|
Gummivore
A gummivore is an omnivorous animal whose diet consists primarily of the gums and saps of trees (about 90%) and insects for protein. Notable gummivores include arboreal, terrestrial primates like certain marmosets and lemurs. These animals that live off of the injuries of trees live from about 8m off of the ground up to the canopies. The feeding habit of gummivores is gummivory.Plavcan, J. M., & Kay, R. (1962). Reconstructing behavior in the primate fossil record. (pp. 165–170). New York, NY: Kluwer Academic/ Plenum Publishers. Retrieved froGoogle Books./ref> Specific traits An Old World example of a gummivore is fork-marked lemurs, whose diet is about 90% gum exudates from a tree's branches or trunk.Merrit, J. (2010). The biology of small mammals. (pp. 89–93). Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press. Retrieved froGoogle Books./ref> Lemurs have a “ tooth comb”, made up of the lower incisors and canines. Fork-marked lemurs have more robust toothcombs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth Enamel
Tooth enamel is one of the four major Tissue (biology), tissues that make up the tooth in humans and many animals, including some species of fish. It makes up the normally visible part of the tooth, covering the Crown (tooth), crown. The other major tissues are dentin, cementum, and Pulp (tooth), dental pulp. It is a very hard, white to off-white, highly mineralised substance that acts as a barrier to protect the tooth but can become susceptible to degradation, especially by acids from food and drink. In rare circumstances enamel fails to form, leaving the underlying dentin exposed on the surface. Features Enamel is the hardest substance in the human body and contains the highest percentage of minerals (at 96%),Ross ''et al.'', p. 485 with water and organic material composing the rest.Ten Cate's Oral Histology, Nancy, Elsevier, pp. 70–94 The primary mineral is hydroxyapatite, which is a crystalline calcium phosphate. Enamel is formed on the tooth while the tooth develops wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primate Behavior
Primates is an order of mammals, which is further divided into the strepsirrhines, which include lemurs, galagos, and lorisids; and the haplorhines, which include tarsiers and simians (monkeys and apes). Primates arose 74–63 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted for life in tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to the challenging environment among tree tops, including large brain sizes, binocular vision, color vision, vocalizations, shoulder girdles allowing a large degree of movement in the upper limbs, and opposable thumbs (in most but not all) that enable better grasping and dexterity. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animals and uncultivated plant species which can exist in their natural habitat, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous to game (hunting), game: those birds and mammals that were trophy hunting, hunted for sport. Wildlife can be found in all ecosystems. Deserts, plains, grasslands, woodlands, forests, and other areas including the most developed urban areas, all have distinct forms of wildlife. While the term in popular culture usually refers to animals that are untouched by human factors, most scientists agree that much wildlife is human impact on the environment, affected by human behavior, human activities. Some wildlife threaten human safety, health, property and quality of life. However, many wild animals, even the dangerous ones, have value to human beings. This value might be economic, educational, or emotio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
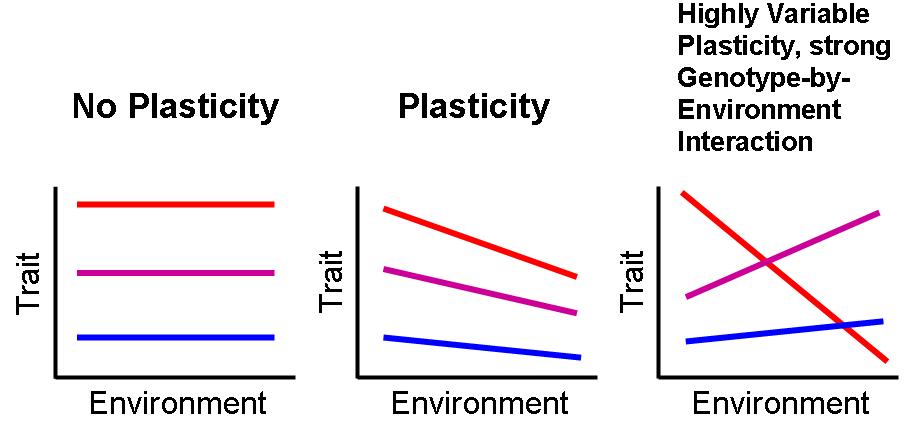
Phenotypic Plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompasses all types of environmentally induced changes (e.g. morphological, physiological, behavioural, phenological) that may or may not be permanent throughout an individual's lifespan. The term was originally used to describe developmental effects on morphological characters, but is now more broadly used to describe all phenotypic responses to environmental change, such as acclimation (acclimatization), as well as learning. The special case when differences in environment induce discrete phenotypes is termed polyphenism. Generally, phenotypic plasticity is more important for immobile organisms (e.g. plants) than mobile organisms (e.g. most animals), as mobile organisms can often move away from unfavourable environments. Nevertheless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactose
Galactose (, ''wikt:galacto-, galacto-'' + ''wikt:-ose#Suffix 2, -ose'', ), sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a monosaccharide sugar that is about as sweetness, sweet as glucose, and about 65% as sweet as sucrose. It is an aldohexose and a C-4 epimer of glucose. A galactose molecule linked with a glucose molecule forms a lactose molecule. Galactan is a polymeric form of galactose found in hemicellulose, and forming the core of the galactans, a class of natural polymeric carbohydrates. D-Galactose is also known as brain sugar since it is a component of glycoproteins (oligosaccharide-protein compounds) found in Nerve tissue, nerve tissue. Etymology The word ''galactose'' was coined by Charles Weissman in the mid-19th century and is derived from Greek language, Greek , , and the generic chemical suffix for sugars ''-ose''. The etymology is comparable to that of the word ''lactose'' in that both contain roots meaning "milk sugar". Lactose is a disaccharide of galactose plus glucose. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivores
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) as food, whether through predation or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (Felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The ursids (bears), for example: while the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a type of anaerobic metabolism which harnesses the redox potential of the reactants to make adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and organic end products. Organic molecules, such as glucose or other sugars, are catabolized and reduced by donating their electrons to other organic molecules (cofactors, coenzymes, etc.). Fermentation is important in several areas of human society. Humans have used fermentation in the production and preservation of food for 13,000 years. It has been associated with health benefits, unique flavor profiles, and making products have better texture. Humans and their livestock also benefit from fermentation from the microbes in the gut that release end products that are subsequently used by the host for energy. Perhaps the most commonly known use for fermentation is at an industrial level to produce commodity chemicals, such as ethanol and lactate. Ethanol is used in a variety of alcoholic beverages (beers, wine, and spirits) while lactate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides (), or polycarbohydrates, are the most abundant carbohydrates found in food. They are long-chain polymeric carbohydrates composed of monosaccharide units bound together by glycosidic linkages. This carbohydrate can react with water (hydrolysis) using amylase enzymes as catalyst, which produces constituent sugars (monosaccharides or oligosaccharides). They range in structure from linear to highly branched. Examples include storage polysaccharides such as starch, glycogen and galactogen and structural polysaccharides such as hemicellulose and chitin. Polysaccharides are often quite heterogeneous, containing slight modifications of the repeating unit. Depending on the structure, these macromolecules can have distinct properties from their monosaccharide building blocks. They may be amorphous or even insoluble in water. When all the monosaccharides in a polysaccharide are the same type, the polysaccharide is called a homopolysaccharide or homoglycan, but when more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bark (botany)
Bark is the outermost layer of Plant stem, stems and roots of woody plants. Plants with bark include trees, woody vines, and shrubs. Bark refers to all the Tissue (biology), tissues outside the vascular cambium and is a nontechnical term. It overlays the wood and consists of the inner bark and the outer bark. The inner bark, which in older Plant stem, stems is living tissue, includes the innermost layer of the periderm. The outer bark on older stems includes the dead tissue on the surface of the stems, along with parts of the outermost periderm and all the tissues on the outer side of the periderm. The outer bark on trees which lies external to the living periderm is also called the Glossary of botanical terms#rhytidome, rhytidome. Products derived from bark include bark shingle siding and wall coverings, spices, and other flavorings, tanbark for tannin, resin, latex, medicines, poisons, various hallucinogenic chemicals, and Cork (material), cork. Bark has been used to make clot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Anatomy
Cat anatomy comprises the anatomical studies of the visible parts of the body of a domestic cat, which are similar to those of other members of the genus ''Felis''. Mouth Permanent teeth Cats are carnivores that have highly specialized teeth. There are four types of permanent teeth that structure the mouth: twelve ''incisors'', four ''Canine tooth, canines, ''ten ''premolars'' and four ''molar (tooth), molars.'' The premolar and first molar are located on each side of the mouth that together are called the carnassial pair. The carnassial pair specialize in cutting food and are parallel to the jaw. The incisors located in the front section of the lower and upper mouth are small, narrow, and have a single root. They are used for grasping and biting food. Deciduous teeth A cat also has a deciduous dentition prior to the formation of the permanent one. This dentition emerges seven days after birth and it is composed of 26 teeth with slight differences. The mouth will have sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates. They range from . Geckos are unique among lizards for their vocalisations, which differ from species to species. Most geckos in the family Gekkonidae use chirping or clicking sounds in their social interactions. Tokay geckos (''Gekko gecko'') are known for their loud mating calls, and some other species are capable of making hissing noises when alarmed or threatened. They are the most species-rich group of lizards, with about 1,500 different species worldwide. All geckos, except species in the family Eublepharidae lack eyelids; instead, the outer surface of the eyeball has a transparent membrane, the brille. They have a fixed lens within each iris that enlarges in darkness to let in more light. Since they cannot blink, species without eyelids generally lick their own brilles whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |