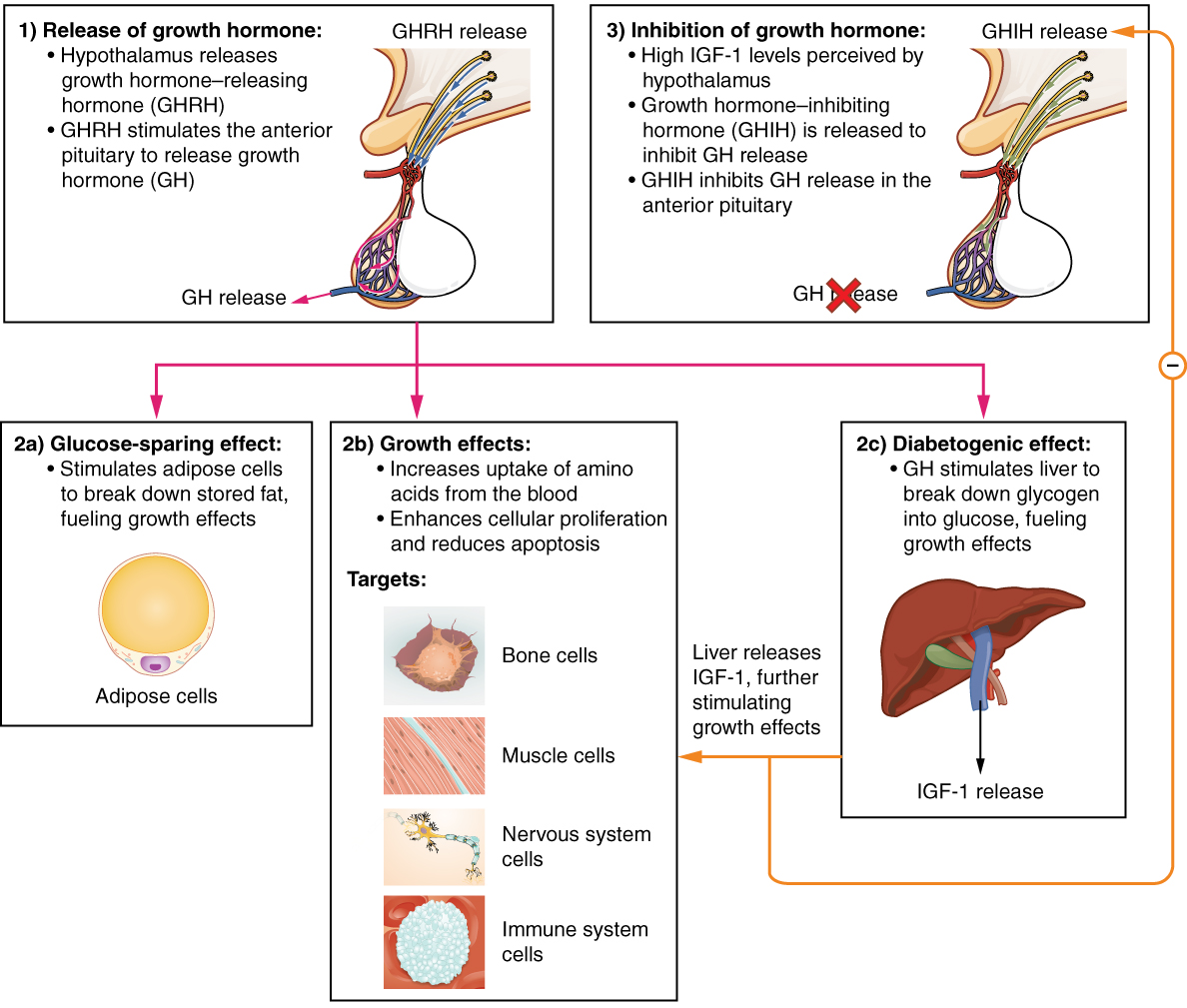
Growth Hormone
Growth hormone (GH) or somatotropin, also known as human growth hormone (hGH or HGH) in its human form, is a peptide hormone that stimulates growth, cell reproduction, and cell regeneration in humans and other animals. It is thus important in human development. GH also stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) and increases the concentration of glucose and free fatty acids. It is a type of mitogen which is specific only to the receptors on certain types of cells. GH is a 191-amino acid, single-chain polypeptide that is synthesized, stored and secreted by somatotropic cells within the lateral wings of the anterior pituitary gland. A recombinant form of HGH called somatropin ( INN) is used as a prescription drug to treat children's growth disorders and adult growth hormone deficiency. In the United States, it is only available legally from pharmacies by prescription from a licensed health care provider. In recent years in the United States, some health ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gigantism
Gigantism (, ''gígas'', "wiktionary:giant, giant", plural γίγαντες, ''gígantes''), also known as giantism, is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average height, average. In humans, this condition is caused by over-production of growth hormone in childhood. It is a rare disorder resulting from increased levels of growth hormone before the fusion of the Epiphyseal plate, growth plate which usually occurs at some point soon after puberty. This increase is most often due to abnormal tumor growths on the pituitary gland. Gigantism should not be confused with acromegaly, the adult form of the disorder, characterized by Somatic (biology), somatic enlargement specifically in the extremities and face. Cause Gigantism is characterized by an excess of growth hormone (GH). The excess of growth hormone that brings about gigantism is virtually always caused by pituitary growths (adenomas). These adenomas are on the Anterior pituitary, anteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromegaly
Acromegaly is a disorder that results in excess growth of certain parts of the human body. It is caused by excess growth hormone (GH) after the growth plates have closed. The initial symptom is typically enlargement of the hands and feet. There may also be an enlargement of the forehead, jaw, and nose. Other symptoms may include joint pain, thicker skin, deepening of the voice, headaches, and Visual impairment, problems with vision. Complications of the disease may include type 2 diabetes, sleep apnea, and high blood pressure. Signs and symptoms Features that may result from a high level of GH or expanding tumor include: * Headaches * Enlargement of the hands, feet, nose, lips, and ears, and a general thickening of the skin * Soft tissue swelling of internal organs, notably the heart with the attendant weakening of its muscularity, and the kidneys, also the vocal cords resulting in a characteristic thick, deep voice and slowing of speech * Generalized expansion of the skull at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due To 21-hydroxylase Deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency (CAH) is a genetic disorder characterized by impaired production of cortisol in the adrenal glands. It is classified as an inherited metabolic disorder. CAH is an autosomal recessive condition since it results from inheriting two copies of the faulty '' CYP21A2'' gene responsible for 21-hydroxylase enzyme deficiency. The most common forms of CAH are: ''classical'' form, usually diagnosed at birth, and ''nonclassical'', late onset form, typically diagnosed during childhood or adolescence, although it can also be identified in adulthood when seeking medical help for fertility concerns or other related issues, such as PCOS or menstrual irregularities. Carriers for the alleles of the nonclassical forms may have no symptoms, such form of CAH is sometimes called ''cryptic'' form. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in all its forms accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of all types of conge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a group of Genetic disorder#Autosomal recessive, autosomal recessive disorders characterized by impaired cortisol synthesis. It results from the deficiency of one of the five enzymes required for the Biosynthesis, synthesis of cortisol in the adrenal cortex. Most of these disorders involve excessive or deficient production of hormones such as glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, or sex steroids, and can alter development of primary sex characteristic, primary or secondary sex characteristics in some affected infants, children, or adults. It is one of the most common autosomal recessive disorders in humans. Types CAH can occur in various forms. The clinical presentation of each form is different and depends to a large extent on the underlying enzyme defect, its precursor retention, and deficient products. Classical forms appear in infancy and nonclassical forms appear in late childhood. The presentation in patients with classic CAH can be fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inborn Errors Of Steroid Metabolism
An inborn error of steroid metabolism is an inborn error of metabolism due to defects in steroid metabolism. Types A variety of conditions of abnormal steroidogenesis exist due to genetic mutations in the steroidogenic enzymes involved in the process, of which include: Generalized * 20,22-Desmolase (P450scc) deficiency: blocks production of all steroid hormones from cholesterol * 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency: impairs progestogen and androgen metabolism; prevents the synthesis of estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids; causes androgen deficiency in males and androgen excess in females * Combined 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency: impairs progestogen metabolism; prevents androgen, estrogen, and glucocorticoid synthesis; causes mineralocorticoid excess * Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: prevents production of numerous but not all sex steroids, as well as other metabolic reactions Androgen- and estrogen-specific * Isolated 17,20-ly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cushing's Syndrome
Cushing's syndrome is a collection of signs and symptoms due to prolonged exposure to glucocorticoids such as cortisol. Signs and symptoms may include high blood pressure, abdominal obesity but with thin arms and legs, reddish stretch marks, a round red face due to facial plethora, a fat lump between the shoulders, weak muscles, weak bones, acne, and fragile skin that heals poorly. Women may have more hair and irregular menstruation or loss of menses, with the exact mechanisms of why still unknown. Occasionally there may be changes in mood, headaches, and a chronic feeling of tiredness. Cushing's syndrome is caused by either excessive cortisol-like medication, such as prednisone, or a tumor that either produces or results in the production of excessive cortisol by the adrenal glands. Cases due to a pituitary adenoma are known as Cushing's disease, which is the second most common cause of Cushing's syndrome after medication. A number of other tumors, often referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary Adenoma
Pituitary adenomas are tumors that occur in the pituitary gland. Most pituitary tumors are benign, approximately 35% are invasive and just 0.1% to 0.2% are carcinomas.Pituitary Tumors Treatment (PDQ®)–Health Professional Version NIH National Cancer Institute Pituitary adenomas represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasia, neoplasms, with an estimated prevalence, prevalence rate in the general population of approximately 17%. Non-invasive and non-secreting pituitary adenomas are considered to be Benign tumors, benign in the literal as well as the clinical sense, though a 2011 meta-analysis of available research showed that research to either support or refute this assumption was scant and of questionable qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrenal Hyperplasia
The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three main zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis. The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |