|
Green Earth
Green earth, also known as terre verte and Verona green, is an inorganic pigment derived from the minerals celadonite and glauconite. Its chemical formula is .Common Medieval Pigments d-scholarship.pitt.edu. Retrieved August 29, 2016. First used by the ancient Romans, green earth has been identified on wall paintings at and .Terre Verte. https://www.library.cornell.edu/preservation/paper/4PigAtlasWestern1.pdf. Retrieved August 30, 2016. The Renaissance painter and writer |
Derwent Cumberland Pencil Company
Derwent (formerly the "Cumberland Pencil Company") is a brand of pencils, art materials, and other stationery. The business began in 1832 in Cumberland under the name of "Banks, Son & Co". The company was bought by US corporation ACCO Brands (known then as Rexel) in 1980, and became a brand of their product range. on ACCO website (11 Oct 2020) History Keswick remained well known for producing the finest pencils in the world. Previously the pencils had been made by hand in small workshops, but in 1832, the first pencil factory in the area was opened by 'Banks, Son & Co'. This company passed through several hands before becoming the "Cumberland Pencil Company" in 1916.Pencil range Derwent colour pencils have traditionally been sold in tins of 12, 24, 36 and 72 different colours. They are also availab ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pigment
A pigment is a powder used to add or alter color or change visual appearance. Pigments are completely or nearly solubility, insoluble and reactivity (chemistry), chemically unreactive in water or another medium; in contrast, dyes are colored substances which are soluble or go into solution at some stage in their use. Dyes are often organic compounds whereas pigments are often inorganic compound, inorganic. Pigments of prehistoric and historic value include ochre, charcoal, and lapis lazuli. Economic impact In 2006, around 7.4 million tons of inorganic chemistry, inorganic, organic chemistry, organic, and special pigments were marketed worldwide. According to an April 2018 report by ''Bloomberg Businessweek'', the estimated value of the pigment industry globally is $30 billion. The value of titanium dioxide – used to enhance the white brightness of many products – was placed at $13.2 billion per year, while the color Ferrari red is valued at $300 million each yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celadonite
Celadonite is a mica group mineral, a phyllosilicate of potassium, iron in both oxidation states, aluminium and hydroxide with formula . It crystallizes in the monoclinic system and usually forms massive aggregates of prismatic crystallites or, more commonly, in dull clay masses. It is soft with a Mohs hardness of 2 and a specific gravity of 3. It forms vesicle fillings and linings in altered basaltic lavas. Early research suggests this mineral has ties to weakly metamorphosed plutonic rocks during formation, and is also found with montmorillonite clays or zeolite crystals. Association with zeolites may indicate these minerals favor the same underlying conditions of crystal growth. It was first described in 1847 on Monte Baldo, near Verona, Italy. The name is from the French ''celadon,'' for sea-green. It is one of two minerals, along with glauconite, used in making the pigment known as green earth, which was an important pigment for the decoration of Joseon buildings (so mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glauconite
Glauconite is an iron potassium phyllosilicate ( mica group) mineral of characteristic green color which is very friable and has very low weathering resistance. It crystallizes with a monoclinic geometry. Its name is derived from the Greek () meaning 'bluish green', referring to the common blue-green color of the mineral; its sheen ( mica glimmer) and blue-green color. Its color ranges from olive green, black green to bluish green, and yellowish on exposed surfaces due to oxidation. In the Mohs scale it has a hardness of 2, roughly the same as gypsum. The relative specific gravity range is 2.4–2.95. It is normally found as dark green rounded concretions with the dimensions of a sand grain. It can be confused with chlorite (also of green color) or with a clay mineral. Glauconite has the chemical formula . Glauconite particles are one of the main components of greensand, glauconitic siltstone and glauconitic sandstone. Glauconite has been called a marl in an old and br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dura-Europos
Dura-Europos was a Hellenistic, Parthian Empire, Parthian, and Ancient Rome, Roman border city built on an escarpment above the southwestern bank of the Euphrates river. It is located near the village of Al-Salihiyah, Deir ez-Zor Governorate, Salhiyé, in present-day Syria. Dura-Europos was founded around 300 BC by Seleucus I Nicator, who founded the Seleucid Empire as one of the Diadochi of Alexander the Great. In 113 BC, Parthians conquered the city, and held it, with one brief Roman intermission (114 AD), until 165 AD. Under Parthian rule, it became an important provincial administrative centre. The ancient Rome, Romans decisively captured Dura-Europos in 165 AD and greatly enlarged it as their easternmost stronghold in Mesopotamia, until it was captured by the Sasanian Empire after a Siege of Dura Europos (256), siege in 256–257 AD. Its population was deported, and the abandoned city eventually became covered by sand and mud and disappeared from sight. Dura-Europos is of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cennino Cennini
Cennino d'Andrea Cennini (; – before 1427) was an Italian painter influenced by Giotto. He was a student of Agnolo Gaddi in Florence. Gaddi trained under his father, called Taddeo Gaddi, who trained with Giotto. He is remembered mainly for having authored ''Il libro dell'arte''. Cennini was born in Colle di Val d'Elsa, present-day Tuscany. After training as an artist with Agnolo Gaddi in Florence he worked at the court of Francesco Novello da Carrara in Padua for some years before apparently returning to Colle di Val d'Elsa. His book ''Il libro dell'arte'' is a "how to" on late Medieval and early Renaissance painting, and thought to have been written around the turn of the 15th century. It contains information on pigments, brushes, drawing, panel painting, the art of fresco, painting on fabrics and casting, amongst other techniques and tricks. Theophilus (Roger of Helmerhausen), in his treatise ''On Divers Arts'' (1125), mentions oil painting, and so does Cennini, in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
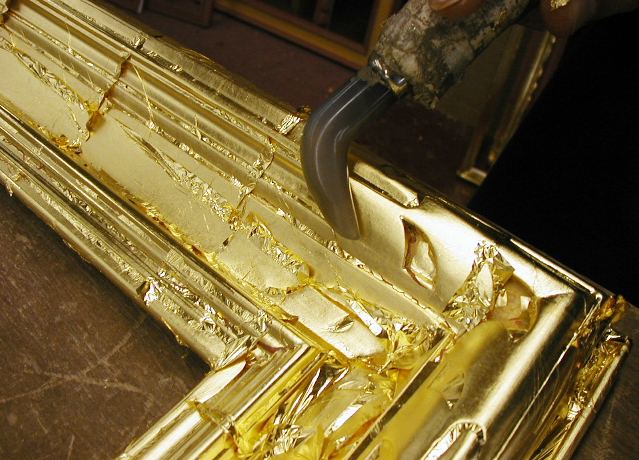
Gilded
Gilding is a decorative technique for applying a very thin coating of gold over solid surfaces such as metal (most common), wood, porcelain, or stone. A gilded object is also described as "gilt". Where metal is gilded, the metal below was traditionally silver in the West, to make silver-gilt (or ''vermeil'') objects, but gilt-bronze is commonly used in China, and also called ormolu if it is Western. Methods of gilding include hand application and gluing, typically of gold leaf, chemical gilding, and electroplating, the last also called gold plating. Parcel-gilt (partial gilt) objects are only gilded over part of their surfaces. This may mean that all of the inside, and none of the outside, of a chalice or similar vessel is gilded, or that patterns or images are made up by using a combination of gilt and ungilted areas. Gilding gives an object a gold appearance at a fraction of the cost of creating a solid gold object. In addition, a solid gold piece would often be too soft or to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of . It has the same crystal structure as corundum () and ilmenite (). With this it forms a complete solid solution at temperatures above . Hematite occurs naturally in black to steel or silver-gray, brown to reddish-brown, or red colors. It is mined as an important ore mineral of iron. It is electrically conductive. Hematite varieties include ''kidney ore'', ''martite'' ( pseudomorphs after magnetite), ''iron rose'' and ''specularite'' ( specular hematite). While these forms vary, they all have a rust-red streak. Hematite is not only harder than pure iron, but also much more brittle. The term ''kidney ore'' may be broadly used to describe botryoidal, mammillary, or reniform hematite. Maghemite is a polymorph of hematite (γ-) with the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Blue
Egyptian blue, also known as calcium copper silicate (CaCuSi4O10 or CaOCuO(SiO2)4 (calcium copper tetrasilicate)) or cuprorivaite, is a pigment that was used in ancient Egypt for thousands of years. It is considered to be the first synthetic pigment. Egyptian blue is produced from a mixture of silica, lime, copper, and an alkali. Its color is due to a calcium-copper tetrasilicate CaCuSi4O10 of the same composition as the naturally occurring mineral cuprorivaite. It was first synthesized in Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty and used extensively until the end of the Roman period in Europe, after which its use declined significantly. Apart from Egypt, it has also been found in the Near East, the Eastern Mediterranean, and the limits of the Roman Empire. It is unclear whether the pigment's existence elsewhere was a result of parallel invention or evidence of the technology's spread from Egypt to those areas. After the Roman era, Egyptian blue fell out of use and, thereafter, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on Scratch hardness, scratch hardness comparison. Large calcite crystals are used in optical equipment, and limestone composed mostly of calcite has numerous uses. Other polymorphs of calcium carbonate are the minerals aragonite and vaterite. Aragonite will change to calcite over timescales of days or less at temperatures exceeding 300 °C, and vaterite is even less stable. Etymology Calcite is derived from the German , a term from the 19th century that came from the Latin word for Lime (material), lime, (genitive ) with the suffix ''-ite'' used to name minerals. It is thus a Doublet (linguistics), doublet of the word ''wikt:chalk, chalk''. When applied by archaeology, archaeologists and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dolomite (mineral)
Dolomite () is an anhydrous carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate, ideally The term is also used for a sedimentary carbonate rock composed mostly of the mineral dolomite (see Dolomite (rock)). An alternative name sometimes used for the dolomitic rock type is dolostone. History As stated by Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure the mineral dolomite was probably first described by Carl Linnaeus in 1768. In 1791, it was described as a rock by the French natural history, naturalist and geologist Déodat Gratet de Dolomieu (1750–1801), first in buildings of the old city of Rome, and later as samples collected in the County_of_Tyrol, Tyrolean Alps. Nicolas-Théodore de Saussure first named the mineral (after Dolomieu) in March 1792. Properties The mineral dolomite crystallizes in the trigonal, trigonal-rhombohedral system. It forms white, tan, gray, or pink crystals. Dolomite is a double carbonate, having an alternating structural arrangement of calcium and magnesium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |