|
Helmeted Hornbill
The helmeted hornbill (''Rhinoplax vigil'') is a very large bird in the hornbill family. It is found on the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Thailand and Myanmar. The casque (helmetlike structure on the head) accounts for some 11% of its 3 kg weight. Unlike any other hornbill, the casque is almost solid, and is used in head-to-head combat among males. It is a belief among the Punan Bah that a large helmeted hornbill guards the river between life and death. Description It has mostly blackish plumage, except that the belly and legs are white and the tail is white with a black band near the tip of each feather. The tail is long and the two central tail feathers are much longer than the others, giving the bird a total length greater than that of any other hornbill species. The body length is , not counting the tail feathers, which boost the length a further . One male weighed in weight while two females averaged about . Although sometimes considered the largest Asian hornbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantin Wilhelm Lambert Gloger
Constantin Wilhelm Lambert Gloger (17 September 1803 near Grottkau, Silesia, Kingdom of Prussia – 30 December 1863 in Berlin) was a German zoologist and ornithologist. Gloger was the first person to recognise the structural differences between swallows and swifts, and also the first to put up artificial bat boxes. He was the originator of what is now known as Gloger's rule Gloger's rule is an ecogeographical rule which states that within a species of endotherms, more heavily pigmented forms tend to be found in more humid environments, e.g. near the equator. It was named after the zoologist Constantin Wilhelm Lamb ..., which states that dark pigments increase in races of animals (birds were the examples in which he originally noticed the pattern) living in warm and humid habitats. He put forward this theory in his ''Das Abändern der Vögel durch Einfluss des Klimas'' (1833). The exact way this pattern is actually caused is still unclear, but in birds it has been suggested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megalaimidae
Megalaimidae, the Asian barbets, are a family of birds, comprising two genera with 35 species native to the forests of the Indomalayan realm from Tibet to Indonesia. They were once clubbed with all barbets in the family Capitonidae but the Old World species have been found to be distinctive and are considered, along with the Lybiidae and Ramphastidae, as sister groups. Taxonomy In the past the species were placed in three genera, ''Caloramphus'', ''Megalaima'' and ''Psilopogon'', but studies show that ''Psilopogon'' to be nested within the clade of ''Megalaima''. Since members of this clade are better treated under a single genus, they have been moved to the genus ''Psilopogon'' which was described and erected earlier than ''Megalaima'' and is therefore chosen on the basis of taxonomic priority principles. Nearly all members of the family are now in the genus ''Psilopogon'', with the exception of those in ''Caloramphus'', which are thought to have Genetic divergence, genetically d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
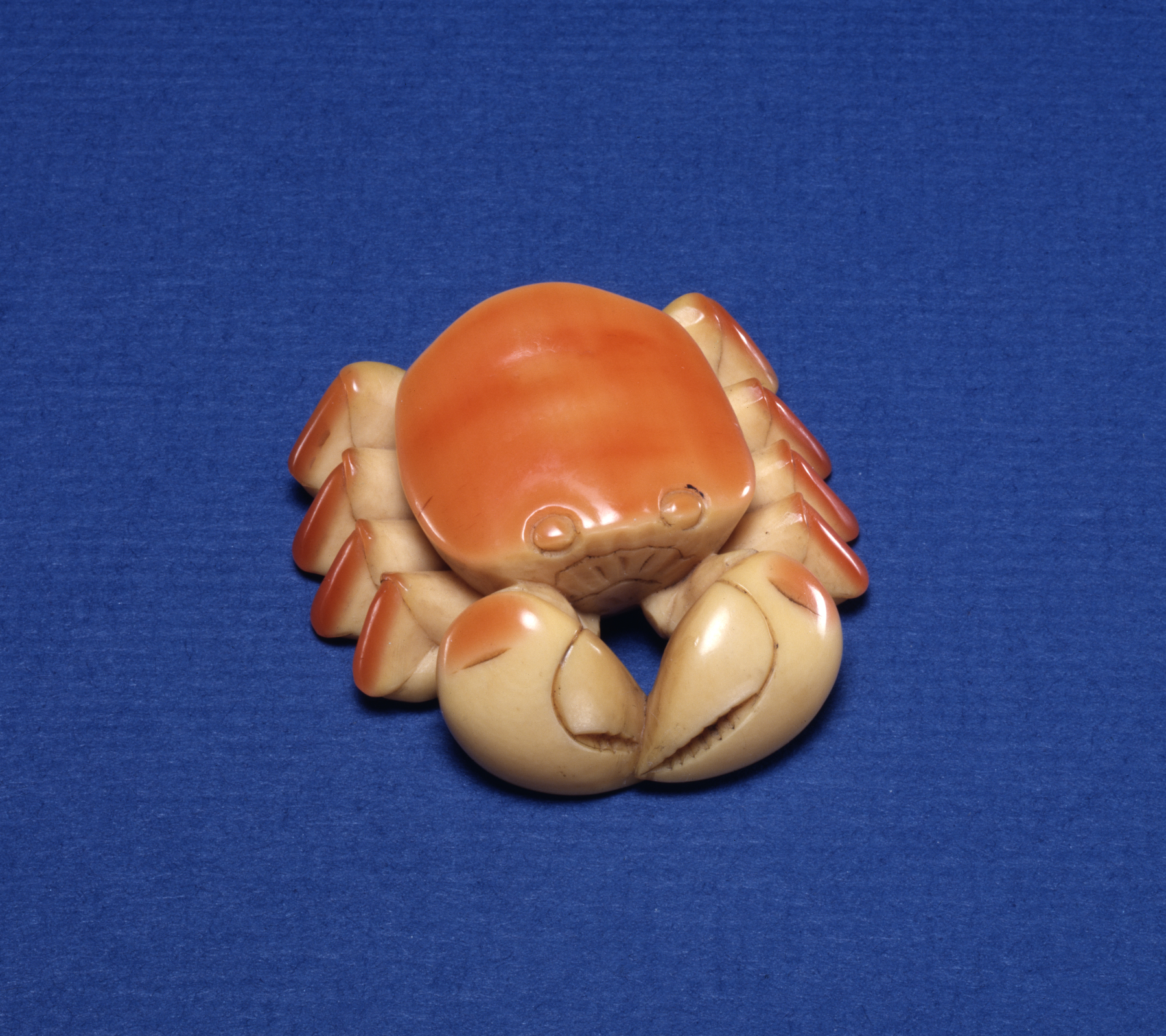
Hornbill Ivory
Hornbill ivory (also called "golden jade" or ''calao ivoire'' in French) is a precious ornamental material derived from the helmeted hornbill (''Buceros vigil''), a large bird of the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, and Borneo. Many hornbill species have "casques", decorative growths on the upper mandible of the bill. In most, the casque has a spongy structure, but in the helmeted hornbill it is solid keratin. This material, hornbill ivory, has a texture suggesting ivory but is softer. As it grows it is golden yellow, but the bird rubs its casque on its preen gland, whose oily secretion tints the surface of the casque bright red. Native peoples in the helmeted hornbill's range, such as the Kenyah and Kelabit, have long carved the casques. In Malaysia, hornbill-ivory rings were said to change colour when near poisonous food. The Chinese encountered the material in the 14th century and it soon became an important trade item at Brunei. According to Tom Harrisson, writing in the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurong Bird Park
Jurong Bird Park was an aviary and tourist attraction in Jurong, Singapore between 1971 and 2023. The largest such bird park in Asia, it covered an area of on the western slope of Jurong Hill, the highest point in the Jurong region. It was one of the parks managed by Mandai Wildlife Reserve, which are also the managers of Singapore Zoo, Night Safari and River Wonders. In 2016, the Mandai Wildlife Group announced that the Jurong Bird Park would be relocated to a much larger park at Mandai Lake Road by 2020, consolidating with the three existing wildlife parks together with a new Rainforest Park to form an integrated nature and wildlife precinct known as the Mandai Wildlife Reserve. In 2021, the group announced that the park's successor in Mandai would be named Bird Paradise. In 2022, it was announced that Jurong Bird Park would close on 3 January 2023 to finalise its move to Bird Paradise at Mandai. History The idea of a permanent aviary was first conceived by Goh Keng Swe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai Baht
The baht (; , ; currency sign, sign: ฿; ISO 4217, code: THB) is the official currency of Thailand. It is divided into 100 ''satang'' (, ). Prior to decimalisation, the baht was divided into eight ''fueang'' (, ), each of eight ''at'' (, ). The issuance of currency is the responsibility of the Bank of Thailand. Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, SWIFT ranked the Thai baht as the 10th-most-frequently used world payment currency as of December 2023. History ImageSize = width:1500 height:auto barincrement:15 PlotArea = top:10 bottom:30 right:130 left:20 AlignBars = justify DateFormat = yyyy Period = from:1250 till:2050 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:50 start:1250 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:10 start:1250 Colors = id:canvas value:rgb(1,1,1) id:r value:rgb(0.5,0,0) id:p value:rgb(1,0.1,0.6) id:o value:rgb(1,0.3,0) id:y value:rgb(0.9,0.7,0.1) id:g value:rgb(0,0.4,0) id:m value:rgb(0,0.8,0) id:b value:r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traffic (conservation Programme)
TRAFFIC (Trade Records Analysis of Flora and Fauna in Commerce), also known as the Wildlife Trade Monitoring Network, is a global non-governmental organization monitoring the trade in wild plants and animals. TRAFFIC focuses on preserving biodiversity and sustainable legal wildlife trade while working against unsustainable illegal wildlife trade. It was originally created in 1976 as a specialist group of the Species Survival Commission of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and evolved into a strategic alliance of the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) and the IUCN. History 1990s TRAFFIC established 13 more offices worldwide in Europe (1990), East/Southern Africa (1991), and East Asia (1994). The organization focused on trade issues including tiger, agarwood, and rhino, leading to the establishment of The Bad Ivory Database System (BIDS), the foundation for the ETIS (Elephant Trade Information System). TRAFFIC's first major initiative in Africa inves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CITES
CITES (shorter acronym for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975. Its aim is to ensure that international trade (import/export) in specimens of animals and plants included under CITES does not threaten the survival of the species in the wild. This is achieved via a system of permits and certificates. CITES affords varying degrees of protection to more than 40,900 species. , the Secretary-General of CITES is Ivonne Higuero. Background CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. There are three workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List Of Threatened Species
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is an inventory of the global conservation status and extinction risk of biological species. A series of Regional Red Lists, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit, are also produced by countries and organizations. The goals of the Red List are to provide scientifically based information on the status of species and subspecies at a global level, to draw attention to the magnitude and importance of threatened biodiversity, to influence national and international policy and decision-making, and to provide information to guide actions to conserve biological diversity. Major species assessors include BirdLife International, the Institute of Zoology (the research division of the Zoological Society of London), the World Conservation Monitoring Centre, and many Specialist Groups within th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critically Endangered
An IUCN Red List critically endangered (CR or sometimes CE) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild. As of December 2023, of the 157,190 species currently on the IUCN Red List, 9,760 of those are listed as critically endangered, with 1,302 being possibly extinct and 67 possibly extinct in the wild. The IUCN Red List provides the public with information regarding the conservation status of animal, fungi, and plant species. It divides various species into seven different categories of conservation that are based on habitat range, population size, habitat, threats, etc. Each category represents a different level of global extinction risk. Species that are considered to be critically endangered are placed within the "Threatened" category. As the IUCN Red List does not consider a species extinct until extensive targeted surveys have been conducted, species that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near Threatened
A near-threatened species is a species which has been Conservation status, categorized as "Near Threatened" (NT) by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as that may be vulnerable to Endangered species, endangerment in the near future, but it does not currently qualify for the threatened status. The IUCN notes the importance of reevaluating near-threatened taxon, taxa at appropriate intervals. The rationale used for near-threatened taxa usually includes the criteria of Vulnerable species, vulnerable which are plausible or nearly met, such as reduction in numbers or range. Those designated since 2001 that depend on conservation efforts to not become threatened are no longer separately considered conservation-dependent species. IUCN Categories and Criteria version 2.3 Before 2001, the IUCN used the version 2.3 Categories and Criteria to assign conservation status, which included a separate category for conservation-dependent species ("Conservation Dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |