|
Heqin
''Heqin'', also known as marriage alliance, refers to the historical practice of Chinese monarchs marrying princesses—usually members of minor branches of the ruling family—to rulers of neighboring states. It was often adopted as an appeasement strategy with an enemy state that was too powerful to defeat on the battlefield. The policy was not always effective. It implied an equal diplomatic status between the two monarchs. As a result, it was controversial and had many critics. Lou Jing (, later granted the imperial surname Liu 劉), the architect of the policy, proposed granting the eldest daughter of Emperor Gaozu of Han to Modu Chanyu of the Xiongnu. His proposal was adopted and implemented with a treaty in 198BC, following the Battle of Baideng two years prior. Wang Zhaojun, of the Han dynasty, and Princess Wencheng, of the Tang dynasty, are among the most famous heqin princesses. The 20th-century scholar Wang Tonglin praised heqin for facilitating the "melting of ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modu Chanyu
Modu () was the son of Touman and the founder of the empire of the Xiongnu. He came to power by ordering his men to kill his father in 209 BCE. Modu ruled from 209 to 174 BCE. He was a military leader under his father Touman and later ''chanyu'' of the Xiongnu Empire, based on the Mongolian Plateau. He secured the throne and established a powerful Xiongnu Empire by successfully unifying the tribes of the Mongolian–Manchurian grassland in response to the loss of Xiongnu pasture lands to invading Qin forces commanded by Meng Tian in 215 BCE. While Modu rode and then furthered the wave of militarization and effectively centralized Xiongnu power, the Qin quickly fell into disarray with the death of the first emperor in 210 BCE, leaving Modu a free hand to expand his empire into one of the largest of his time. The eastern border stretched as far as the Liao River, the western borders of the empire reached the Pamir Mountains, whilst the northern border reached Lake Baikal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wu Of Han
Emperor Wu of Han (156 – 29 March 87BC), born Liu Che and courtesy name Tong, was the seventh Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 141 to 87 BC. His reign lasted 54 years – a record not broken until the reign of the Kangxi Emperor more than 1,800 years later – and remains the record for ethnic Han Chinese, Han emperors. His reign resulted in a vast expansion of geopolitical influence for the Sinosphere, Chinese civilization, and the development of a strong centralized state via governmental policies, economical reorganization and promotion of a hybrid legalism (Chinese philosophy), Legalist–Confucianism, Confucian doctrine. In the field of historical social and cultural studies, Emperor Wu is known for his religious innovations and patronage of the poetic and musical arts, including the development of the Music Bureau, Imperial Music Bureau into a prestigious entity. It was also during his reign that cultural contact with western Eurasia was greatly incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
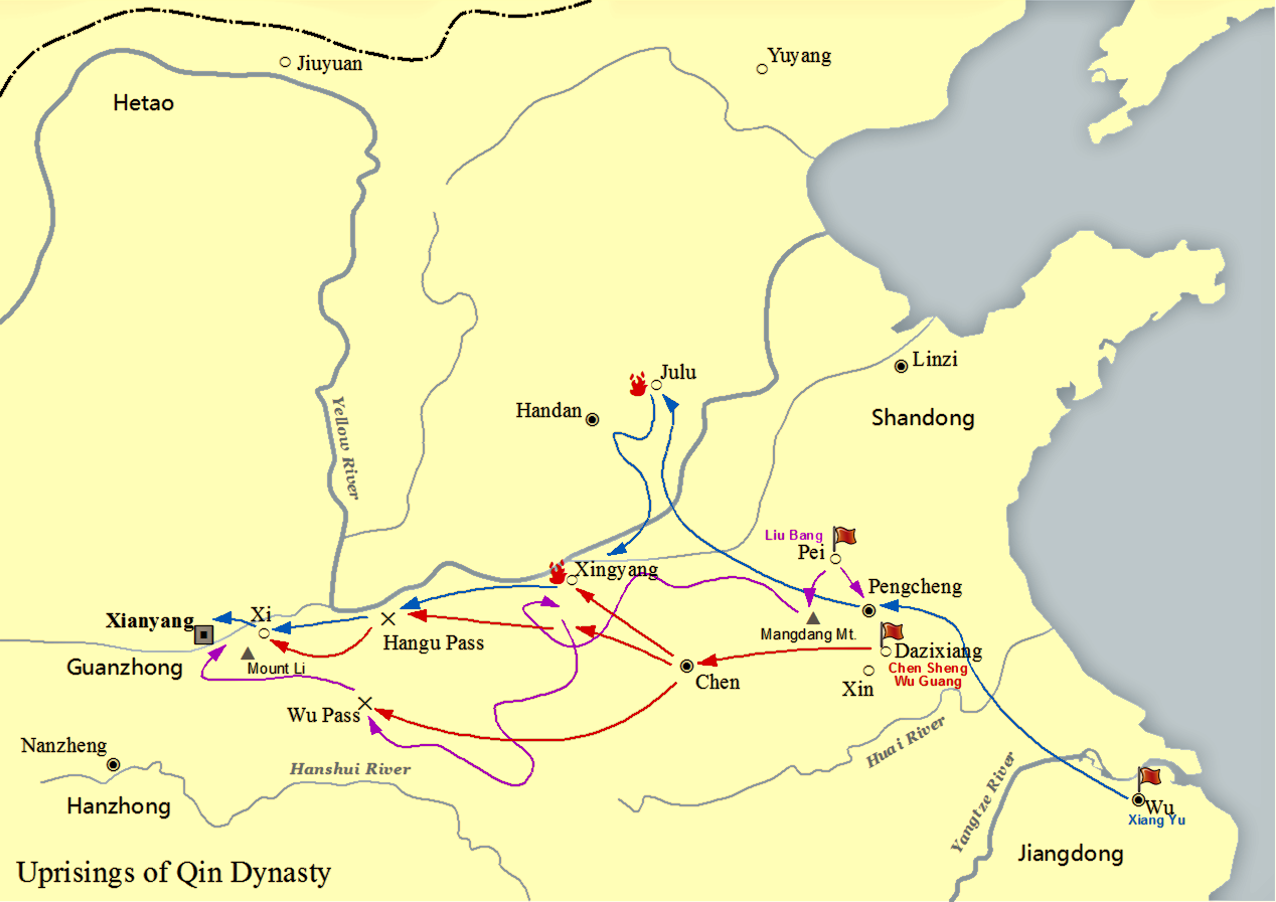
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC9 AD, 25–220 AD) established by Liu Bang and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by the short-lived Qin dynasty (221–206 BC) and a warring interregnum known as the Chu–Han Contention (206–202 BC), and it was succeeded by the Three Kingdoms period (220–280 AD). The dynasty was briefly interrupted by the Xin dynasty (9–23 AD) established by the usurping regent Wang Mang, and is thus separated into two periods—the #Western Han (202 BC – 9 AD), Western Han (202 BC9 AD) and the #Eastern Han (25–220 AD), Eastern Han (25–220 AD). Spanning over four centuries, the Han dynasty is considered a Golden ages of China, golden age in Chinese history, and had a permanent impact on Chinese identity in later periods. The majority ethnic group of modern China refer to themselves as the "Han people" or "Han Chinese". The spoken Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, the supreme leader after 209 BC, founded the Xiongnu Empire. After overthrowing their previous overlords, the Yuezhi, the Xiongnu became the dominant power on the steppes of East Asia, centred on the Mongolian Plateau. The Xiongnu were also active in areas now part of Siberia, Inner Mongolia, Gansu and Xinjiang. Their relations with the Chinese dynasties to the south-east were complex—alternating between various periods of peace, war, and subjugation. Ultimately, the Xiongnu were defeated by the Han dynasty in a Han–Xiongnu Wars, centuries-long conflict, which led to the confederation splitting in two, and forcible resettlement of large numbers of Xiongnu within Han borders. During the Sixteen Kingdoms era, listed as one of the "Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junchen
Junchen (, Old Chinese ( ZS): *''kun-gin''; r. 161–126 BCE) was the son and successor to Laoshang Chanyu. As ''chanyu'' of the Xiongnu Empire, Junchen outlived the Han emperors Wen (r. 180–157 BC) and Jing (r. 157–141 BC). He died during the reign of the Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141–87 BC). All three Han emperors confirmed the ''heqin'' peace and kinship treaty with the Xiongnu. Life Junchen succeeded his father, Laoshang Chanyu, in 161 BCE. Although peace with the Han dynasty generally persisted under his reign, Xiongnu raids still occurred in 158, 148, 144, and 142 BCE. The Chinese annals note that mutual relations were imperiled on a number of occasions, which included appeals of the Chinese contenders for the Xiongnu's assistance and protection, the Xiongnu's retaliatory raids as punishments for violation of the treaty terms, and one direct Chinese assault against the ''Chanyu''. The Xiongnu were especially sensitive about unimperiled trade relations, which were one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao Xin (general)
Zhao Xin () was a prominent Xiongnu general in the late 2nd century BCE during the Han–Xiongnu War. He defected first to the Han dynasty then back to the Xiongnu. Life In 131 BCE, Zhao Xin defected from the Xiongnu to the Han, and he became known as the Marquis of Xi ( zh, 翕侯). His name was probably adopted during his service to the Han. He was one of the six generals led by Wei Qing during a Han expedition against the Xiongnu in 123 BCE, and led a 3,000-strong vanguard force along with fellow general Su Jian. Although the two Han campaigns were successful, Zhao Xin was defeated and surrendered to the Xiongu. Su Jian's forces were also defeated, but he managed to escape. In 119 BCE, Zhao Xin is recorded as acting on behalf of the Xiongnu to broker a ''heqin'' marriage with the Han. Though leading to debate at the Han court, the proposal was rejected. A Xiongnu fortress named after Zhao Xin was constructed near the Khangai Mountains, soon after his submission to Yizhix ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wusun
The Wusun ( ) were an ancient semi-Eurasian nomads, nomadic Eurasian Steppe, steppe people of unknown origin mentioned in Chinese people, Chinese records from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD. The Wusun originally lived between the Qilian Mountains and Dunhuang (Gansu) near the Yuezhi. Around 176 BC the Xiongnu raided the lands of the Yuezhi, who subsequently attacked the Wusun, killing their king and seizing their land. The Xiongnu adopted the surviving Wusun prince and made him one of their generals and leader of the Wusun. Around 162 BC the Yuezhi were driven into the Ili River Valley in Jetisu, Zhetysu, Dzungaria and Tian Shan, which had formerly been inhabited by the Saka. The Wusun then resettled in Gansu as vassals of the Xiongnu. In 133–132 BC, the Wusun drove the Yuezhi out of the Ili Valley and settled the area. The Wusun then became close allies of the Han dynasty and remained a powerful force in the region for several cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Gaozu Of Han
Emperor Gaozu of Han (2561 June 195 BC), also known by his given name Liu Bang, was the founder and first emperor of the Han dynasty, reigning from 202 to 195 BC. He is considered by traditional Chinese historiography to be one of the greatest emperors in history, credited with establishing the first Pax Sinica, one of China's longest golden ages. Liu Bang was among the few dynastic founders to have been born in a peasant family. He initially entered the Qin dynasty bureaucracy as a minor law enforcement officer in his home town in Pei County, within the conquered state of Chu. During the political chaos following the death of Qin Shi Huang, who had been the first emperor in Chinese history, Liu Bang renounced his civil service position and became a rebel leader, taking up arms against the Qin dynasty. He outmanoeuvred rival rebel leader Xiang Yu to invade the Qin heartland and forced the surrender of the Qin ruler Ziying in 206 BC. After the fall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Jieyou
Princess Jieyou (; 121 BC – 49 BC), born Liu Jieyou (), was a Chinese princess sent to marry the leader of the Wusun kingdom as part of the Western Han Chinese policy of heqin. Biography As the granddaughter of the disgraced Prince Liu Wu (劉戊) who had taken part in the disastrous Rebellion of the Seven States, her status was low enough that she was sent to replace Princess Liu Xijun (劉細君) after her untimely death and marry the Wusun king Cunzhou (岑陬). After his death, she married his cousin and successor, Wengguimi (翁歸靡), to whom she bore five children including Yuanguimi (元貴靡). Jieyou lived among the Wusun for fifty years and did much work to foster relations between the surrounding kingdoms and the Han. She was particularly reliant upon her attendant, Feng Liao, whom she dispatched as an emissary to Wusun kingdoms and even to the Han Court. She faced opposition from pro-Xiongnu members of the Wusun royalty, particularly Wengguimi’s Xiongnu wife. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Wen Of Han
Emperor Wen of Han (; 203/02 – 6 July 157 BC), personal name Liu Heng (), was the fifth Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 180 until his death in 157 BC. The son of Emperor Gaozu of Han, Emperor Gao and Empress Dowager Bo, Consort Bo, his reign provided a much needed stability within the ruling Liu clan after the unstable and violent regency of Empress Lü, who went after numerous members of the clan. The prosperous reigns of Emperor Wen and his son Emperor Jing of Han, Emperor Jing are highly regarded by historians, being referred to as the Rule of Wen and Jing. He was one only four List of emperors of the Han dynasty, Western Han emperors to receive a temple name, along with Emperor Gaozu of Han, Emperor Gaozu, Emperor Wu of Han, Emperor Wu, and Emperor Xuan of Han. When Emperor Gaozu suppressed the rebellion of Dai (), he made Liu Heng Prince of Dai. Since Emperor Gaozu's death, power had been in the hands of his wife, Empress Lü, the empress dowager. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emperor Jing Of Han
Emperor Jing of Han (188 BC – 9 March 141 BC), born Liu Qi, was the sixth Emperor of China, emperor of the Han dynasty from 157 to 141 BC. His reign saw the limiting of the power of the feudal kings and princes which resulted in the Rebellion of the Seven States in 154 BC. Emperor Jing managed to crush the revolt and princes were thereafter denied rights to appoint ministers for their fiefs. This move helped to consolidate central power which paved the way for the long reign of his son Emperor Wu of Han. Emperor Jing had a complicated personality. He continued his father Emperor Wen of Han, Emperor Wen's policy of general non-interference with the people, reduced tax and other burdens, and promoted government thrift. He continued and magnified his father's policy of reduction in criminal sentences. His light governance of the people was due to the Taoist influences of his mother, Empress Dou (Wen), Empress Dou. Still, during his reign he arrested and imprisoned Zhou Yafu, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |