|
Harmonious Society
The Harmonious Society (also known as Socialist Harmonious Society) is a socioeconomic concept in China that is recognized as a response to the increasing alleged social injustice and inequality emerging in mainland Chinese society as a result of unchecked economic growth, which has led to social conflict. The governing philosophy has therefore shifted around economic growth to overall societal balance and harmony. Along with a moderately prosperous society, it was set to be one of the national goals for the ruling Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The concept of social harmony dates back to ancient China, to the time of Confucius. As a result, the philosophy has also been characterized as a form of New Confucianism. In modern times, it developed into a key feature of CCP general secretary Hu Jintao's signature ideology of the Scientific Outlook on Development developed in the mid-2000s, being re-introduced by the Hu–Wen Administration during the 10th National People's Congre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
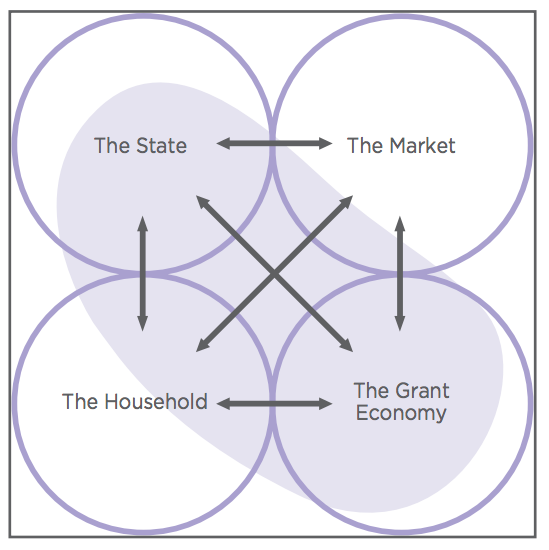
Socioeconomics
Economic sociology is the study of the social cause and effect of various economic phenomena. The field can be broadly divided into a classical period and a contemporary one, known as "new economic sociology". The classical period was concerned particularly with modernity and its constituent aspects, including rationalisation, secularisation, urbanisation, and social stratification. As sociology arose primarily as a reaction to capitalist modernity, economics played a role in much classic sociological inquiry. The specific term "economic sociology" was first coined by William Stanley Jevons in 1879, later to be used in the works of Émile Durkheim, Max Weber and Georg Simmel between 1890 and 1920. Weber's work regarding the relationship between economics and religion and the cultural " disenchantment" of the modern West is perhaps most representative of the approach set forth in the classic period of economic sociology. Contemporary economic sociology may include studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asia Times
''Asia Times'' (), formerly known as ''Asia Times Online'', is a Hong Kongbased English language news media publishing group, covering politics, economics, business, and culture from an Asian perspective. ''Asia Times'' publishes in English and simplified Chinese. History The Hong Kong website is self-described successor to Bangkok-based print newspaper ''Asia Times'' that was launched in 1995 and closed in mid-1997, using the domain asiatimes.com. ''Asia Times Online'' was created early in 1999, at atimes.com, describing itself as a successor in "publication policy and editorial outlook" to the print newspaper ''Asia Times'', owned by Sondhi Limthongkul, a Thai media mogul and leader of the People's Alliance for Democracy, who later sold his business. The new publishing company is Asia Times Holdings Limited, incorporated and registered in Hong Kong. Many reporters from the ''Asia Times'' print edition continued their careers as journalists, and a group of those contribu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Jacques
Martin Jacques (born 1945) is a British journalist, editor, academic, political commentator and author. Early life and education Jacques was born in October 1945 in the city of Coventry, then in Warwickshire, now in the West Midlands, the son of Dennis Jacques and Dorothy Preston, a mathematics undergraduate at Royal Holloway College, University of London in the late 1930s. Both parents worked in an aircraft factory during the war and during this period joined the Communist Party of Great Britain. They subsequently both became school teachers. He was brought up in Coventry. Jacques was educated at King Henry VIII School, a direct grant grammar school in Coventry, followed by the University of Manchester, where he graduated with a first-class Honours degree in economics in 1967 and stayed on to take an MA (Econ) in 1968. He then went on to King's College, Cambridge, where he studied for a PhD on 'The emergence of "responsible" trade unionism, a study of the "new dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a politics, political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. A country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. A state may be a unitary state or some type of federation, federal union; in the latter type, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated state, federated polities that make up the federation, and they may have some of the attributes of a sovereign state, except being under their federation and without the same capacity to act internationally. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include "province", "Region#Administrative regions, region" or other terms.) For most of prehistory, people lived in stateless societies. The earliest forms of states arose about 5,500 years ago. Over time societies became more Social stratification, stratified and developed institutions leading to Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnomusicology (academic Journal)
The Society for Ethnomusicology is, with the International Council for Traditional Music and thBritish Forum for Ethnomusicology one of three major international associations for ethnomusicology. Its mission is "to promote the research, study, and performance of music in all historical periods and cultural contexts." Officially founded in 1955, its origins extend back to November, 1953 at the annual meeting of the American Anthropological Association in Philadelphia with an informal agreement between Willard Rhodes, David McAllester, and Alan P. Merriam. These three traveled together to the annual meeting of the American Musicological Society in New Haven to enlist the support of musicologist Charles Seeger in their endeavor to create a new academic society. This meeting resulted in the launch of the ''Ethno-musicology Newsletter'', ethnomusicology's first dedicated serial publication, containing notes about current field research projects, a bibliography, and list of recordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Of Music
The ''Classic of Music'' () was a Confucian classic text lost by the time of the Han dynasty. It is sometimes referred to as the "Sixth Classic" (for example, by Sima Qian) and is thought to have been important in the traditional interpretations of the ''Classic of Poetry''. Qing dynasty scholar Shao Yichen ( 邵懿辰, 18101861) proposed that the book never existed, but more usually it is thought that all copies were destroyed during the burning of books and burying of scholars. A few traces remain in other surviving works, including the '' Zuo Zhuan'', the '' Rites of Zhou'', and the extremely redacted, poor-quality Record of Music contained in the '' Classic of Rites''. As accounted in the '' Book of Han'', Dou Gong 竇公 (5-4 cc. BC), a musician of the state of Wei possessed a copy of the ''Classic of Music'' which was presented to the Emperor Han Wen-di. However, the text is associated with the ''Dàsīyuè zhī zhí'' (大司樂之職) section of the ''Rites of Zhou,'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ru Jia
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius in the Hundred Schools of Thought era (c. 500 BCE), Confucianism integrates philosophy, ethics, and social governance, with a core focus on virtue, social harmony, and familial responsibility. Confucianism emphasizes virtue through self-cultivation and communal effort. Key virtues include '' ren'' (benevolence), '' yi'' (righteousness), '' li'' (propriety), '' zhi'' (wisdom), and '' xin'' (sincerity). These values, deeply tied to the notion of ''tian'' (heaven), present a worldview where human relationships and social order are manifestations of sacred moral principles.. While Confucianism does not emphasize an omnipotent deity, it upholds ''tian'' as a transcendent moral order. Confucius regarded himself as a transmitter of cultural va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yin And Yang
Originating in Chinese philosophy, yin and yang (, ), also yinyang or yin-yang, is the concept of opposite cosmic principles or forces that interact, interconnect, and perpetuate each other. Yin and yang can be thought of as complementary and at the same time opposing forces that interact to form a dynamic system in which the whole is greater than the assembled parts and the parts are as important for the cohesion of the whole. In Chinese cosmology, the universe creates itself out of a primary chaos of primordial qi or material energy, organized into the cycles of yin and yang, force and motion leading to form and matter. "Yin" is retractive, passive and contractive in nature, while "yang" is repelling, active and expansive in principle; this dichotomy in some form, is seen in all things in nature—patterns of change and difference. For example, biological, psychological and seasonal cycles, the historical evolution of landscapes over days, weeks, years to eons. The origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition's character or atmosphere. In classical music, tempo is typically indicated with an instruction at the start of a piece (often using conventional Italian terms) and, if a specific metrical pace is desired, is usually measured in beat (music), beats per minute (bpm or BPM). In modern classical compositions, a "metronome mark" in beats per minute, indicating only measured speed and not any form of expression, may supplement or replace the normal tempo marking, while in modern genres like electronic dance music, tempo will typically simply be stated in bpm. Tempo (the underlying pulse of the music) is one of the three factors that give a piece of music its texture (music), texture. The others are meter (music), meter, which is indicated by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin (music)
The ''guqin'' (; ) is a plucked seven-string Chinese musical instrument. It has been played since ancient times, and has traditionally been favoured by scholars and literati as an instrument of great subtlety and refinement, as highlighted by the quote "a gentleman does not part with his ''qin'' or '' se'' without good reason," as well as being associated with the ancient Chinese philosopher Confucius. It is sometimes referred to by the Chinese as "the father of Chinese music" or "the instrument of the sages". The ''guqin'' is not to be confused with the ''guzheng'', another Chinese long stringed instrument also without frets, but with moveable bridges under each string. Traditionally, the instrument was simply referred to as the "''qin''" (琴) but by the twentieth century the term had come to be applied to many other musical instruments as well: the '' yangqin'' hammered dulcimer, the ''huqin'' family of bowed string instruments, and the Western piano (''gangqin'' (钢琴)) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China, and is variously described as a tradition, philosophy, Religious Confucianism, religion, theory of government, or way of life. Founded by Confucius in the Hundred Schools of Thought era (c. 500 BCE), Confucianism integrates philosophy, ethics, and social governance, with a core focus on virtue, Harmonious Society, social harmony, and Filial piety, familial responsibility. Confucianism emphasizes virtue through self-cultivation and communal effort. Key virtues include ''Ren (philosophy), ren'' (benevolence), ''Yi (philosophy), yi'' (righteousness), ''Li (Confucianism), li'' (propriety), ''Wisdom, zhi'' (wisdom), and ''Xin (virtue), xin'' (sincerity). These values, deeply tied to the notion of ''tian'' (heaven), present a worldview where human relationships and social order are manifestations of sacred moral principles.. While Confucianism does not emphasize an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
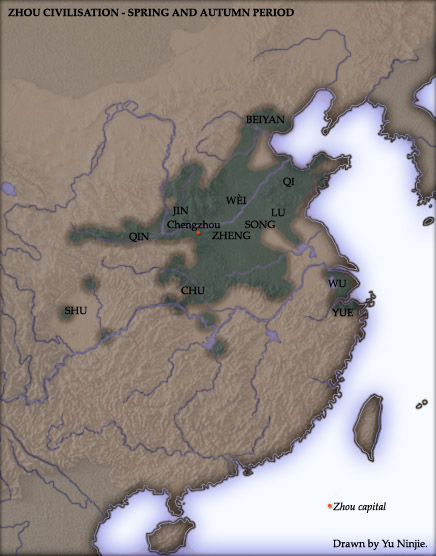
Eastern Zhou
The Eastern Zhou (256 BCE) is a period in Chinese history comprising the latter two-thirds of the Zhou dynasty. The period follows the Western Zhou era and is named due to the Zhou royal court relocating the capital eastward from Fenghao (in present-day Xi'an, Shaanxi province) to Chengzhou (near present-day Luoyang, Henan province) after the fall and sacking of the old capital in the hand of Quanrong barbarians. The Eastern Zhou era was characterised by the progressively weakened authority of the Zhou royal house, and correspondingly increasing autonomy and military ambitions of various feudal states. It is subdivided into two periods: the Spring and Autumn period (), during which the ancient aristocracy still held nominal influence in a large number of separate polities; and the Warring States period (221 BCE), which saw the complete decentralization, escalation of interstate warfare and regional administrative sophistication. History According to traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |