|
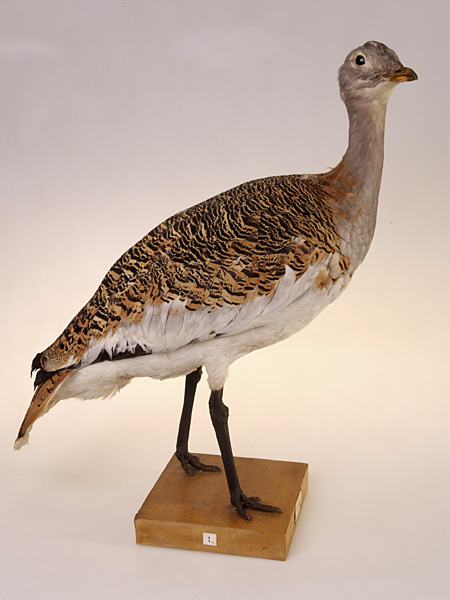
Great Bustard
The great bustard (''Otis tarda'') is a bird in the bustard family, and the only living member of the genus ''Otis (bird), Otis''. It breeds in open grasslands and farmland from northern Morocco, South Europe, South and Central Europe to temperate Central Asia, Central and East Asia. European populations are mainly resident, but Asian populations bird migration, migrate farther south in winter. Endangered species, Endangered as of 2023, it had been listed as a Vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List since 1996. Portugal and Spain now host about 60% of the world's great bustard population. The species was local extinction, extirpated in Great Britain in the 19th century, when the last bird was shot in 1832. Since 1998, The Great Bustard Group have helped Species reintroduction, reintroduce it to England on Salisbury Plain, a British Army training area. Here, the lack of public access and disturbance allows them the seclusion they desire as a large, ground-nesting bird. Taxonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Reintroduction
Species reintroduction is the deliberate release of a species into the wild, from captivity or other areas where the organism is capable of survival. The goal of species reintroduction is to establish a healthy, Genetic diversity, genetically diverse, self-sustaining population to an area where it has been extirpated, or to augment an existing population. Species that may be eligible for reintroduction are typically Threatened species, threatened or endangered in the wild. However, reintroduction of a species can also be for pest control; for example, wolves being reintroduced to a wild area to curb an overpopulation of deer. Because reintroduction may involve returning native species to localities where they had been extirpated, some prefer the term "reestablishment". Humans have been reintroducing species for food and pest control for thousands of years. However, the practice of reintroducing for conservation is much younger, starting in the 20th century. Methods for sourcing i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flying And Gliding Animals
A number of animals are capable of aerial locomotion, either by powered flight or by gliding (flight), gliding. This trait has appeared by evolution many times, without any single common ancestor. Flight has evolved at least four times in separate animals: insects, pterosaurs, birds, and bats. Gliding has evolved on many more occasions. Usually the development is to aid Canopy (biology), canopy animals in getting from tree to tree, although there are other possibilities. Gliding, in particular, has evolved among rainforest animals, especially in the rainforests in Asia (most especially Borneo) where the trees are tall and widely spaced. Several species of aquatic animals, and a few amphibians and reptiles have also evolved this gliding flight ability, typically as a means of evading predators. Types Animal aerial locomotion can be divided into two categories: powered and unpowered. In unpowered modes of locomotion, the animal uses aerodynamic forces exerted on the body due to wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dabao
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Dabao may refer to: * Da Bao, a large Chinese steamed bun *Dabao (打包), a Chinese loanword for take-out Places * Dabao, Hebei (), a town in Zhuolu County, Hebei * Dabao, Gansu (), a town in Kang County, Gansu * Dabao, Sichuan (), a town in Ebian Yi Autonomous County, Sichuan Historical eras *Dabao (, 550–551), era name used by Emperor Jianwen of Liang *Dabao (, 958–971), era name used by Liu Chang (Southern Han) Liu Chang (; 942–980), originally Liu Jixing (劉繼興), was the fourth, last and youngest Emperor of China, emperor of China's Southern Han, Southern Han dynasty during the warring Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period, reigning from 958 u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulisse Aldrovandi
Ulisse Aldrovandi (11 September 1522 – 4 May 1605) was an Italian naturalist, the moving force behind Bologna's botanical garden, one of the first in Europe. Carl Linnaeus and the comte de Buffon reckoned him the father of natural history studies. He is usually referred to, especially in older scientific literature in Latin, as Aldrovandus; his name in Italian is equally given as Aldroandi. Life Aldrovandi was born in Bologna to Teseo Aldrovandi and his wife, a noble but poor family. His father was a lawyer, and Secretary to the Senate of Bologna, but died when Ulisse was seven years old. His widowed mother wanted him to become a jurist. Initially he was sent to apprentice with merchants as a scribe for a short time when he was 14 years old, but after studying mathematics, Latin, law, and philosophy, initially at the University of Bologna, and then at the University of Padua in 1545, he became a notary. His interests successively extended to philosophy and logic, which he com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
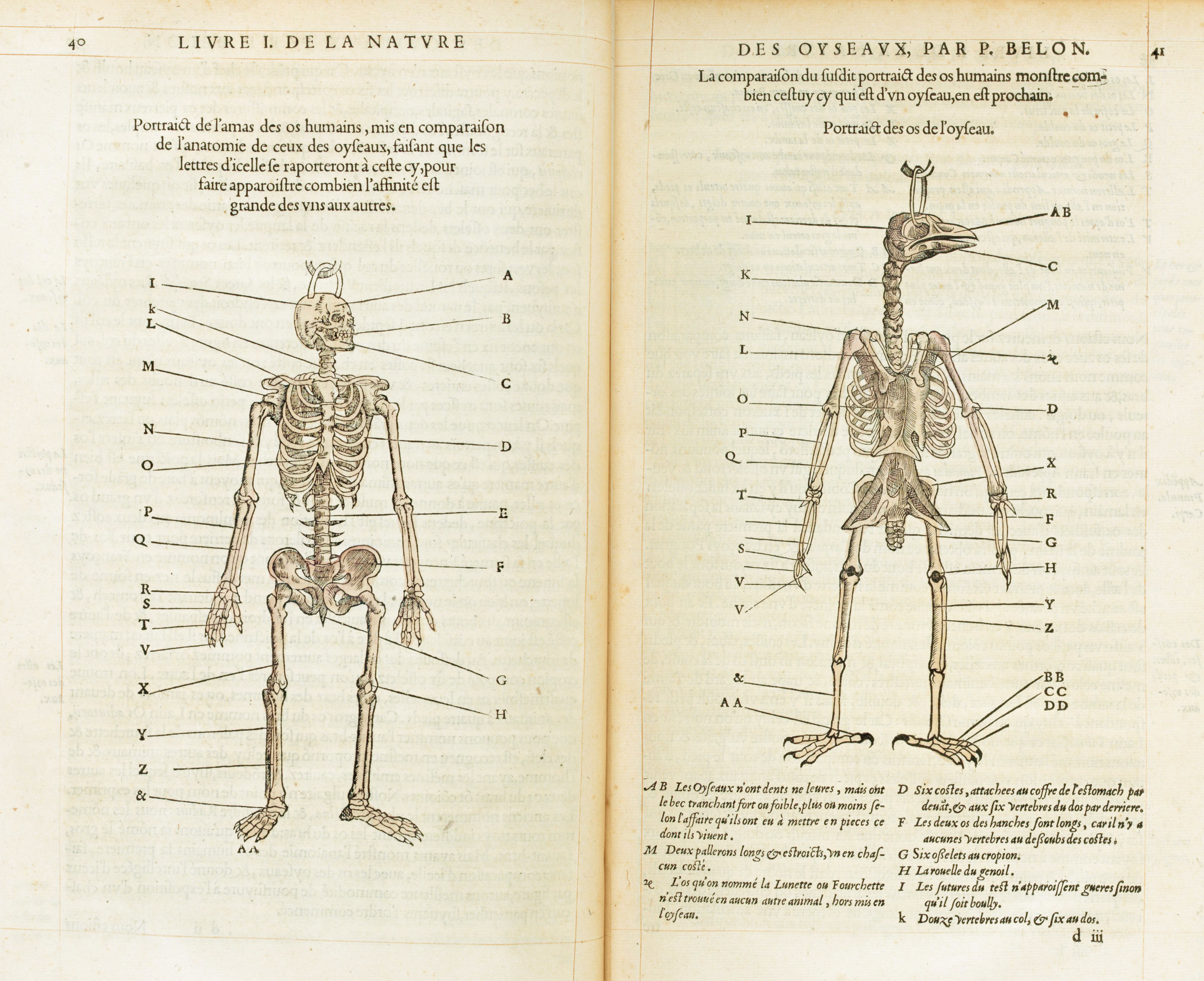
Pierre Belon
Pierre Belon (1517–1564) was a French traveller, natural history, naturalist, writer and diplomat. Like many others of the Renaissance period, he studied and wrote on a range of topics including ichthyology, ornithology, botany, comparative anatomy, architecture and Egyptology. He is sometimes known as Pierre Belon du Mans, or, in the Latin in which his works appeared, as Petrus Bellonius Cenomanus. The Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov (known for Ivan Pavlov#Legacy, Pavlov's dogs) called him the "prophet of comparative anatomy". Life Belon was born in 1517 at the hamlet of Souletière near Cérans-Foulletourte in the Pays de la Loire. Nothing is known about his descent. Somewhere between 1532 and 1535 he started working as an apprentice to René des Prez, born in Foulletourte but by then an apothecary to the bishop of Clermont, Guillaume Duprat. Between 1535 and 1538 he entered the service of René du Bellay, bishop of Le Mans, who allowed him to study medicine at the University ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area around Rome, Italy. Through the expansion of the Roman Republic, it became the dominant language in the Italian Peninsula and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. It has greatly influenced many languages, Latin influence in English, including English, having contributed List of Latin words with English derivatives, many words to the English lexicon, particularly after the Christianity in Anglo-Saxon England, Christianization of the Anglo-Saxons and the Norman Conquest. Latin Root (linguistics), roots appear frequently in the technical vocabulary used by fields such as theology, List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names, the sciences, List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes, medicine, and List of Latin legal terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/24 79), known in English as Pliny the Elder ( ), was a Roman Empire, Roman author, Natural history, naturalist, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the Roman emperor, emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic (''Natural History''), a comprehensive thirty-seven-volume work covering a vast array of topics on human knowledge and the natural world, which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is Lost literary work, no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus, and Suetonius. Tacitus may have used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural History (Pliny)
The ''Natural History'' () is a Latin work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. Despite the work's title, its subject area is not limited to what is today understood by natural history; Pliny himself defines his scope as "the natural world, or life". It is encyclopedic in scope, but its structure is not like that of a modern encyclopedia. It is the only work by Pliny to have survived, and the last that he published. He published the first 10 books in AD 77, but had not made a final revision of the remainder at the time of Pliny the Elder#Death, his death during the Eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. The rest was published posthumously by Pliny's nephew, Pliny the Younger. The work is divided into 37 books, organised into 10 volumes. These cover topics including astronomy, mathematics, geography, ethn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Helm
Christopher Alexander Roger Helm (born Dundee, 1 February 1937 – 20 January 2007) was a Scottish book publisher, notably of ornithology related titles, including the ''Helm Identification Guides''. Born in Dundee, he was raised in Forfar, where his father was a Presbyterian minister. The family moved to Tunbridge Wells at the start of World War II, and he was educated at Harrow School, then, after active duty in Cyprus with the Highland Light Infantry (as National Service), he graduated in classics and law from Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge in 1960. Having worked for Macmillan, he set up and, in turn, sold each of Croom Helm (founded in 1972, bought by Associated Book Publishers in 1986 and merged into the Routledge imprint in 1992), Christopher Helm Publishers and Pica Press (both of the latter pair being bought by A & C Black, now part of Bloomsbury Publishing Plc). He was an active member of the council of the British Ornithologists' Union, becoming vice-presid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |