|
Haemorrhagic Fever With Renal Syndrome
Hantavirus hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) is a hemorrhagic fever caused by hantaviruses. Symptoms usually occur 12–16 days after exposure to the virus and come in five distinct phases: febrile, hypotensive, low urine production (oliguric), high urine production (diuretic), and recovery. Early symptoms include headache, lower back pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloody stool, the appearance of spots on the skin, bleeding in the respiratory tract, and renal symptoms such as kidney swelling, excess protein in urine, and blood in urine. During the hypotensive phase, blood pressure lowers due to microvascular leakage. Renal failure then causes the diuretic phase, before recovering and increasing urine production as disease progression improves. The severity of symptoms varies depending on which virus causes HFRS and ranges from a mild illness to severe. The case fatality rate likewise varies by virus, at less than 1% up to 15%. HFRS is caused mainly by four viruses in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantavirus
''Orthohantavirus'' is a genus of viruses that includes all hantaviruses (family ''Hantaviridae'') that cause disease in humans. Orthohantaviruses, hereafter referred to as hantaviruses, are naturally found primarily in rodents. In general, each hantavirus is carried by one rodent species and each rodent that carries a hantavirus carries one hantavirus species. Hantaviruses in their natural reservoirs usually cause an asymptomatic, persistent infection. In humans, however, hantaviruses cause two diseases: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) and hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS). HFRS is mainly caused by hantaviruses in Africa, Asia, and Europe, called Old World hantaviruses, and HPS is usually caused by hantaviruses in the Americas, called New World hantaviruses. Hantaviruses are transmitted mainly through aerosols and droplets that contain rodent excretions, as well as through contaminated food, bites, and scratches. Environmental factors such as rainfall, temperature, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Reservoir
In Infection, infectious disease ecology and epidemiology, a natural reservoir, also known as a disease reservoir or a reservoir of infection, is the population of organisms or the specific environment in which an infectious pathogen naturally lives and reproduces, or upon which the pathogen primarily depends for its survival. A reservoir is usually a living Host (biology), host of a certain species, such as an animal or a plant, inside of which a pathogen survives, often (though not always) without causing disease for the reservoir itself. By some definitions a reservoir may also be an environment external to an organism, such as a volume of contaminated air or water. Because of the enormous variety of infectious microorganisms capable of causing disease, precise definitions for what constitutes a natural reservoir are numerous, various, and often conflicting. The reservoir concept applies only for pathogens capable of infecting more than one host population and only with respect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) or RNA replicase is an enzyme that catalyzes the self-replication, replication of RNA from an RNA template. Specifically, it catalyzes synthesis of the RNA strand Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary to a given RNA template. This is in contrast to typical DNA-dependent RNA polymerases, which all organisms use to catalyze the transcription (genetics), transcription of RNA from a DNA template. RdRp is an essential protein encoded in the genomes of most RNA-containing viruses that lack a DNA stage, including SARS-CoV-2. Some eukaryotes also contain RdRps, which are involved in RNA interference and differ structurally from viral RdRps. History Viral RdRps were discovered in the early 1960s from studies on mengovirus and polio virus when it was observed that these viruses were not sensitive to actinomycin D, a drug that inhibits cellular DNA-directed RNA synthesis. This lack of sensitivity suggested the action of a virus-specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative-strand RNA Virus
Negative-strand RNA viruses (−ssRNA viruses) are a group of related viruses that have Sense (molecular biology), negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented. Negative-strand RNA viruses constitute the phylum ''Negarnaviricota'', in the kingdom ''Orthornavirae'' and realm ''Riboviria''. They are descended from a common ancestor that was a Double-stranded RNA viruses, double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) virus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin Nombre Virus Hanta TEM 1137 Lores
In religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law or a law of the deities. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered immoral, selfish, shameful, harmful, or alienating might be termed "sinful". Etymology From Middle English , , , , from Old English ("sin"), from Proto-West Germanic *sunnju, from Proto-Germanic *sunjō ('truth', 'excuse') and *sundī, *sundijō ("sin"), from Proto-Indo-European *h₁s-ónt-ih₂, from *h₁sónts ("being, true", implying a verdict of "truly guilty" against an accusation or charge), from *h₁es- ("to be"); compare Old English ("true"; see sooth). Doublet of suttee. Bahá'í Baháʼís consider humans to be naturally good, fundamentally spiritual beings. Human beings were created because of God's immeasurable love for us. However, the Baháʼí teachings compare the human heart to a mirror, which, if turned away fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
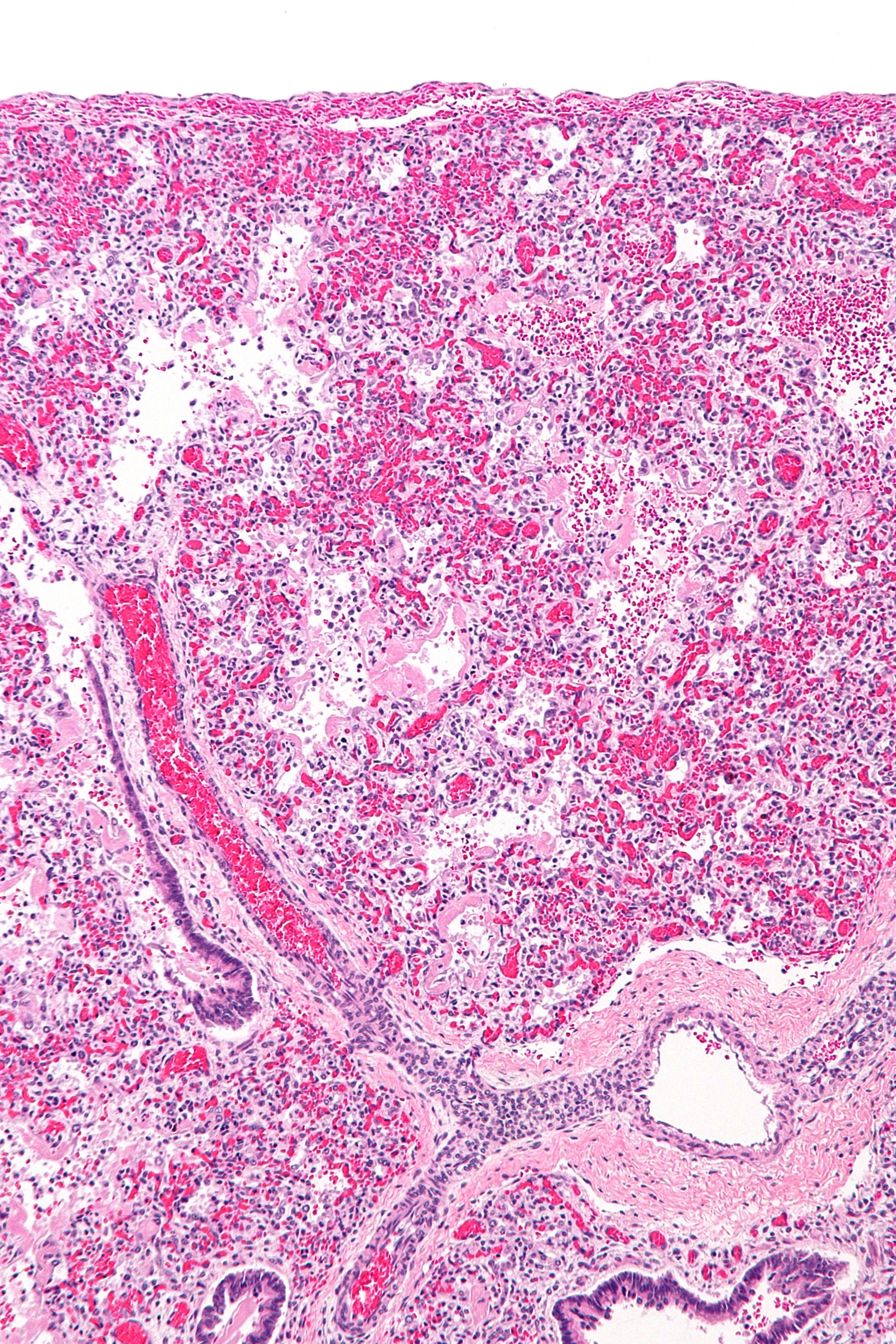
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a type of respiratory failure characterized by rapid onset of widespread inflammation in the lungs. Symptoms include shortness of breath (dyspnea), rapid breathing (tachypnea), and bluish skin coloration (cyanosis). For those who survive, a decreased quality of life is common. Causes may include sepsis, pancreatitis, trauma, pneumonia, and aspiration. The underlying mechanism involves diffuse injury to cells which form the barrier of the microscopic air sacs of the lungs, surfactant dysfunction, activation of the immune system, and dysfunction of the body's regulation of blood clotting. In effect, ARDS impairs the lungs' ability to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. Adult diagnosis is based on a PaO2/FiO2 ratio (ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen) of less than 300 mm Hg despite a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of more than 5 cm H2O. Cardiogenic pulmonary edema, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
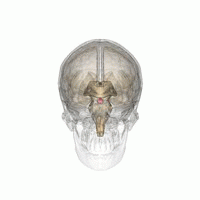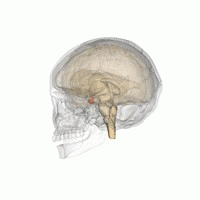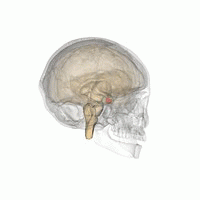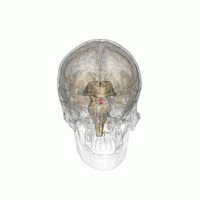
Empty Sella Syndrome
Empty sella syndrome is the condition when the pituitary gland shrinks or becomes flattened, filling the sella turcica with cerebrospinal fluid instead of the normal pituitary. It can be discovered as part of the diagnostic workup of pituitary disorders, or as an incidental finding when imaging the brain. Signs and symptoms If there are symptoms, people with empty sella syndrome can have headaches and vision loss. Additional symptoms would be associated with hypopituitarism. Additional symptoms are as follows: * Abnormality of the middle ear ossicles * Cryptorchidism * Dolichocephaly * Arnold-Chiari type I malformation * Meningocele * Patent ductus arteriosus * Muscular hypotonia * Platybasia Cause The cause of this condition is divided into primary and secondary, as follows: * The cause of this condition in terms of ''secondary empty sella syndrome'' happens when a tumor or surgery damages the gland, this is an acquired manner of the condition. * patients with idiop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), also called hantavirus cardiopulmonary syndrome (HCPS), is a severe respiratory disease caused by hantaviruses. The main features of illness are microvascular leakage and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Symptoms occur anywhere from one to eight weeks after exposure to the virus and come in three distinct phases. First, there is an early phase with flu-like symptoms such as fever, muscle aches, headache, and shortness of breath, as well as low platelet count. Second, there is cardiopulmonary phase during which people experience elevated or irregular heart rate, cardiogenic shock, and pulmonary capillary leakage, which can lead to respiratory failure, low blood pressure, and buildup of fluid in the lungs and chest cavity. The final phase is recovery, which typically takes months, but difficulties with breathing can persist for up to two years. The disease has a case fatality rate of 30 to 60 percent. Death usually occurs suddenly during the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism is the decreased (''hypo'') secretion of one or more of the eight hormones normally produced by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain. If there is decreased secretion of one specific pituitary hormone, the condition is known as selective hypopituitarism. If there is decreased secretion of most or all pituitary hormones, the term panhypopituitarism (''pan'' meaning "all") is used. The signs and symptoms of hypopituitarism vary, depending on which hormones are under-secreted and on the underlying cause of the abnormality. The diagnosis of hypopituitarism is made by blood tests, but often specific scans and other investigations are needed to find the underlying cause, such as tumors of the pituitary, and the ideal treatment. Most hormones controlled by the secretions of the pituitary can be replaced by tablets or injections. Hypopituitarism is a rare disease, but may be significantly under-diagnosed in people with previous traumatic brain injury. The first de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjunctiva
In the anatomy of the eye, the conjunctiva (: conjunctivae) is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium and stratified cuboidal epithelium (depending on the zone). The conjunctiva is highly Angiogenesis, vascularised, with many microvessels easily accessible for imaging studies. Structure The conjunctiva is typically divided into three parts: Blood supply Blood to the bulbar conjunctiva is primarily derived from the ophthalmic artery. The blood supply to the palpebral conjunctiva (the eyelid) is derived from the external carotid artery. However, the circulations of the bulbar conjunctiva and palpebral conjunctiva are linked, so both bulbar conjunctival and palpebral conjunctival vessels are supplied by both the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery, to varying extents. Nerve supply Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoptysis
Hemoptysis or haemoptysis is the discharge of blood or blood-stained sputum, mucus through the mouth coming from the bronchi, larynx, vertebrate trachea, trachea, or lungs. It does not necessarily involve coughing. In other words, it is the airway bleeding. This can occur with lung cancer, infections such as tuberculosis, bronchitis, or pneumonia, and certain cardiovascular conditions. Hemoptysis is considered massive at . In such cases, there are always severe injuries. The primary danger comes from choking, rather than bleeding, blood loss. Diagnosis * Past history, history of present illness, family history ** history of tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis, mitral stenosis, etc. ** history of cigarette smoking, occupational diseases by exposure to silica dust, etc. * Blood ** duration, frequency, amount ** Amounts of blood: large amounts of blood, or there is blood-streaked sputum ** Probable source of bleeding: Is the blood coughed up, or vomited? * Bloody sput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars were two conflicts that took place in the Balkans, Balkan states in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan states of Kingdom of Greece (Glücksburg), Greece, Kingdom of Serbia, Serbia, Kingdom of Montenegro, Montenegro and Kingdom of Bulgaria, Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defeated it, in the process stripping the Ottomans of their European provinces, leaving only East Thrace, Eastern Thrace under Ottoman control. In the Second Balkan War, Bulgaria fought against the other four combatants of the first war. It also faced an attack from Kingdom of Romania, Romania from the north. The Ottoman Empire lost the bulk of its territory in Europe. Although not involved as a combatant, Austria-Hungary became relatively weaker as a much enlarged Serbia pushed for union of the South Slavs, Slavic peoples. The war set the stage for the July Crisis, July crisis of 1914 and as a prelude to the First World War. By the early 20th century, Bul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |