|
Grey Warbler
The grey warbler (''Gerygone igata''), also known by its Māori name or outside New Zealand as the grey gerygone, is an insectivorous bird in the family Acanthizidae endemic to New Zealand. It is sometimes known as the teetotum or rainbird. Its natural habitat is forests, but also tends to occupy lower vegetation habitats. These insectivorous birds feed on insects living in shrubs, and often feed on the wing. They are found throughout New Zealand, as well as offshore islands where shrub exists. They also flourish in suburban areas where there is vegetation present. Description The grey warbler has a long tail that is darker than its grey-brown body, with white tail end markings as well as a white tail underside. There is little sexual dimorphism between males and females, aside from females usually being smaller than males. Warblers are especially small; weighing around 6.5g with an average length of only around 10cm. Adults have a signature ruby red eye, while juveniles have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean René Constant Quoy
Jean René Constant Quoy (10 November 1790 in Maillé, Vendée, Maillé – 4 July 1869 in Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, Rochefort) was a French naval surgeon, zoologist and anatomist. In 1806, he began his medical studies at the school of naval medicine at Rochefort, Charente-Maritime, Rochefort, afterwards serving as an auxiliary-surgeon on a trip to the Antilles (1808–1809). After earning his medical doctorate in 1814 at Montpellier, he was surgeon-major on a journey to Réunion (1814–1815). Along with Joseph Paul Gaimard, he served as naturalist and surgeon aboard the ''Uranie'' under Louis de Freycinet from 1817 to 1820, and on the ''French ship Astrolabe (1817), Astrolabe'' (1826–1829) under the command of Jules Dumont d'Urville. In July 1823 he and Gaimard presented a paper to the Académie royale des Sciences on the origin of coral reefs, taking issue with the then widespread belief that these were constructed by coral polyps from bases in very deep water and arguin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerygone Flaviventris, Gray
''Gerygone'' (), the gerygones or peep-warblers, is a genus of bird in the family Acanthizidae. The genus ranges from Southeast Asia through New Guinea and Australia to New Zealand and the Chatham Islands. Most of the species are found in Australia and New Guinea; only one, the golden-bellied gerygone, has managed to cross Wallace's Line and colonise as far as Thailand, Malaysia and the Philippines. Gerygones are insectivores which obtain most of their food by gleaning and snatching in the foliage of trees and bushes. They are small, mostly weighing an average of 6–7 g, and show little variation in size across their range, except for the insular Chatham Islands gerygone, which is nearly twice as large as the rest of the genus. Their songs are described as "simple but delightful", many descending in pitch, and some species are excellent mimics. "Gerygone" means "born of sound" (Magrath 2003). Taxonomy In 1838 the English ornithologist John Gould introduced the genus ''Psi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offspring
In biology, offspring are the young creation of living organisms, produced either by sexual reproduction, sexual or asexual reproduction. Collective offspring may be known as a brood or progeny. This can refer to a set of simultaneous offspring, such as the chick (young bird), chicks hatched from one clutch (eggs), clutch of eggs, or to all offspring produced over time, as with the brood (honeybee), honeybee. Offspring can occur after mating, artificial insemination, or as a result of cloning. Human offspring (lineal descendant, descendants) are referred to as children; male children are sons and female children are daughters (see Kinship). Overview Offspring contains many parts and properties that are precise and accurate in what they consist of, and what they define. As the offspring of a new species, also known as a child or f1 generation, consist of genes of the father and the mother, which is also known as the parent generation. Each of these offspring contains numerous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predation
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the Host (biology), host) and parasitoidism (which always does, eventually). It is distinct from Scavenger, scavenging on dead prey, though many predators also scavenge; it overlaps with Herbivore, herbivory, as Seed predation, seed predators and destructive frugivores are predators. Predation behavior varies significantly depending on the organism. Many predators, especially carnivores, have evolved distinct hunting strategy, hunting strategies. Pursuit predation involves the active search for and pursuit of prey, whilst ambush predation, ambush predators instead wait for prey to present an opportunity for capture, and often use stealth or aggressive mimicry. Other predators are opportunism, opportunistic or om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
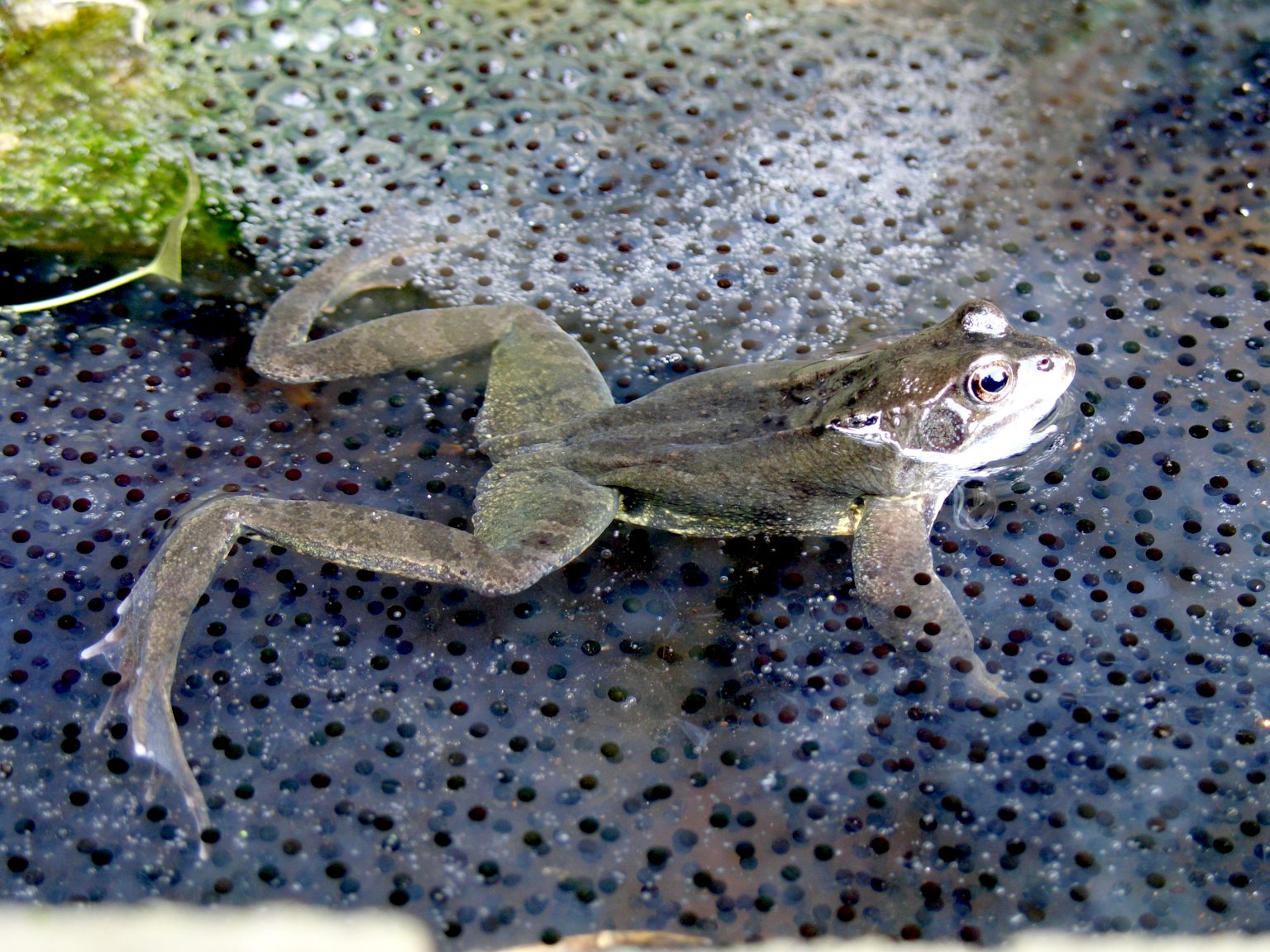
Hatchling
In oviparous biology, a hatchling is a newly hatched fish, amphibian, reptile, or bird. A group of mammals called monotremes lay eggs, and their young are hatchlings as well. Fish Fish hatchlings generally do not receive parental care, similar to reptiles. Like reptiles, fish hatchlings can be affected by xenobiotic compounds. For example, exposure to xenoestrogens can feminize fish. As well, hatchlings raised in water with high levels of carbon dioxide demonstrate unusual behaviour, such as being attracted to the scent of predators. This change could be reversed by immersion into gabazine water, leading to the hypothesis that acidic waters affect hatchling brain chemistry. Amphibians The behavior of an amphibian hatchling, commonly referred to as a tadpole, is controlled by a few thousand neurons. 99% of a ''Xenopus'' hatchling's first day after hatching is spent hanging from a thread of mucus secreted from near its mouth will eventually form; if it becomes detached from this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Begging In Animals
Begging in animals is when an animal solicits being given resources by another animal. This is usually a young animal soliciting food from their parents, brood hosts or other adults. However, the resource is sometimes non-food related or may be solicited by adult animals. Begging behavior is most widely studied in birds, however, mammals, amphibians, and invertebrates perform begging displays. Generally in food solicitation, begging behavior is instinctive, although in some instances it is learned (e.g. pet cats and dogs). While the ultimate causation for begging is an increase in the animal's individual fitness, several theories have been proposed for how food begging evolved proximate causes including scramble competition, honest signalling of need, and cooperative begging by siblings. Various types of information such as nutritional status or immunocompetence can be transmitted with auditory and visual begging signals and the behavior can be modulated by several factors such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal Sac
A fecal sac (also spelled faecal sac) is a mucous membrane, generally white or clear with a dark end, that surrounds the feces of some species of nestling birds. It allows parent birds to more easily remove Feces, fecal material from the bird nest, nest. The nestling usually produces a fecal sac within seconds of being fed; if not, a waiting adult may prod around the youngster's cloaca to stimulate excretion. Young birds of some species adopt specific postures or engage in specific behaviors to signal that they are producing fecal sacs. For example, nestling curve-billed thrashers raise their posteriors in the air, while young cactus wrens shake their bodies. Other species deposit the sacs on the rim of the nest, where they are likely to be seen (and removed) by parent birds. Not all species generate fecal sacs. They are most prevalent in passerines and their near relatives, which have Altriciality, altricial young that remain in the nest for longer periods. In some species, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatin
Gelatin or gelatine () is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics. Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein fibrils into smaller peptides; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin desserts, most gummy candy and marshmallows, ice creams, dips, and yogurts. Gelatin for cooking comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, ingestion takes place by absorbing a substance through the cell membrane. Besides nutritional items, substances that may be ingested include medication (where ingestion is termed oral administration), recreational drugs, and substances considered inedible, such as foreign bodies or excrement. Ingestion is a common route taken by pathogenic organisms and poisons entering the body. Ingestion can also refer to a mechanism picking up something and making it enter an internal hollow of that mechanism, e.g. "''a grille was fitted to prevent the pump from ingesting driftwood''". Pathogens Some pathogens are transmitted via ingestion, including viruses, bacteria, and parasites. Most commonly, this takes place via the faecal-oral route. An interm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Range
A home range is the area in which an animal lives and moves on a periodic basis. It is related to the concept of an animal's territory which is the area that is actively defended. The concept of a home range was introduced by W. H. Burt in 1943. He drew maps showing where the animal had been observed at different times. An associated concept is the utilization distribution which examines where the animal is likely to be at any given time. Data for mapping a home range used to be gathered by careful observation, but in more recent years, the animal is fitted with a transmission collar or similar GPS device. The simplest way of measuring the home range is to construct the smallest possible convex polygon around the data but this tends to overestimate the range. The best known methods for constructing utilization distributions are the so-called bivariate Gaussian or normal distribution kernel density methods. More recently, nonparametric methods such as the Burgman and Fox's alp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spider Web
A spider web, spiderweb, spider's web, or cobweb (from the archaic word ''Wikt:coppe, coppe'', meaning 'spider') is a structure created by a spider out of proteinaceous spider silk extruded from its spinnerets, generally meant to catch its prey. Spider webs have existed for at least 100 million years, as witnessed in a rare find of Early Cretaceous amber from Sussex, in southern England. Many spiders build webs specifically to trap and catch insects to eat. However, not all spiders catch their prey in webs, and some do not build webs at all. The term "spider web" is typically used to refer to a web that is apparently still in use (i.e., clean), whereas "cobweb" refers to a seemingly abandoned (i.e., dusty) web. However, the word "cobweb" is also used by biologists to describe the tangled three-dimensional web of some spiders of the family Theridiidae. While this large family is known as the cobweb spiders, they actually have a huge range of web architectures; other names for thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
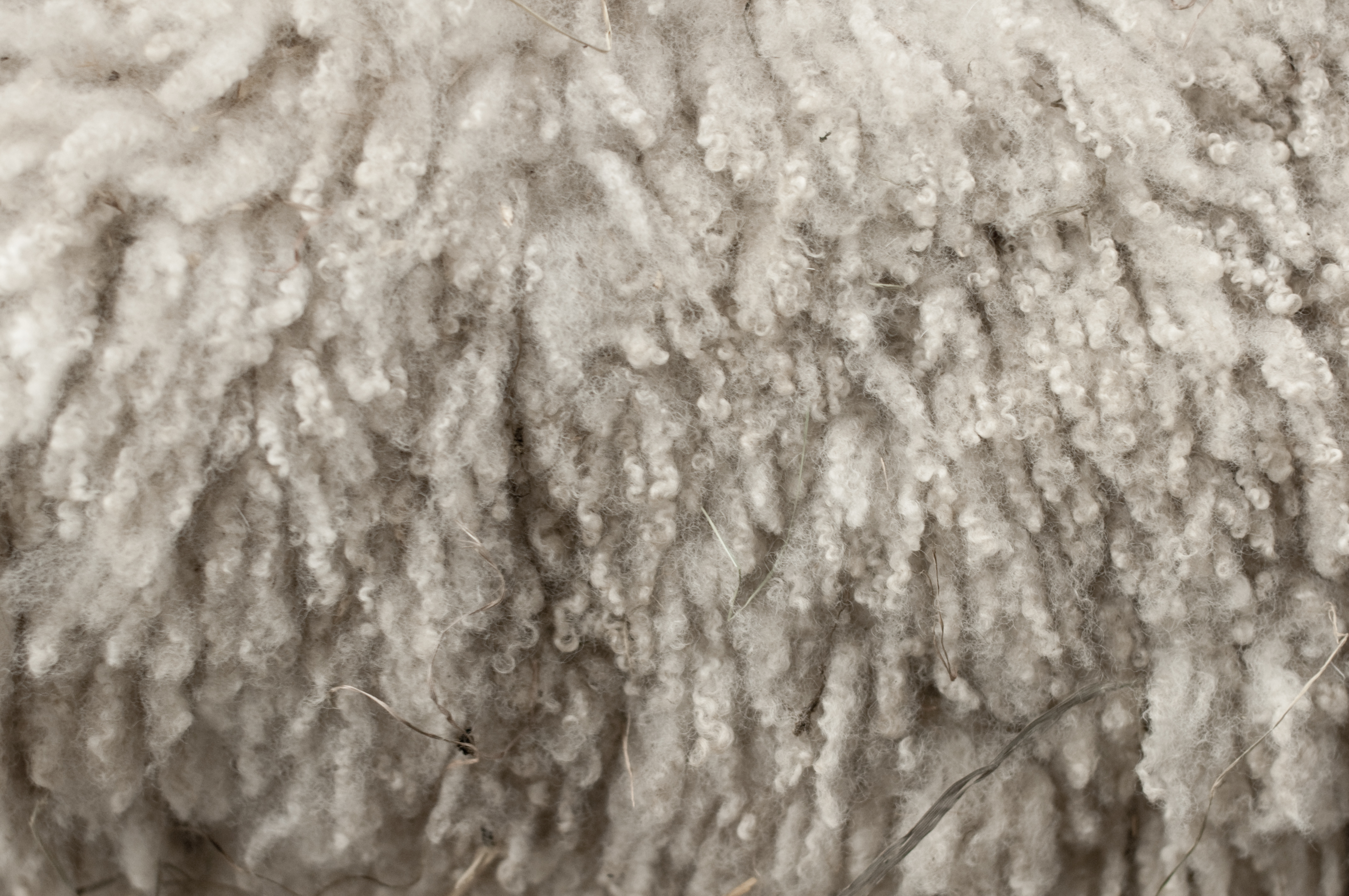
Wool
Wool is the textile fiber obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have some properties similar to animal wool. As an animal fiber, wool consists of protein together with a small percentage of lipids. This makes it chemically quite distinct from cotton and other plant fibers, which are mainly cellulose. Characteristics Wool is produced by follicles which are small cells located in the skin. These follicles are located in the upper layer of the skin called the epidermis and push down into the second skin layer called the dermis as the wool fibers grow. Follicles can be classed as either primary or secondary follicles. Primary follicles produce three types of fiber: kemp, medullated fibers, and true wool fibers. Secondary follicles only produce true wool fibers. Medullated fibers share nearly identical characteristics to hair and are long but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |