|
Haplogroup T (mtDNA)
Haplogroup T is a human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) haplogroup. It is believed to have originated around 25,100 years ago in the Near East. Origins Mitochondrial clade T derives from the haplogroup JT, which also gave rise to the mtDNA haplogroup J. The T maternal clade is thought to have emanated from the Near East. Distribution The basal haplogroup T* is found among Algerians in Oran (1.67%) and Reguibate Sahrawi (0.93%).S5 Table/ref> It is also distributed among the Soqotri (1.2%). Haplogroup T is present at low frequencies throughout Western and Central Asia and Europe, with varying degrees of prevalence and certainly might have been present in other groups from the surrounding areas. T is found in approximately 10% of native Europeans. It is also common among modern day Iranians. Based on a sample of over 400 modern day Iranians, the T haplogroup represents roughly 8.3% of the population (about 1 out of 12 individuals), with the more specific T1 subtype constituting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Asia
West Asia (also called Western Asia or Southwest Asia) is the westernmost region of Asia. As defined by most academics, UN bodies and other institutions, the subregion consists of Anatolia, the Arabian Peninsula, Iran, Mesopotamia, the Armenian highlands, the Levant, the island of Cyprus, the Sinai Peninsula and the South Caucasus. The region is separated from Africa by the Isthmus of Suez in Egypt, and separated from Europe by the waterways of the Turkish Straits and the watershed of the Greater Caucasus. Central Asia lies to its northeast, while South Asia lies to its east. Twelve seas surround the region (clockwise): the Aegean Sea, the Sea of Marmara, the Black Sea, the Caspian Sea, the Persian Gulf, the Gulf of Oman, the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden, the Red Sea, the Gulf of Aqaba, the Gulf of Suez, and the Mediterranean Sea. West Asia contains the majority of the similarly defined Middle East. The ''Middle East'' is a political term invented by Western geographers that has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronovo
The Andronovo culture is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1150 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." spanning from the southern Urals to the upper Yenisei River in central Siberia and western Xinjiang in the east. In the south, the Andronovo sites reached Tajikistan and Uzbekistan. It is agreed among scholars that the Andronovo culture was Indo-Iranian.: "Archaeologists are now generally agreed that the Andronovo culture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower Egypt were amalgamated by Menes, who is believed by the majority of List of Egyptologists, Egyptologists to have been the same person as Narmer. The history of ancient Egypt unfolded as a series of stable kingdoms interspersed by the "Periodization of ancient Egypt, Intermediate Periods" of relative instability. These stable kingdoms existed in one of three periods: the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom of the Early Bronze Age; the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom of the Middle Bronze Age; or the New Kingdom of Egypt, New Kingdom of the Late Bronze Age. The pinnacle of ancient Egyptian power was achieved during the New Kingdom, which extended its rule to much of Nubia and a considerable portion of the Levant. After this period, Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechta-Afalou
Mechta-Afalou, also known as Mechtoid or Paleo-Berber, are a population that inhabited parts of North Africa during the late Paleolithic and Mesolithic. They are associated with the Iberomaurusian archaeological culture. The name Mechta-Afalou comes from the large number of skeletons found in the Afalou bou Rhummel site in Béjaïa in Algeria. Ginette Aumassip. '' 4. L’homme de Mechta el-Arbi, dernier descendant de l’Atlanthrope ? '', in ''L'Algérie des premiers hommes''. Éditions de la Maison des sciences de l’homme. 31 March 2017. Bioanthropology Mechtoids are believed to have been assimilated during the Neolithic and early Bronze Age by the makers of the ensuing Capsian culture. In 1999, the anthropologists Colin Groves & Alan Thorne in studying three Northern African samples from the Pleistocene/Holocene, found Taforalt was morphologically "Caucasoid" and resembled late Pleistocene Europeans, while Afalou was more intermediate in traits. In contrast to both, the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
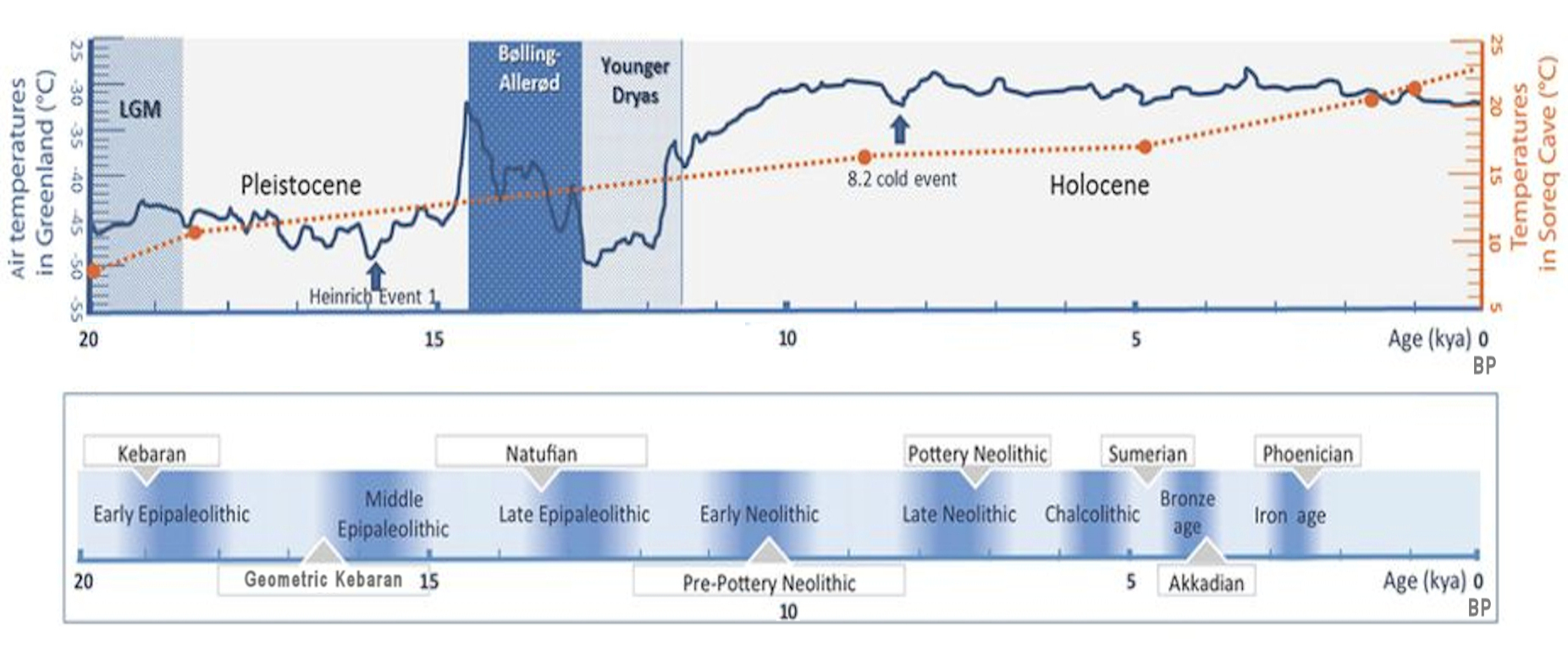
Epipaleolithic
In archaeology, the Epipalaeolithic or Epipaleolithic (sometimes Epi-paleolithic etc.) is a period occurring between the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic during the Stone Age. Mesolithic also falls between these two periods, and the two are sometimes confused or used as synonyms. More often, they are distinct, referring to approximately the same period of time in different geographic areas. Epipaleolithic always includes Epipalaeolithic Near East, this period in the Levant and, often, the rest of the Near East. It sometimes includes parts of Southeast Europe, where Mesolithic is much more commonly used. Mesolithic very rarely includes the Levant or the Near East; in Europe, Epipalaeolithic is used, though not very often, to refer to the early Mesolithic. The Epipalaeolithic has been defined as the "final Upper Palaeolithic industries occurring at the end of the final Last glacial period, glaciation which appear to merge technologically into the Mesolithic". The period is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberomaurusian
The Iberomaurusian is a backed bladelet lithic industry found near the coasts of Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. It is also known from a single major site in Libya, the Haua Fteah, where the industry is known as the Eastern Oranian.The "Western Oranian" would refer to the Iberomaurusian in Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia, but this expression is seldom used. The Iberomaurusian seems to have appeared around the time of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), somewhere between c. 25,000 and 23,000 cal BP. It would have lasted until the early Holocene, c. 11,000 cal BP. The name "Iberomaurusian" means "of Iberia and Mauretania", the latter being a Latin name for northwest Africa. Paul Maurice Pallary (1909) coined this termPallary, P., 1909. Instructions pour la recherche préhistorique dans le Nord-Ouest de l'Afrique, Algiers. to describe assemblages from the site of La Mouillah in the belief that the industry extended over the strait of Gibraltar into the Iberian Peninsula. This theory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Udmurts
The Udmurts (, ) are a Permian (Finno-Ugric) ethnic group in Eastern Europe, who speak the Udmurt language. They mainly live in the republic of Udmurtia in Russia. Etymology The name ''Udmurt'' comes from * 'meadow people,' where the first part represents the Permic root * meaning 'meadow, glade, turf, greenery'. The second part, ''murt'', means 'person' (cf. Komi , Mari , Mordvin ''mirď-''), probably an early borrowing from an Iranian language (such as Scythian): * or * meaning 'person, man' (cf. Persian ). This, in turn, is thought to have been borrowed from the Indo-Aryan term * 'man', literally 'mortal, one who is bound to die' (< 'to die'), compare 'young warrior' and Old Indic 'chariot warrior', both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the north; Poland and Slovakia to the west; Hungary, Romania and Moldova to the southwest; and the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov to the south and southeast. Kyiv is the nation's capital and List of cities in Ukraine, largest city, followed by Kharkiv, Odesa, and Dnipro. Ukraine's official language is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. Humans have inhabited Ukraine since 32,000 BC. During the Middle Ages, it was the site of early Slavs, early Slavic expansion and later became a key centre of East Slavs, East Slavic culture under the state of Kievan Rus', which emerged in the 9th century. Kievan Rus' became the largest and most powerful realm in Europe in the 10th and 11th centuries, but gradually disintegrated into rival regional powers before being d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey to the south, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, and Romania to the north. It covers a territory of and is the tenth largest within the European Union and the List of European countries by area, sixteenth-largest country in Europe by area. Sofia is the nation's capital and List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, largest city; other major cities include Burgas, Plovdiv, and Varna, Bulgaria, Varna. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Karanovo culture (6,500 BC). In the 6th to 3rd century BC, the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Ancient Macedonians, Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, trib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
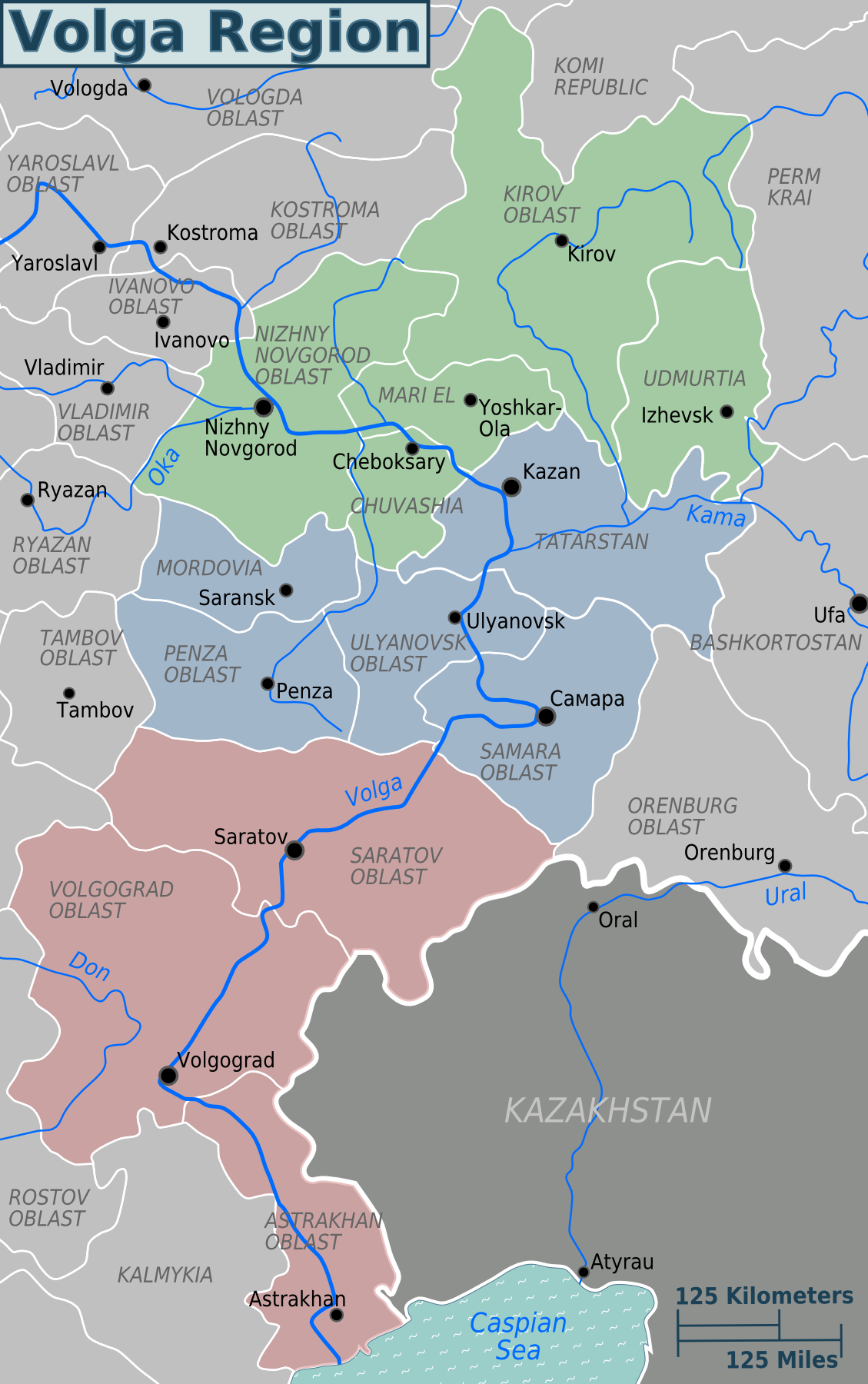
Volga Region
The Volga region, known as the ( , ; rus, Поволжье, r=Povolžje, p=pɐˈvoɫʐje; ), is a historical region in Russia that encompasses the drainage basin of the Volga River, the longest river in Europe, in central and southern European Russia. The Volga region is culturally separated into three sections: * Upper Volga Region – from the Volga River's source in Tver Oblast to the mouth of the Oka River in Nizhny Novgorod; * Middle Volga Region – from the mouth of the Oka River to the mouth of the Kama River south of Kazan; * Lower Volga Region – from the mouth of the Kama River to the Volga Delta in the Caspian Sea, in Astrakhan Oblast. The geographic boundaries of the region are vague, and the term ''Volga region'' is used to refer primarily to the Middle and Lower sections, which are included in the Volga Federal District and Volga economic region. Geography The Volga Region is almost entirely within the East European Plain, with a notable distinction contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE and its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from approximately 4500 BCE to 2500 BCE during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the proto-Indo-European homeland, original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamna Culture
The Yamnaya ( ) or Yamna culture ( ), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–Caspian steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BC. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaeological excavations near the Donets River in 1901–1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: () is a Russian adjective that means (), as these people buried their dead in tumuli (kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. Research in recent years has found that Mykhailivka, on the lower Dnieper River, Ukraine, formed the core Yamnaya culture (c. 3600–3400 BC). The Yamnaya culture is of particular interest to archaeologists and linguists, as the widely accepted Kurgan hypothesis posits that the people who produced the Yamnaya culture spoke a stage of the Proto-Indo-European language. The speakers of the Prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |