|
Greatsword
The English language terminology used in the classification of swords is imprecise and has varied widely over time. There is no historical dictionary for the universal names, classification, or terminology of swords; a sword was simply a single-edged or double-edged knife that grew incrementally longer and more complex with technological advances. Historical terms without a universal consensus of definition (e.g. "arming sword", "broadsword", "long sword", etc.) were used to label weapons of similar appearance but of different historical periods, regional cultures, and fabrication technology. These terms were often described in relation to other unrelated weapons, without regard to their intended use and fighting style. In modern history, many of these terms have been given specific, often arbitrary meanings that are unrelated to any of their historical meanings. Terminology Some of these terms originate contemporaneously with the weapons which they describe. Others are modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
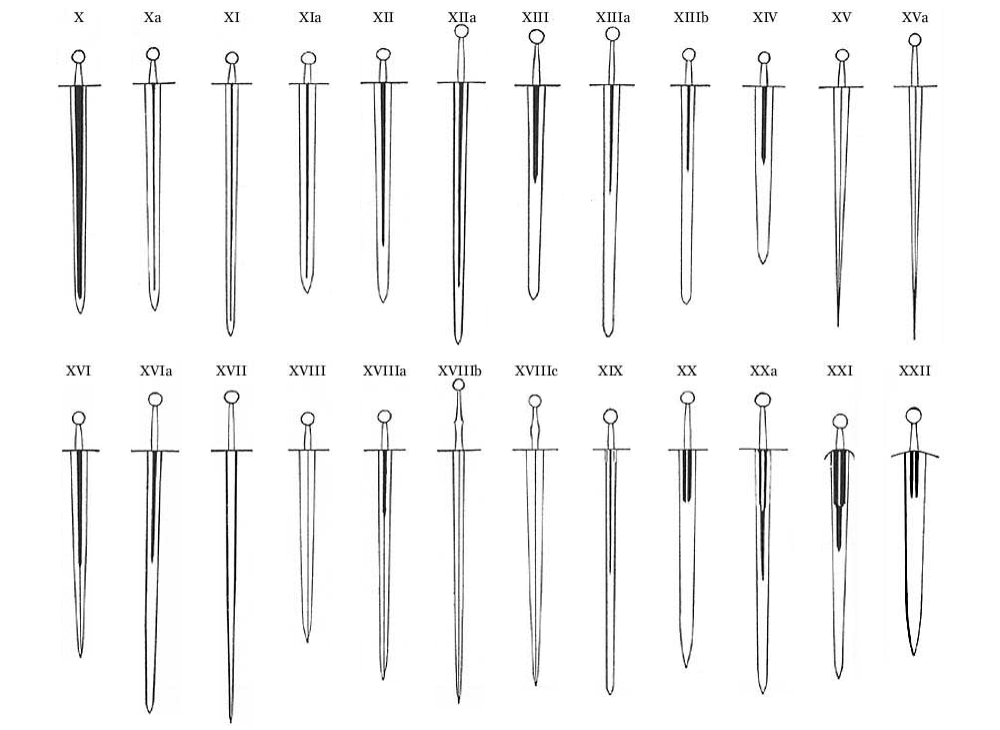
Oakeshott Typology
The Oakeshott typology is a way to define and catalogue the medieval sword based on physical form. It categorises the swords of the European Middle Ages (roughly 11th to 16th centuries) into 13 main types, labelled X through XXII. The historian and illustrator Ewart Oakeshott introduced it in his 1960 treatise ''The Archaeology of Weapons: Arms and Armour from Prehistory to the Age of Chivalry''. The system is a continuation of Jan Petersen's typology of the Viking sword, which Petersen introduced in ''De Norske Vikingsverd'' ("The Norwegian Viking Swords") in 1919. In 1927, the system was simplified by R. E. M. Wheeler to only seven types, labelled I through VII. Oakeshott slightly expanded the system with two transitional types, VIII and IX, and then he started work on his own typology. Among the many reasons for his typology, Oakeshott found date classification unreliable during his research. He wrote that the weapons' dates of manufacture, use, and retirement have been grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Long Sword
A longsword (also spelled as long sword or long-sword) is a type of European sword characterized as having a cruciform hilt with a grip for primarily two-handed use (around ), a straight double-edged blade of around , and weighing approximately . The "longsword" type exists in a morphological continuum with the medieval knightly sword and the Renaissance-era Zweihänder. It was prevalent during the late medieval and Renaissance periods (approximately 1350 to 1550), with early and late use reaching into the 11th and 17th centuries. Names English The longsword has many names in the English language, which, aside from variant spellings, include terms such as "bastard sword" and "hand-and-a-half sword." Of these, "bastard sword" is the oldest, its use being contemporaneous with the weapon's heyday. The French ' and the English "bastard sword" originate in the 15th or 16th century, originally in the general sense of "irregular sword, sword of uncertain origin", but by the mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estoc
The French estoc is a type of sword, also called a tuck in English, in use from the 14th to the 17th century. It is characterized by a cruciform hilt with a grip for two-handed use and a straight, edgeless, but sharply pointed blade around in length. It is noted for its ability to pierce mail armor. Description The estoc was a variation of the longsword designed for fighting against mail armor or plate armor. It was long, straight and stiff with no cutting edge, just a point. Examples from Poland are more than long, with a blade of ; however, others show a more manageable , with a blade. Such swords average about with no specimen weighing more than . Blade cross-sections can be triangular, square, rhomboid, or flat hexagonal. This geometry leaves hardly any cutting capability as a sharpened edge could simply not be ground but allowed the weapon to be lengthy, stiff, and very acutely pointed. Early on, the estoc was hung from the saddle when on horseback and simply hung fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claymore
A claymore (; from , "great sword") is either the Scottish variant of the late medieval two-handed sword or the Scottish variant of the basket-hilted sword. The former is characterised as having a cross hilt of forward-sloping quillons with quatrefoil terminations and was in use from the 15th to 17th centuries. The word ''claymore'' was first used in reference to basket-hilted swords during the 18th century in Scotland and parts of England. This description was maybe not used during the 17th century, when basket-hilted swords were the primary military swords across Europe, but these basket-hilted, broad-bladed swords remained in service with officers of Scottish regiments into the 21st century. After the Acts of Union in 1707 (when Scottish and English regiments were integrated together), the swords were seen as a mark of distinction by Scottish officers over the more slender sabres used by their English contemporaries: a symbol of physical strength and prowess, and a link t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighting Game
The fighting game video game genre, genre involves combat between multiple characters, often (but not limited to) one-on-one battles. Fighting game combat often features mechanics such as Blocking (martial arts), blocking, grappling, counter-attacking, and chaining attacks together into "Combo (video games), combos". Characters generally engage hand-to-hand combat, often with martial arts, but some may include weaponry. Battles are usually set in a fixed-size arena along a two-dimensional Plane (mathematics), plane, where characters navigate the plane horizontally by walking or dashing, and vertically by jumping. Some games allow limited movement in 3D space, such as ''Tekken (video game), Tekken'' and Soulblade while some are set in fully three-dimensional environments without restricting characters' movement, such as Power Stone (video game), ''Power Stone'' and ''Naruto: Ultimate Ninja Storm''; these are sometimes referred to as "3D arena" fighting games. The fighting game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Walter Scott
Sir Walter Scott, 1st Baronet (15 August 1771 – 21 September 1832), was a Scottish novelist, poet and historian. Many of his works remain classics of European literature, European and Scottish literature, notably the novels ''Ivanhoe'' (1819), ''Rob Roy (novel), Rob Roy'' (1817), ''Waverley (novel), Waverley'' (1814), ''Old Mortality'' (1816), ''The Heart of Mid-Lothian'' (1818), and ''The Bride of Lammermoor'' (1819), along with the narrative poems ''Marmion (poem), Marmion'' (1808) and ''The Lady of the Lake (poem), The Lady of the Lake'' (1810). He had a major impact on European and American literature, American literature. As an advocate and legal administrator by profession, he combined writing and editing with his daily work as Clerk of Session and Sheriff court, Sheriff-Depute of Selkirkshire. He was prominent in Edinburgh's Tory (political faction), Tory establishment, active in the Royal Highland and Agricultural Society of Scotland, Highland Society, long time a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsknechte
The (singular: , ), also rendered as Landsknechts or Lansquenets, were German mercenaries used in pike and shot formations during the early modern period. Consisting predominantly of pikemen and supporting foot soldiers, their front line was formed by '' Doppelsöldner'' ("double-pay men") renowned for their use of '' Zweihänder'' and arquebus. They formed the bulk of the Holy Roman Empire's Imperial Army from the late 15th century to the early 17th century, fighting in the Habsburg-Valois wars, the Habsburg-Ottoman wars, and the European wars of religion. Although prone to mutiny if unpaid and divided within their ranks between Catholics and Lutherans, the ''Landsknechte'' were well-armed and experienced warriors, recruitable in large numbers throughout Germany and Austria by the Holy Roman Emperor. This guaranteed both quantity and quality to the Imperial military for a century and a half. At their peak during the reign of Charles V of Habsburg, and under the leadersh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the Periodization, period of History of Europe, European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1350, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and Plague (disease), plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. Kingdom of France, France and Kingdom of England, England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
427 20100912 Bt Shanghai Museum (4987754808)
4 (four) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 3 and preceding 5. It is a square number, the smallest semiprime and composite number, and is considered unlucky in many East Asian cultures. Evolution of the Hindu-Arabic digit Brahmic numerals represented 1, 2, and 3 with as many lines. 4 was simplified by joining its four lines into a cross that looks like the modern plus sign. The Shunga would add a horizontal line on top of the digit, and the Kshatrapa and Pallava evolved the digit to a point where the speed of writing was a secondary concern. The Arabs' 4 still had the early concept of the cross, but for the sake of efficiency, was made in one stroke by connecting the "western" end to the "northern" end; the "eastern" end was finished off with a curve. The Europeans dropped the finishing curve and gradually made the digit less cursive, ending up with a digit very close to the original Brahmin cross. While the shape of the character fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |