|
Half-side Formula
In spherical trigonometry, the half side formula relates the angles and lengths of the sides of spherical triangles, which are triangles drawn on the surface of a sphere and so have curved sides and do not obey the formulas for plane triangles. For a triangle \triangle ABC on a sphere, the half-side formula is. \begin \tan \tfrac12 a &= \sqrt \end where are the angular lengths (measure of central angle, arc lengths normalized to a sphere of unit radius) of the sides opposite angles respectively, and S = \tfrac12 (A+B+ C) is half the sum of the angles. Two more formulas can be obtained for b and c by permuting the labels A, B, C. The polar dual relationship for a spherical triangle is the ''half-angle formula'', \begin \tan \tfrac12 A &= \sqrt \end where semiperimeter s = \tfrac12 (a + b + c) is half the sum of the sides. Again, two more formulas can be obtained by permuting the labels A, B, C. Half-tangent variant The same relationships can be written as rational equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the edge (geometry), sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
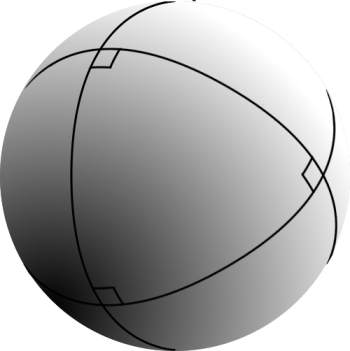
Spherical Triangle
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Geometry
300px, A sphere with a spherical triangle on it. Spherical geometry or spherics () is the geometry of the two-dimensional surface of a sphere or the -dimensional surface of higher dimensional spheres. Long studied for its practical applications to astronomy, navigation, and geodesy, spherical geometry and the metrical tools of spherical trigonometry are in many respects analogous to Euclidean plane geometry and trigonometry, but also have some important differences. The sphere can be studied either ''extrinsically'' as a surface embedded in 3-dimensional Euclidean space (part of the study of solid geometry), or ''intrinsically'' using methods that only involve the surface itself without reference to any surrounding space. Principles In plane (Euclidean) geometry, the basic concepts are points and (straight) lines. In spherical geometry, the basic concepts are points and great circles. However, two great circles on a plane intersect in two antipodal points, unlike coplan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle
A triangle is a polygon with three corners and three sides, one of the basic shapes in geometry. The corners, also called ''vertices'', are zero-dimensional points while the sides connecting them, also called ''edges'', are one-dimensional line segments. A triangle has three internal angles, each one bounded by a pair of adjacent edges; the sum of angles of a triangle always equals a straight angle (180 degrees or π radians). The triangle is a plane figure and its interior is a planar region. Sometimes an arbitrary edge is chosen to be the ''base'', in which case the opposite vertex is called the ''apex''; the shortest segment between the base and apex is the ''height''. The area of a triangle equals one-half the product of height and base length. In Euclidean geometry, any two points determine a unique line segment situated within a unique straight line, and any three points that do not all lie on the same straight line determine a unique triangle situated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Angle
A central angle is an angle whose apex (vertex) is the center O of a circle and whose legs (sides) are radii intersecting the circle in two distinct points A and B. Central angles are subtended by an arc between those two points, and the arc length is the central angle of a circle of radius one (measured in radians). The central angle is also known as the arc's angular distance. The arc length spanned by a central angle on a sphere is called '' spherical distance''. The size of a central angle is or (radians). When defining or drawing a central angle, in addition to specifying the points and , one must specify whether the angle being defined is the convex angle (<180°) or the reflex angle (>180°). Equivalently, one must specify whether the movement from point to point is clockwise or counterclockwise. Formulas If the intersection points and of the legs of the angle with the circle form a diameter, then is a straight angle. (In radians, .) Let be the min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Sphere
In mathematics, a unit sphere is a sphere of unit radius: the locus (mathematics), set of points at Euclidean distance 1 from some center (geometry), center point in three-dimensional space. More generally, the ''unit -sphere'' is an n-sphere, -sphere of unit radius in -dimensional Euclidean space; the unit circle is a special case, the unit -sphere in the Euclidean plane, plane. An (Open set, open) unit ball is the region inside of a unit sphere, the set of points of distance less than 1 from the center. A sphere or ball with unit radius and center at the origin (mathematics), origin of the space is called ''the'' unit sphere or ''the'' unit ball. Any arbitrary sphere can be transformed to the unit sphere by a combination of translation (geometry), translation and scaling (geometry), scaling, so the study of spheres in general can often be reduced to the study of the unit sphere. The unit sphere is often used as a model for spherical geometry because it has constant sectional cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Law Of Cosines
In spherical trigonometry, the law of cosines (also called the cosine rule for sides) is a theorem relating the sides and angles of spherical triangles, analogous to the ordinary law of cosines from plane trigonometry. Given a unit sphere, a "spherical triangle" on the surface of the sphere is defined by the great circles connecting three points , and on the sphere (shown at right). If the lengths of these three sides are (from to (from to ), and (from to ), and the angle of the corner opposite is , then the (first) spherical law of cosines states:Romuald Ireneus 'Scibor-MarchockiSpherical trigonometry ''Elementary-Geometry Trigonometry'' web page (1997).W. Gellert, S. Gottwald, M. Hellwich, H. Kästner, and H. Küstner, ''The VNR Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics'', 2nd ed., ch. 12 (Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, 1989). \cos c = \cos a \cos b + \sin a \sin b \cos C\, Since this is a unit sphere, the lengths , and are simply equal to the angles (in radians) subte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Haversines
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior, with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been variously described as a science and as the art of justice. State-enforced laws can be made by a legislature, resulting in statutes; by the executive through decrees and regulations; or by judges' decisions, which form precedent in common law jurisdictions. An autocrat may exercise those functions within their realm. The creation of laws themselves may be influenced by a constitution, written or tacit, and the rights encoded therein. The law shapes politics, economics, history and society in various ways and also serves as a mediator of relations between people. Legal systems vary between jurisdictions, with their differences analysed in comparative law. In civil law jurisdictions, a legislature or other central body codifies and consolidates the law. In common law systems, judges m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |