|
Heat Content
Heat content may refer to: * Enthalpy, measure of energy in a thermodynamic system * Heat of combustion, amount of heat released by combustion of a quantity of substance * Ocean heat content Ocean heat content (OHC) or ocean heat uptake (OHU) is the energy absorbed and stored by oceans, and is thus an important indicator of global warming. Ocean heat content is calculated by measuring ocean temperature at many different locations and ..., thermal energy stored in ocean water * Heat content (fuel), industrial term for heat energy available from a unit of fuel {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enthalpy
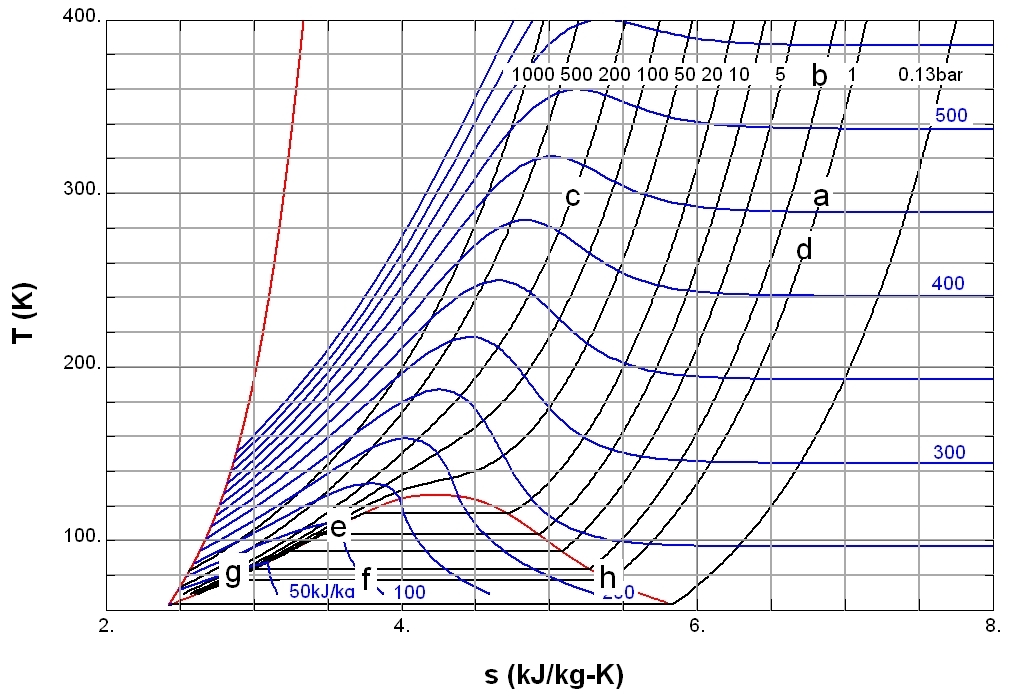
Enthalpy () is the sum of a thermodynamic system's internal energy and the product of its pressure and volume. It is a state function in thermodynamics used in many measurements in chemical, biological, and physical systems at a constant external pressure, which is conveniently provided by the large ambient atmosphere. The pressure–volume term expresses the work (physics), work W that was done against constant external pressure P_\text to establish the system's physical dimensions from V_\text=0 to some final volume V_\text (as W=P_\text\Delta V), i.e. to make room for it by displacing its surroundings. The pressure-volume term is very small for solids and liquids at common conditions, and fairly small for gases. Therefore, enthalpy is a stand-in for energy in chemical systems; Bond energy, bond, Lattice energy, lattice, solvation, and other chemical "energies" are actually enthalpy differences. As a state function, enthalpy depends only on the final configuration of internal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Of Combustion
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it. The ''calorific value'' is the total energy released as heat when a substance undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions. The chemical reaction is typically a hydrocarbon or other organic molecule reacting with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water and release heat. It may be expressed with the quantities: * energy/ mole of fuel * energy/mass of fuel * energy/volume of the fuel There are two kinds of enthalpy of combustion, called high(er) and low(er) heat(ing) value, depending on how much the products are allowed to cool and whether compounds like are allowed to condense. The high heat values are conventionally measured with a bomb calorimeter. Low heat values are calculated from high heat value test data. They may also be calculated as the difference be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Heat Content
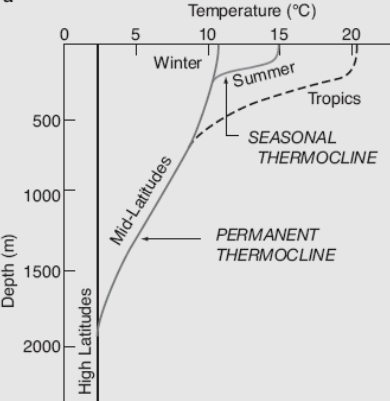
Ocean heat content (OHC) or ocean heat uptake (OHU) is the energy absorbed and stored by oceans, and is thus an important indicator of global warming. Ocean heat content is calculated by measuring ocean temperature at many different locations and depths, and integrating the areal density of a change in enthalpic energy over an ocean basin or entire ocean. Between 1971 and 2018, a steady upward trendNOAA National Centers for Environmental Information, Assessing the Global Climate in 2024, published online January 2025, Retrieved on March 2, 2025 from https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/news/global-climate-202413. in ocean heat content accounted for over 90% of Earth's excess energy from global warming. Scientists estimate a 1961–2022 warming trend of 0.43±0.08W/m², accelerating at about 0.15±0.04W/m² perdecade. By 2020, about one third of the added energy had propagated to depths below 700 meters. In 2024, the world's oceans were again the hottest in the historical record and excee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |