|
Gynecological Cancer
Gynecologic cancer is a type of cancer that affects the female reproductive system, including ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, vaginal cancer, cervical cancer, and vulvar cancer. Gynecological cancers comprise 10-15% of women's cancers, mainly affecting women past reproductive age but posing threats to fertility for younger patients. The most common route for treatment is combination therapy, consisting of a mix of both surgical and non-surgical interventions (radiotherapy, chemotherapy). In the United States, 82,000 women are diagnosed with gynecologic cancer annually. In 2013, an estimated 91,730 were diagnosed. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms usually vary depending on the type of cancer. The most common symptoms across all gynecological cancers are abnormal vaginal bleeding, vaginal discharge, pelvic pain and urination difficulties. Vulvar cancer * Pruritus: persistent itch in the vulva * Vulvar bleeding * Vulvar pain, soreness or tenderness * Burning sensation when u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix (: cervices) or cervix uteri is a dynamic fibromuscular sexual organ of the female reproductive system that connects the vagina with the uterine cavity. The human female cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervix is approximately 4 cm long with a diameter of approximately 3 cm and tends to be described as a cylindrical shape, although the front and back walls of the cervix are contiguous. The size of the cervix changes throughout a woman's life cycle. For example, women in the fertile years of their reproductive cycle tend to have larger cervixes than postmenopausal women; likewise, women who have produced offspring have a larger cervix than those who have not. In relation to the vagina, the part of the cervix that opens to the uterus is called the ''internal os'' and the opening of the cervix in the vagina is called the ''external os''. Between them is a conduit commonly called the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paclitaxel
Paclitaxel, sold under the brand name Taxol among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi's sarcoma, cervical cancer, and pancreatic cancer. It is administered by intravenous injection. There is also an albumin-bound formulation. Common side effects include hair loss, bone marrow suppression, numbness, allergic reactions, muscle pains, and diarrhea. Other side effects include heart problems, increased risk of infection, and lung inflammation. There are concerns that use during pregnancy may cause birth defects. Paclitaxel is in the taxane family of medications. It works by interference with the normal function of microtubules during cell division. Paclitaxel was isolated in 1971 from the Pacific yew and approved for medical use in 1993. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It has been made from precursors, and through cell culture. Medical use Paclitaxel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cisplatin
Cisplatin is a chemical compound with chemical formula, formula ''cis''-. It is a coordination complex of platinum that is used as a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of cancers. These include testicular cancer, ovarian cancer, cervical cancer, bladder cancer, head and neck cancer, esophageal cancer, lung cancer, mesothelioma, brain tumors and neuroblastoma. It is given by intravenous, injection into a vein. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, hearing problems including severe hearing loss, nephrotoxicity, kidney damage, and vomiting. Other serious side effects include numbness, trouble walking, allergic reactions, electrolyte problems, and heart disease. Use during pregnancy can cause harm to the developing fetus. Cisplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications. It works in part by binding to DNA and inhibiting DNA replication, its replication. Cisplatin was first reported in 1845 and licensed for medical use in 1978 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carboplatin
Carboplatin, sold under the brand name Paraplatin among others, is a chemotherapy medication used to treat a number of forms of cancer. This includes ovarian cancer, lung cancer, head and neck cancer, brain cancer, and neuroblastoma. It is administered by injection into a vein sometimes via a port. Side effects generally occur. Common side effects include low blood cell levels, nausea, and electrolyte problems. Other serious side effects include allergic reactions and mutagenesis. It may be carcinogenic, but further research is needed to confirm this. Use during pregnancy may result in harm to the baby. Carboplatin is in the platinum-based antineoplastic family of medications and works by interfering with duplication of DNA. Carboplatin was developed as a less toxic analogue of cisplatin. It was patented in 1972 and approved for medical use in 1989. It is on the 2023 World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical uses Carboplatin is used to treat a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ-cell Cancer
A germ cell tumor (GCT) is a neoplasm derived from primordial germ cells. Germ-cell tumors can be cancerous or benign. Germ cell tumors typically originate from the gonads (ovary and testis), but can arise in other areas of the body. Extragonadal GCTs are thought to result from abnormal migration of germ cell precursors during development of the embryo. Classification GCTs are classified by their histology, regardless of location in the body. However, as more information about the genetics of these tumors become available, they may be classified based on specific gene mutations that characterize specific tumors. They are broadly divided in two classes: * The germinomatous or seminomatous germ-cell tumors (GGCT, SGCT) include only germinoma and its synonyms dysgerminoma and seminoma. * The nongerminomatous or nonseminomatous germ-cell tumors (NGGCT, NSGCT) include all other germ-cell tumors, pure and mixed. The two classes reflect an important clinical difference. Compared with ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulvar Cancer
Vulvar cancer is a cancer of the vulva, the outer portion of the female genitals. It most commonly affects the labia majora. Less often, the labia minora, clitoris, or Bartholin's glands are affected. Symptoms include a lump, itchiness, changes in the skin, or bleeding from the vulva. Risk factors include vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), HPV infection, genital warts, smoking, and many sexual partners. Most vulvar cancers are squamous cell cancers. Other types include adenocarcinoma, melanoma, sarcoma, and basal cell carcinoma. Diagnosis is suspected based on physical examination and confirmed by tissue biopsy. Routine screening is not recommended. Prevention may include HPV vaccination. Standard treatments may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and biologic therapy. Vulvar cancer newly affected about 44,200 people and resulted in 15,200 deaths globally in 2018. In the United States, it newly occurred in about 6,070 people with 1,280 deaths a year. Onset is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Cancer
Vaginal cancer is an extraordinarily rare form of cancer that develops in the tissue of the vagina. Primary vaginal cancer originates from the vaginal tissue – most frequently Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina, squamous cell carcinoma, but primary vaginal adenocarcinoma, sarcoma, and melanoma have also been reported – while secondary vaginal cancer involves the metastasis of a cancer that originated in a different part of the body. Secondary vaginal cancer is more common. Signs of vaginal cancer may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, dysuria, Rectal tenesmus, tenesmus, or pelvic pain, though as many as 20% of women diagnosed with vaginal cancer are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis. Vaginal cancer occurs more frequently in women over age 50, and the mean age of diagnosis of vaginal cancer is 60 years. It often can be cured if found and treated in early cancer staging, stages. Surgery alone or surgery combined with pelvic Radiation therapy, radiation is typically used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands (Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Lymphatic vessel#Afferent vessels, Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
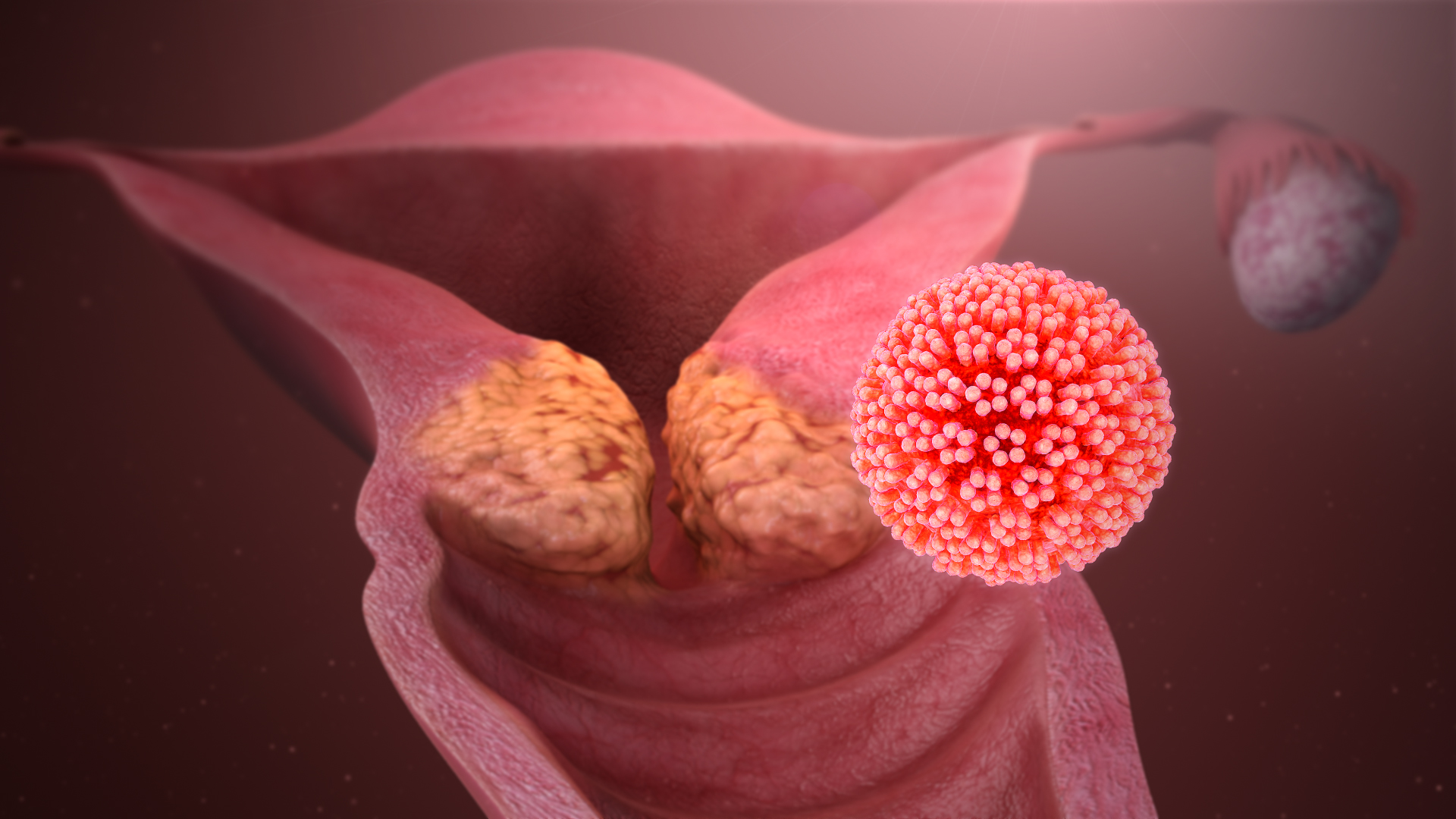
Human Papilloma Virus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. All warts are caused by HPV. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV, and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of all cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by the ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 200 types have been described. An individual can become infected wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |