|
Hemiptera
Hemiptera (; ) is an order of insects, commonly called true bugs, comprising more than 80,000 species within groups such as the cicadas, aphids, planthoppers, leafhoppers, assassin bugs, bed bugs, and shield bugs. They range in size from to around , and share a common arrangement of piercing-sucking mouthparts. The name "true bugs" is sometimes limited to the suborder Heteroptera. Entomologists reserve the term ''bug'' for Hemiptera or Heteroptera,Gilbert Waldbauer. ''The Handy Bug Answer Book.'' Visible Ink, 1998p. 1. which does not include other arthropods or insects of other orders such as ants, bees, beetles, or butterflies. In some varieties of English, all terrestrial arthropods (including non-insect arachnids and myriapods) also fall under the colloquial understanding of ''bug''. Many insects with "bug" in their common name, especially in American English, belong to other orders; for example, the lovebug is a fly and the Maybug and ladybug are beetles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leafhopper
Leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family (biology), family Cicadellidae: based on the type genus ''Cicadella''. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and are covered with hairs that facilitate the spreading of a secretion over their bodies that acts as a water repellent and carrier of pheromones. They undergo a partial metamorphosis, and have various host associations, varying from very generalized to very specific. Some species have a cosmopolitan distribution, or occur throughout the temperate and tropical regions. Some are pests or Vector (epidemiology), vectors of plant viruses and phytoplasmas. The family is distributed all over the world, and constitutes the second-largest hemipteran family, with at least 20,000 described species. They belong to a lineage traditionally treated as infraorder Cicadomorpha in the suborder Auchenorrhy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Insect
Insects (from Latin ') are Hexapoda, hexapod invertebrates of the class (biology), class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (Insect morphology#Head, head, Thorax (insect anatomy), thorax and abdomen (insect anatomy), abdomen), three pairs of jointed Arthropod leg, legs, compound eyes, and a pair of antenna (biology), antennae. Insects are the most diverse group of animals, with more than a million described species; they represent more than half of all animal species. The insect nervous system consists of a insect brain, brain and a ventral nerve cord. Most insects reproduce Oviparous, by laying eggs. Insects Respiratory system of insects, breathe air through a system of Spiracle (arthropods), paired openings along their sides, connected to Trachea#Invertebrates, small tubes that take air directly to the tissues. The blood therefore does not carry oxygen; it is only partly contained in ves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cicada
The cicadas () are a superfamily, the Cicadoidea, of insects in the order Hemiptera (true bugs). They are in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, along with smaller jumping bugs such as leafhoppers and froghoppers. The superfamily is divided into two families, the Tettigarctidae, with two species in Australia, and the Cicadidae, with more than 3,000 species Taxonomy (biology)#Taxonomic descriptions, described from around the world; many species remain Undescribed taxon, undescribed. Nearly all cicada species are annual cicadas with the exception of the few North American periodical cicada species, genus ''Magicicada'', which in a given region emerge en masse every 13 or 17 years. Cicadas have prominent eyes set wide apart, short antennae, and membranous front wings. They have an exceptionally loud song, produced in most species by the rapid buckling and unbuckling of drum-like tymbals. The earliest known fossil Cicadomorpha appeared in the Upper Permian period; extant species occur a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving Viviparity, live birth to female Nymph (biology), nymphs—who may also be already Pregnancy, pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Developmental biology, Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Alate, Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In Temperate climate, temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs. The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Shield Bug
Pentatomidae is a family of insects belonging to the order Hemiptera, generally called shield bugs or stink bugs. Pentatomidae is the largest family in the superfamily Pentatomoidea, and contains around 900 genera and over 4700 species.Robert G. Foottit, Peter H. Adler ''Insect Biodiversity: Science and Society'', John Wiley and Sons, 2009, As hemipterans, the pentatomids have piercing sucking mouthparts, and most are phytophagous, including several species which are severe pests on agricultural crops. However, some species, particularly in the subfamily Asopinae, are predatory and may be considered beneficial. Etymology The name "Pentatomidae" is from the Greek ''pente'' meaning "five" and ''tomos'' meaning "section", and refers to the five segments of their antennae. Pentatomids are generally called "shield bugs" in British English, or "stink bugs" in American English. However, the term shield bugs is also applied broadly to include several related families (e.g. Acant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aphids
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects in the Taxonomic rank, family Aphididae. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white Eriosomatinae, woolly aphids. A typical life cycle involves flightless females giving Viviparity, live birth to female Nymph (biology), nymphs—who may also be already Pregnancy, pregnant, an adaptation scientists call telescoping generations—without the involvement of males. Developmental biology, Maturing rapidly, females breed profusely so that the number of these insects multiplies quickly. Alate, Winged females may develop later in the season, allowing the insects to colonize new plants. In Temperate climate, temperate regions, a phase of sexual reproduction occurs in the autumn, with the insects often overwintering as eggs. The life cycle of some species involves an alternation between two species of host plants, for example between an annual crop and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ants
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of 22,000 species have been classified. They are easily identified by their geniculate (elbowed) antennae and the distinctive node-like structure that forms their slender waists. Ants form colonies that range in size from a few dozen individuals often living in small natural cavities to highly organised colonies that may occupy large territories with sizeable nest that consist of millions of individuals or into the hundreds of millions in super colonies. Typical colonies consist of various castes of sterile, wingless females, most of which are workers (ergates), as well as soldiers (dinergates) and other specialised groups. Nearly all ant colonies also have some fertile males called "drones" and one or more fertile females called "queens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Planthopper
A planthopper is any insect in the infraorder Fulgoromorpha, in the suborder Auchenorrhyncha, a group exceeding 12,500 described species worldwide. The name comes from their remarkable resemblance to leaves and other plants of their environment and that they often "hop" for quick transportation in a similar way to that of grasshoppers. However, planthoppers generally walk very slowly. Distributed worldwide, all members of this group are plant-feeders, though few are considered pests. Fulgoromorphs are most reliably distinguished from the other Auchenorrhyncha by two features; the bifurcate (Y-shaped) anal vein in the forewing, and the thickened, three-segmented antennae, with a generally round or egg-shaped second segment (pedicel) that bears a fine filamentous arista. Overview Planthoppers are laterally flattened and hold their broad wings vertically, in a tent-like fashion, concealing the sides of the body and part of the legs. Nymphs of many planthoppers produce wax from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bees
Bees are winged insects closely related to wasps and ants, known for their roles in pollination and, in the case of the best-known bee species, the western honey bee, for producing honey. Bees are a monophyletic lineage within the superfamily Apoidea. They are currently considered a clade, called Anthophila. There are over 20,000 known species of bees in seven recognized biological families. Some speciesincluding honey bees, bumblebees, and stingless beeslive socially in colonies while most species (>90%)including mason bees, carpenter bees, leafcutter bees, and sweat beesare solitary. Bees are found on every continent except Antarctica, in every habitat on the planet that contains insect-pollinated flowering plants. The most common bees in the Northern Hemisphere are the Halictidae, or sweat bees, but they are small and often mistaken for wasps or flies. Bees range in size from tiny stingless bee species, whose workers are less than long, to the leafcutter bee '' Megach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Beetles
Beetles are insects that form the Taxonomic rank, order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Holometabola. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 described species, is the largest of all orders, constituting almost 40% of described arthropods and 25% of all known animal species; new species are discovered frequently, with estimates suggesting that there are between 0.9 and 2.1 million total species. However, the number of beetle species is challenged by the number of species in Fly, dipterans (flies) and hymenopterans (wasps). Found in almost every habitat except the sea and the polar regions, they interact with their ecosystems in several ways: beetles often feed on plants and fungi, break down animal and plant debris, and eat other invertebrates. Some species are serious agricultural pests, such as the Colorado potato beetle, while others such as Coccinellidae (ladybirds or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Butterflies
Butterflies are winged insects from the lepidopteran superfamily Papilionoidea, characterized by large, often brightly coloured wings that often fold together when at rest, and a conspicuous, fluttering flight. The oldest butterfly fossils have been dated to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago, though molecular evidence suggests that they likely originated in the Cretaceous. Butterflies have a four-stage life cycle, and like other holometabolous insects they undergo complete metamorphosis. Winged adults lay eggs on the food plant on which their larvae, known as caterpillars, will feed. The caterpillars grow, sometimes very rapidly, and when fully developed, pupate in a chrysalis. When metamorphosis is complete, the pupal skin splits, the adult insect climbs out, expands its wings to dry, and flies off. Some butterflies, especially in the tropics, have several generations in a year, while others have a single generation, and a few in cold locations may take sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
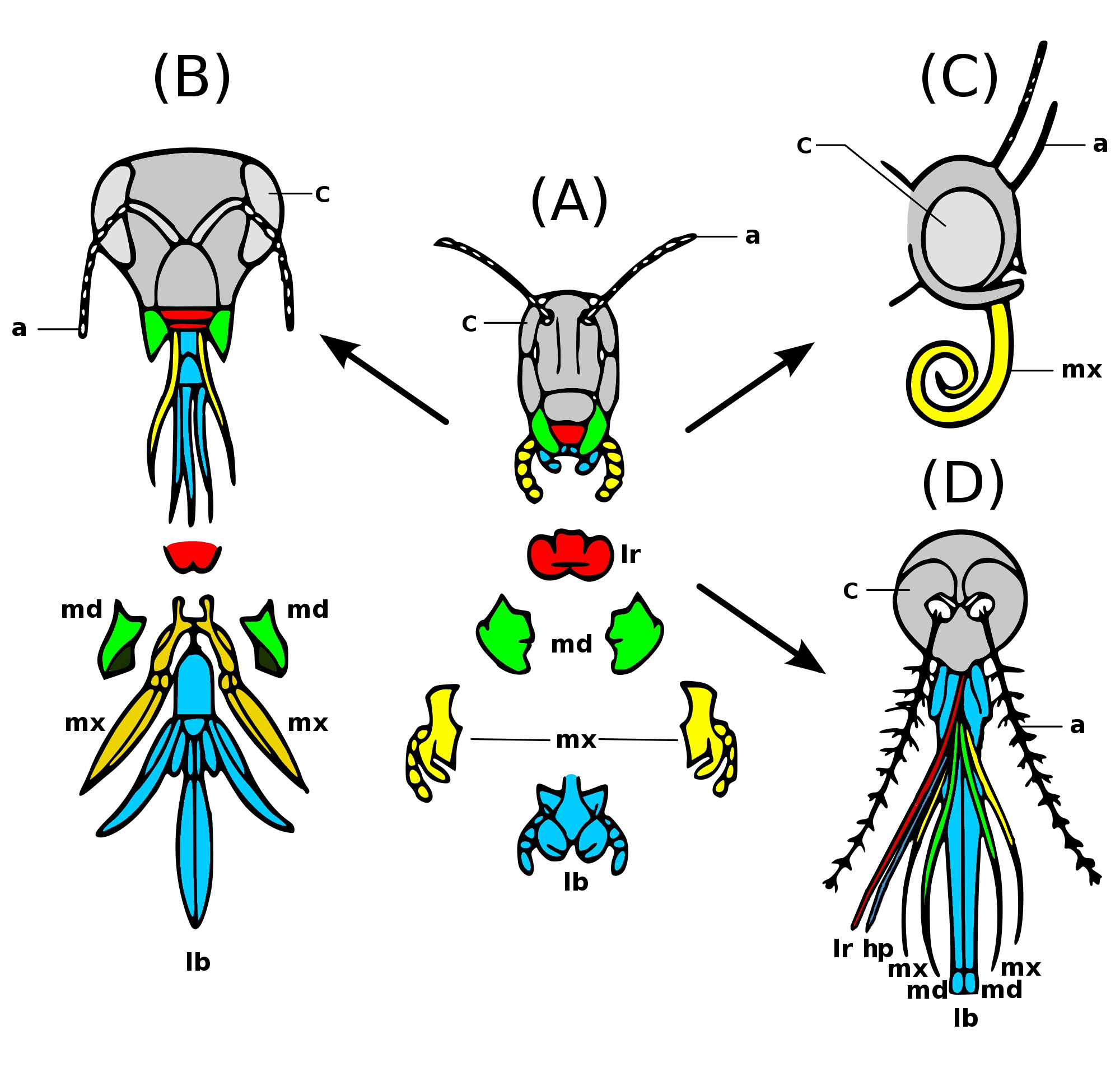
Insect Mouthparts
Insects have arthropod mouthparts, mouthparts that may vary greatly across insect species, as they are adapted to particular modes of feeding. The earliest insects had chewing mouthparts. Most specialisation of mouthparts are for piercing and sucking, and this mode of feeding has evolved a number of times independently. For example, mosquitoes (which are true flies) and aphids (which are Hemiptera, true bugs) both pierce and suck, though female mosquitoes feed on animal blood whereas aphids feed on plant fluids. Evolution Like most external features of arthropods, the mouthparts of Hexapoda are highly derived. Insect mouthparts show a multitude of different functional mechanisms across the wide diversity of insect species. It is common for significant Homology (biology), homology to be conserved, with matching structures forming from matching Primordium, primordia, and having the same evolutionary origin. However, even if structures are almost physically and functionally identica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |