|
High-temperature Engineering Test Reactor
The high-temperature engineering test reactor (HTTR) is a graphite- moderated gas-cooled research reactor in Ōarai, Ibaraki, Japan operated by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency. It uses long hexagonal fuel assemblies, unlike the competing pebble bed reactor designs. HTTR first reached its full design power of 30 MW (thermal) in 1999. Other tests have shown that the core can reach temperatures sufficient for hydrogen production Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, ... via the sulfur-iodine cycle. Technical details The primary coolant is helium gas at a pressure of about , the inlet temperature of , and the outlet temperature of . The fuel is uranium oxide ( enriched to an average of about 6%). See also * Very-high-temperature reactor * Hydrogen economy References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Moderator
In nuclear engineering, a neutron moderator is a medium that reduces the speed of fast neutrons, ideally without capturing any, leaving them as thermal neutrons with only minimal (thermal) kinetic energy. These thermal neutrons are immensely more susceptible than fast neutrons to propagate a nuclear chain reaction of uranium-235 or other fissile isotope by colliding with their atomic nucleus. Water (sometimes called "light water" in this context) is the most commonly used moderator (roughly 75% of the world's reactors). Solid graphite (20% of reactors) and heavy water (5% of reactors) are the main alternatives. Beryllium has also been used in some experimental types, and hydrocarbons have been suggested as another possibility. Moderation Neutrons are normally bound into an atomic nucleus and do not exist free for long in nature. The unbound neutron has a half-life of 10 minutes and 11 seconds. The release of neutrons from the nucleus requires exceeding the binding ener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Reactor
Research reactors are nuclear fission-based nuclear reactors that serve primarily as a neutron source. They are also called non-power reactors, in contrast to power reactors that are used for electricity production, heat generation, or maritime propulsion. Purpose The neutrons produced by a research reactor are used for neutron scattering, non-destructive testing, analysis and testing of materials, production of radioisotopes, research and public outreach and education. Research reactors that produce radioisotopes for medical or industrial use are sometimes called isotope reactors. Reactors that are optimised for beamline experiments nowadays compete with spallation sources. Technical aspects Research reactors are simpler than power reactors and operate at lower temperatures. They need far less fuel, and far less fission products build up as the fuel is used. On the other hand, their fuel requires more highly enriched uranium, typically up to 20% U-235, although some use 93 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ōarai, Ibaraki
is a town located in Ibaraki Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 15,867 in 6,881 households and a population density of . The percentage of the population aged over 65 was 34.0%. The total area of the town is . The Japan Atomic Energy Agency operates a research center in Ōarai with a number of nuclear research reactors, including the Jōyō and High-temperature engineering test reactor facilities. Geography Located on the coast of central Ibaraki Prefecture, Ōarai is located in the flatlands near the Pacific Ocean, and borders Lake Hinuma, the 30th largest body of freshwater in Japan. The Naka River flows through the town. Ōarai and Sun Beach bathing beaches were first to introduce barrier-free bathing beaches for the disabled in Japan. Surrounding municipalities Ibaraki Prefecture * Hitachinaka * Hokota * Ibaraki * Mito Climate Ōarai has a Humid continental climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cold winters with light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Atomic Energy Agency
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is a Japanese atomic energy company. While it inherited the activities of both Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute, JNC and Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute, JAERI, it also inherited the nickname of JAERI, "Genken" 原研, an abbreviated word for "nuclear research". On April 10, 2007, JAEA officially joined the Global Nuclear Energy Partnership, GNEP alliance. The other members in the alliance are Areva, Washington Group International and BWX. It is expected that the experience gained from the Rokkasho centrifuge enrichment plant will be a key contribution from JAEA. On April 1, 2016, JAEA transferred some of its laboratories to the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS), and the NIRS body was renamed to the National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST) which includes existing laboratories of the NIRS. In 2018 JAEA estimated it would need about 1.9 trillion yen ($17.1 billion) to decommis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pebble Bed Reactor
The pebble-bed reactor (PBR) is a design for a graphite- moderated, gas-cooled nuclear reactor. It is a type of very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR), one of the six classes of nuclear reactors in the Generation IV initiative. The basic design features spherical fuel elements called pebbles. These tennis ball-sized elements (approx. in diameter) are made of pyrolytic graphite (which acts as the moderator), and contain thousands of fuel particles called tristructural-isotropic (TRISO) particles. These TRISO particles consist of a fissile material (such as ) surrounded by a ceramic coating of silicon carbide for structural integrity and fission product containment. Thousands of pebbles are amassed to create a reactor core. The core is cooled by a gas that does not react chemically with the fuel elements, such as helium, nitrogen or carbon dioxide. Other coolants such as FLiBe (molten ) have been suggested. The pebble bed design is passively safe. Because the reactor is de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
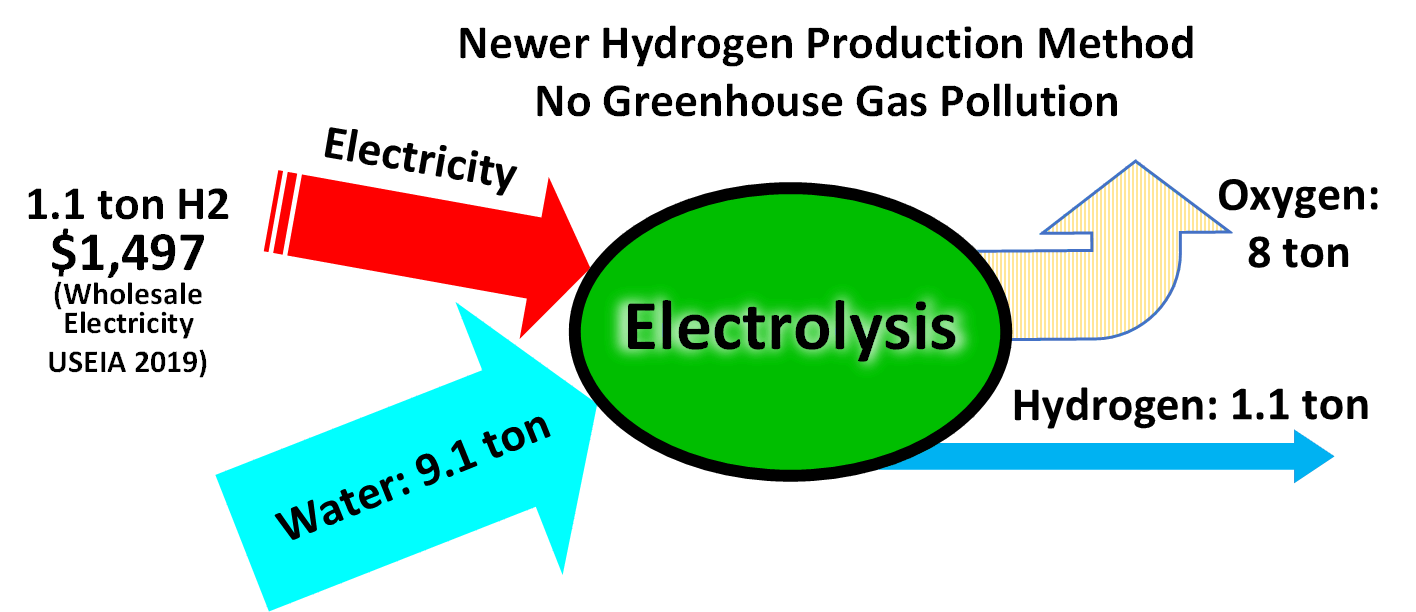
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. When carbon capture and storage is used to remove a large fraction of these emissions, the product is known as ''blue hydrogen''. ''Green hydrogen'' is usually understood to be produced from Renewable energy, renewable electricity via electrolysis of water. Less frequently, definitions of ''green hydrogen'' include hydrogen produced from other low-emission sources such as Biomass (energy), biomass. Producing green hydrogen is currently more expensive than producing gray hydrogen, and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enriched Uranium
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238U with 99.2732–99.2752% natural abundance), uranium-235 (235U, 0.7198–0.7210%), and uranium-234 (234U, 0.0049–0.0059%). 235U is the only nuclide existing in nature (in any appreciable amount) that is fissile with thermal neutrons. Enriched uranium is a critical component for both civil nuclear power generation and military nuclear weapons. Low-enriched uranium (20% 235U, typically >85%) is used for the cores of many nuclear weapons, as well as compact reactors for naval propulsion and research, as well as breeder reactors. There are about 2,000 tonnes of highly enriched uranium in the world. Enrichment methods were first developed on a large scale by the Manhattan Project. Its gaseous diffusion method was used in the 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Very-high-temperature Reactor
A high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR) is a type of gas-cooled nuclear reactor which uses uranium fuel and graphite moderation to produce very high reactor core output temperatures. All existing HTGR reactors use helium coolant. The reactor core can be either a "prismatic block" (reminiscent of a conventional reactor core) or a " pebble-bed" core. China Huaneng Group currently operates HTR-PM, a 250 MW HTGR power plant in Shandong province, China. The high operating temperatures of HTGR reactors potentially enable applications such as process heat or hydrogen production via the thermochemical sulfur–iodine cycle. A proposed development of the HTGR is the Generation IV very-high-temperature reactor (VHTR) which would initially work with temperatures of 750 to 950 °C. History The use of a high-temperature, gas-cooled reactor for power production was proposed by in 1944 by Farrington Daniels, then associate director of the chemistry division at the Univer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Economy
The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not available. In this context, ''hydrogen economy'' encompasses the production of hydrogen and the use of hydrogen in ways that contribute to phasing-out fossil fuels and limiting climate change. Hydrogen can be produced by several means. Most hydrogen produced today is ''gray hydrogen'', made from natural gas through steam methane reforming (SMR). This process accounted for 1.8% of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2021.Greenhouse gas emissions totalled 49.3 Gigatonnes CO2e in 2021. ''Low-carbon hydrogen'', which is made using SMR with carbon capture and storage ('' blue hydrogen''), or through electrolysis of water using renewable power ('' green hydrogen''), accounted for less than 1% of production. Virtually all of the 100 million tonnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JAEA
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is a Japanese atomic energy company. While it inherited the activities of both JNC and JAERI, it also inherited the nickname of JAERI, "Genken" 原研, an abbreviated word for "nuclear research". On April 10, 2007, JAEA officially joined the GNEP alliance. The other members in the alliance are Areva, Washington Group International and BWX. It is expected that the experience gained from the Rokkasho centrifuge enrichment plant will be a key contribution from JAEA. On April 1, 2016, JAEA transferred some of its laboratories to the National Institute of Radiological Sciences (NIRS), and the NIRS body was renamed to the National Institutes for Quantum and Radiological Science and Technology (QST) which includes existing laboratories of the NIRS. In 2018 JAEA estimated it would need about 1.9 trillion yen ($17.1 billion) to decommission 79 facilities over 70 years. Overview *Establishment: October 2005 *Founding Law: The Japan Atomic Energy A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphite Moderated Reactors
:''"Graphite reactor" directs here. For the graphite reactor at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, see X-10 Graphite Reactor.'' A graphite-moderated reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses carbon as a neutron moderator, which allows natural uranium to be used as nuclear fuel. The first artificial nuclear reactor, the Chicago Pile-1, used nuclear graphite as a moderator. Graphite-moderated reactors were involved in two of the best-known nuclear disasters: an untested graphite annealing process contributed to the Windscale fire (but the graphite itself did not catch fire), while a graphite fire during the Chernobyl disaster contributed to the spread of radioactive material. Types Several types of Nuclear graphite, graphite-Neutron moderation, moderated nuclear reactors have been used in commercial electricity generation: *Gas-cooled reactors **Magnox **UNGG reactor **Advanced gas-cooled reactor (AGR) *Water-cooled reactors **RBMK **MKER **EGP-6 **N-Reactor, Hanford N-Reactor (dual us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |