|
High Speed Rail
High-speed rail (HSR) is a type of rail transport network utilising trains that run significantly faster than those of traditional rail, using an integrated system of specialised rolling stock and dedicated tracks. While there is no single definition or standard that applies worldwide, lines built to handle speeds of at least or upgraded lines of at least are generally considered to be high-speed. The first high-speed rail system, the Tōkaidō Shinkansen, began operations in Honshu, Japan, in 1964. Due to the streamlined spitzer-shaped nose cone of the trains, the system also became known by its English nickname bullet train. Japan's example was followed by several European countries, initially in Italy with the Direttissima line, followed shortly thereafter by France, Germany, and Spain. Today, much of Europe has an extensive network with numerous international connections. Construction since the 21st century has led to China taking a leading role in high-speed rail. , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokaido Shinkansen
The is a Japanese high-speed rail line that is part of the nationwide Shinkansen network. Along with the San'yō Shinkansen, it forms a continuous high-speed railway through the Taiheiyō Belt, also known as the Tokaido corridor. Opening in 1964, running between Tokyo Station, Tokyo and Shin-Ōsaka Station, Shin-Ōsaka, it was the world's first high-speed rail line, and it remains one of the world's busiest. Since 1987, it has been operated by the Central Japan Railway Company (JR Central), prior to that by Japanese National Railways (JNR). There are three types of services on the line: from fastest to slowest, they are the limited-stop ''Nozomi (train), Nozomi'', the semi-fast ''Hikari (train), Hikari'', and the all-stop ''Kodama (train), Kodama''. Many ''Nozomi'' and ''Hikari'' trains continue onward to the San'yō Shinkansen, going as far as Fukuoka, Fukuoka, Fukuoka's Hakata Station. The different services operate at mostly the same speed. The line was named a joint List o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In France
France has a large network of high-speed rail lines. As of June 2021, the French high-speed rail network comprises of tracks, making it one of the largest in Europe and the world. As of early 2023, new lines are being constructed or planned. The first French high-speed railway, the LGV Sud-Est, linking the suburbs of Paris and Lyon, opened in 1981. In addition to serving destinations across France, the high-speed rail system is also connected to the United Kingdom, Spain, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, and Italy. The SNCF, France's state-owned rail company, operates both a premium service (TGV inOui) and a budget service ( Ouigo). The French national high-speed rail network follows the spoke-and-hub model, centered on Paris. Besides its main operator, the SNCF, it is also used by Eurostar, Thalys, Deutsche Bahn, Trenitalia France, RENFE, and the Swiss Federal Railways. Tracks The newest high-speed lines allow speeds of in normal operation: orig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Poland
High-speed rail service () commenced in Poland on 14 December 2014, with the introduction of 20 non-tilting New Pendolino trainsets operating on 4 designated lines radiating out from Warsaw. Polish State Railways started passenger service using Pendolino trains operating at a maximum speed of 200 km/h on 80 km line Olszamowice-Zawiercie (part of railway line called PKP rail line 4, CMK, from Warsaw to Katowice/Kraków). From December 2017 there are two 200 km/h sections, 136 km long in total and from December 2020, speed 200 km/h was introduced on 45% of the Warsaw–Gdańsk railway. Till 14 December 2024, all high-speed services operated by PKP in Poland were branded as Express Intercity Premium (EIP). From 15 December 2024, Polish State Railways introduced also locomotive-hauled trains reaching the top speed of 200 km/h, branded as Express InterCity (EIC). Current connections PKP Intercity was initially using only nine sets a day to operate 23 E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Norway
Opened on the 8th of October 1998, the only high-speed rail in Norway, on the Rail transport in Norway, railways of Norway is on Gardermobanen, a 64 kilometer line between Oslo Sentralstasjon, Oslo Central Station and Eidsvoll Station, Eidsvoll via Oslo Airport Station, Oslo Airport. The main service on this route is Flytoget, commuting between Oslo Airport and the metropolitan areas of Oslo at speeds of up to 210 km/h (130 mph). It was extended westwards to include the city of Drammen in 2008, though not at high speed. The high-speed section is also used by express and regional trains between Oslo and Eidsvoll. In September 2010, Jernbaneverket awarded several contracts for research into new high-speed routes in Norway. These focus on six routes; five from Oslo to Bergen, Kristiansand/Stavanger, Trondheim, Gothenburg, and Stockholm, plus a sixth coastal route through Bergen, Haugesund and Stavanger. Background Compared to continental European countries, Norway is far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
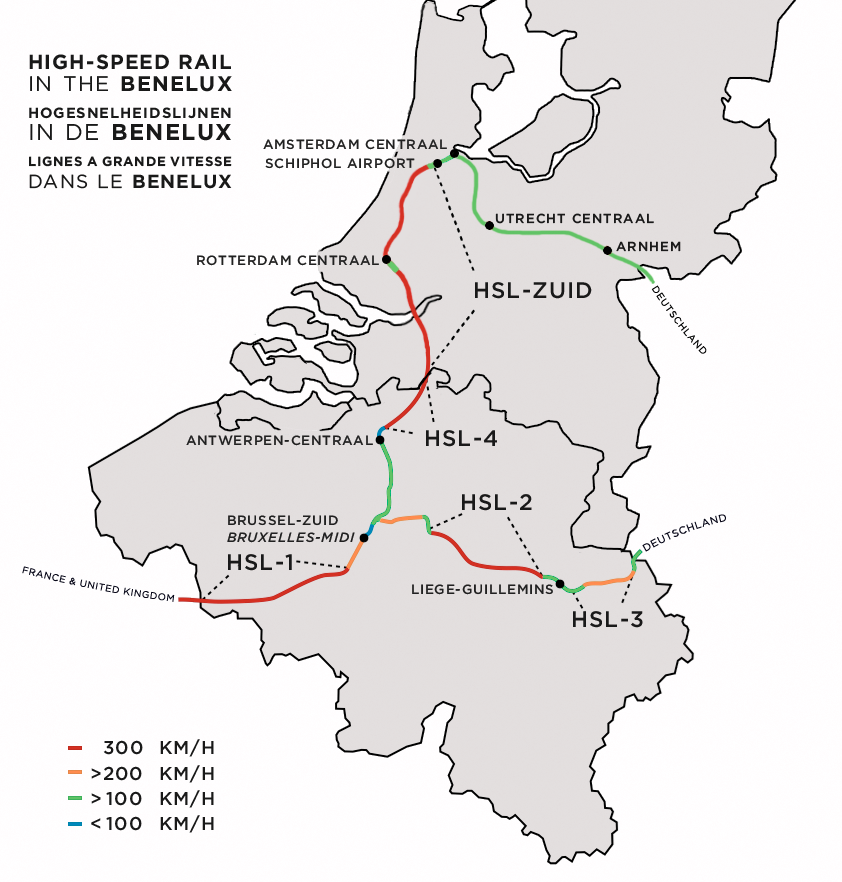
High-speed Rail In The Netherlands
High-speed rail service in the Netherlands started on 13 December 2009 with the dedicated HSL-Zuid line that connects the Randstad via Brussels to the European high-speed rail network. In later years improved traditional rail sections were added to the high-speed network. Proposals for more dedicated high-speed lines were deemed too costly; plans for the HSL-Oost to Germany were mothballed and instead of the Zuiderzeelijn the less ambitious Hanzelijn was built to enable future high-speed service between the northern provinces and the Randstad. As of 2020 three high-speed train services are operative in the Netherlands: Thalys, Intercity Express (ICE), and Eurostar; the short-lived Fyra service was cancelled in 2013 after severe reliability issues. History As early as 1973, the Den Uyl cabinet discussed a high-speed railway line in the Netherlands. It was not until 1988 that the Nederlandse Spoorwegen (NS) started three HSL projects, namely HSL-Zuid, HSL-Oost, and HSL- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Morocco
Morocco's high-speed rail network was created when the first service, Al Boraq, commenced in 2018. This service runs on a line that connects the Moroccan cities of Tangier and Casablanca via Rabat with a 323 km (220 mi) line of which 186 km (116 mi) allows speeds up to 320 km/h (200 mph). As of March 2025 the Casablanca – Tangier high-speed rail line is the only high-speed rail line in the country with an extension to Marrakesh expected to be completed by 2030. Al Boraq and other conventional passenger rail services are operated by Morocco's national railway operator ONCF. Under the ''2040 Rail Strategy'' a total of 1100 km (684 mi) of high-speed rail is planned. The Al Boraq service is the first of its kind on the African continent, and as of March 2025 it is the only high-speed rail service in Africa until the completion of High-speed rail in Egypt, Egypt's high-speed rail project. Rolling stock High-speed service is provided by ONCF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Indonesia
Indonesia operates a single high-speed rail service between the country's capital and largest city Jakarta, and third largest city Bandung. It is branded as Whoosh (short for , ) and operated by Kereta Cepat Indonesia China (KCIC). The Whoosh is the first high-speed railway in Southeast Asia and the Southern Hemisphere. It covers a distance of with a maximum operating speed of , and design speed of KCIC400AF train of , making it the fastest commercially operating railway network in the world, tied with a handful of lines in China. The travel time between the two cities averages 45 minutes, down from 3 hours with the existing railway line. Construction start at August 2018, with the cost of $7.3 billion to build, the line began trial operation with passengers on 7 September 2023 and commercial operations on 17 October 2023. The Whoosh high-speed train has served 6.06 million passengers during a full year in 2024. As of September 2024, there are 62 daily trips of Whoosh. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Finland
Although Finland has no dedicated high-speed rail lines, sections of its rail network are capable of running speeds of up to . The Finnish national railway company VR operates tilting Alstom Pendolino trains. The trains reach their maximum speed of in regular operation on a route between Kerava and Lahti. This portion of track was opened in 2006. The trains can run at on a longer route between Helsinki and Seinäjoki and peak at that speed between Helsinki and Turku. The main railway line between Helsinki and Oulu has been upgraded between Seinäjoki and Oulu to allow for trains to run at speeds between and . Other parts of the Finnish railway network are limited to lower speed. A new service called Allegro started between Helsinki and Saint Petersburg, Russia, in December 2010 with a journey time of 3½ hours. It utilized four trains, with a top speed of which were a Pendolino model, supporting both Finnish and Russian standards. However the service was discontinued in 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Denmark
The first high-speed railway in Denmark was the Copenhagen–Ringsted Line, completed in late 2018 and opened in 2019. Further high-speed lines are currently under planning. Since HSR in Denmark reaches no more than 200 km/h, it can also be described as higher-speed rail. As a part of a long-term green plan for transportation in Denmark in December 2008, the government at the time presented a high-speed strategy for the inter-city train traffic, called ''The Hour Model'' ( Danish: ''Timemodellen''). The strategy contains bringing down the travel time on the three links that connect the four largest cities of Denmark (Copenhagen-Odense-Aarhus-Aalborg) to one hour, thereby decreasing the total travel time between Copenhagen and Aalborg from approximately 4½ hours to 3 hours. The first part of the Hour Model, the new high-speed line between Copenhagen and Ringsted, opened in 2019. After realization of the first three stages of the Hour Model, it can be expanded to Esbjerg and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Belgium
Belgium's high-speed rail network provides mostly international connections from Brussels to France, Germany and The Netherlands. The high-speed network began with the opening of the HSL 1 to France in 1997, and since then high-speed lines have been extended towards Germany with HSL 2 in 2002, HSL 3 from Liège to the German border in 2009, and HSL 4 from Antwerp to the Dutch border in 2009. Services Three international high-speed train services currently operate in Belgium: Eurostar, InterCityExpress (ICE) and TGV. All operators stop at Brussels-South railway station, Brussels-South station, Belgium's largest train station. Some services also stop at Liège-Guillemins railway station, Liège and Antwerpen-Centraal railway station, Antwerp stations. However, these international operators are not allowed to sell tickets between two Belgian cities. Instead, passengers must take a Belgian IC train which uses the same high-speed lines. Eurostar connects Brussels to Amsterdam Centraa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In Austria
The West railway between the capital Vienna and Salzburg is being upgraded. Most new sections have a continuous maximum design speed of . German and Austrian ICE trains operate at a maximum speed of , as do Austrian locomotive-hauled trains (called Railjet) which were launched in 2008. The section between Attnang-Puchheim and Salzburg has not been part of the massive investments during the past decades. Therefore a new high-speed rail line between Köstendorf and Salzburg is being planned by ÖBB. Long distance and freight trains are planned to run through a long new track that is designed for a maximum speed of . This new infrastructure should enable to substantially increase the number of regional trains on the existing tracks and cut travel times for long distance connections by using the new tunnels. Construction works are expected to begin in 2025/2026. The Brenner Base Tunnel under construction will allow speeds of up to . The expected year of completion is 2032. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-speed Rail In China
The high-speed rail (HSR, ) network in the People's Republic of China (PRC) is the List of high-speed railway lines, world's longest and most extensively used. The HSR network encompasses newly built rail lines with a design speed of . China's HSR accounts for two-thirds of the world's total high-speed railway networks. Almost all HSR trains, track and service are owned and operated by the China Railway Corporation under the brand China Railway High-speed (CRH). High-speed rail developed rapidly in China since the mid-2000s. CRH was Campaign to raise the speed of railway travel in China, introduced in April 2007 and the Beijing–Tianjin intercity railway, Beijing-Tianjin intercity rail, which opened in August 2008, was the first passenger dedicated HSR line. Currently, the HSR extends to all Provinces of China, provincial-level administrative divisions and Hong Kong SAR with the exception of Macau SAR. Notable HSR lines in China include the Beijing–Kunming high-speed train, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |