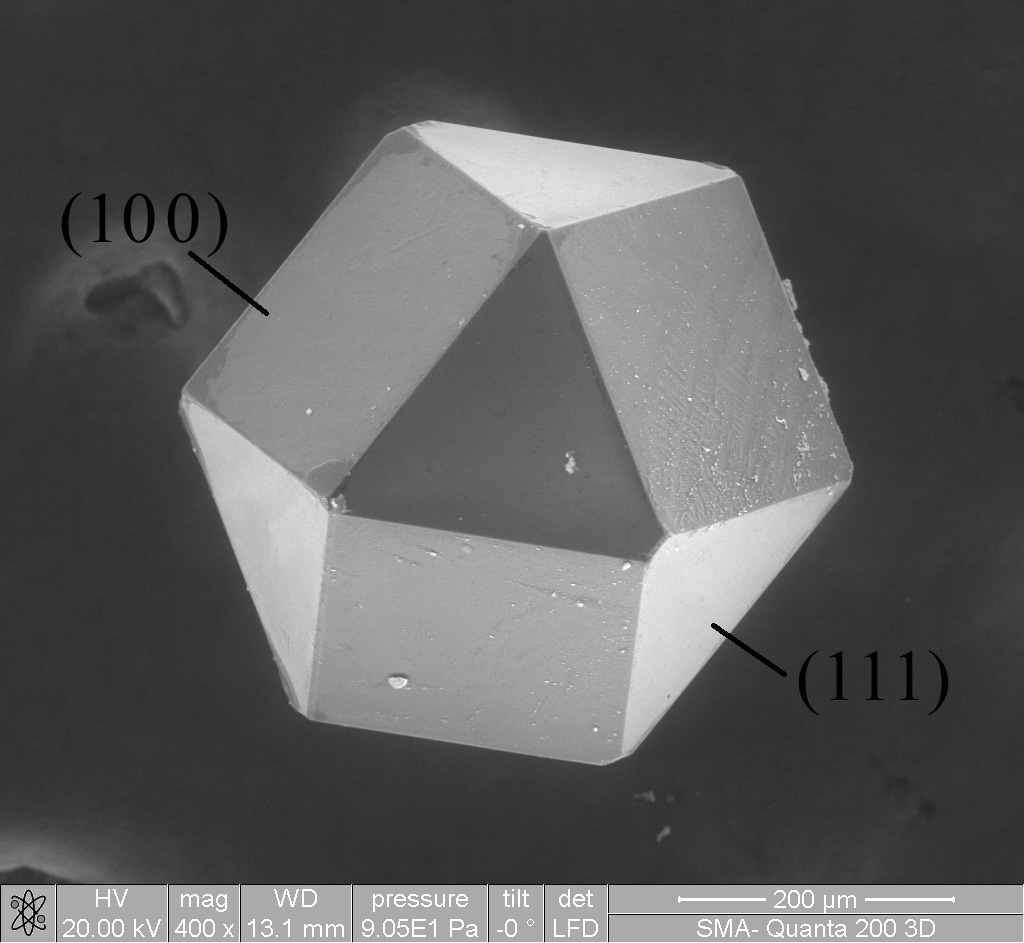
|
Grain Growth
In materials science, grain growth is the increase in size of grains (crystallites) in a material at high temperature. This occurs when recovery and recrystallisation are complete and further reduction in the internal energy can only be achieved by reducing the total area of grain boundary. The term is commonly used in metallurgy but is also used in reference to ceramics and minerals. The behaviors of grain growth is analogous to the coarsening behaviors of grains, which implied that both of grain growth and coarsening may be dominated by the same physical mechanism. Importance of grain growth The practical performances of polycrystalline materials are strongly affected by the formed microstructure inside, which is mostly dominated by grain growth behaviors. For example, most materials exhibit the Hall–Petch effect at room-temperature and so display a higher yield stress when the grain size is reduced (assuming abnormal grain growth has not taken place). At high temperatur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Materials Science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field of researching and discovering materials. Materials engineering is an engineering field of finding uses for materials in other fields and industries. The intellectual origins of materials science stem from the Age of Enlightenment, when researchers began to use analytical thinking from chemistry, physics, and engineering to understand ancient, phenomenological observations in metallurgy and mineralogy. Materials science still incorporates elements of physics, chemistry, and engineering. As such, the field was long considered by academic institutions as a sub-field of these related fields. Beginning in the 1940s, materials science began to be more widely recognized as a specific and distinct field of science and engineering, and major technical universities around the world created dedicated schools for its study. Materials scientists emphasize understanding how the history of a material (''processing'') influences its struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making up a substance. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), with the third being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dopants
A dopant (also called a doping agent) is a small amount of a substance added to a material to alter its physical properties, such as electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant is typically very low compared to the material being doped. When doped into crystalline substances, the dopant's atoms get incorporated into the crystal lattice of the substance. The crystalline materials are frequently either crystals of a semiconductor such as silicon and germanium for use in solid-state electronics, or transparent crystals for use in the production of various laser types; however, in some cases of the latter, noncrystalline substances such as glass can also be doped with impurities. In solid-state electronics using the proper types and amounts of dopants in semiconductors is what produces the p-type semiconductors and n-type semiconductors that are essential for making transistors and diodes. Transparent crystals Lasing media The procedure of doping tiny amounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms/molecules in the sintered material diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating a solid piece. Since the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points, such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy, metallurgical powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compacting of snowfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Refractories
In materials science, a refractory (or refractory material) is a material that is resistant to decomposition by heat or chemical attack and that retains its strength and rigidity at high temperatures. They are inorganic, non-metallic compounds that may be porous or non-porous, and their crystallinity varies widely: they may be crystalline, polycrystalline, amorphous, or composite. They are typically composed of oxides, carbides or nitrides of the following elements: silicon, aluminium, magnesium, calcium, boron, chromium and zirconium. Many refractories are ceramics, but some such as graphite are not, and some ceramics such as clay pottery are not considered refractory. Refractories are distinguished from the ''refractory metals'', which are elemental metals and their alloys that have high melting temperatures. Refractories are defined by ASTM C71 as "non-metallic materials having those chemical and physical properties that make them applicable for structures, or as component ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Zener Pinning
Zener pinning is the influence of a dispersion of fine particles on the movement of low- and high-angle grain boundaries through a polycrystalline material. Small particles act to prevent the motion of such boundaries by exerting a pinning pressure which counteracts the driving force pushing the boundaries. Zener pinning is very important in materials processing as it has a strong influence on recovery, recrystallization and grain growth. Origin of the pinning force A boundary is an imperfection in the crystal structure and as such is associated with a certain quantity of energy. When a boundary passes through an incoherent particle then the portion of boundary that would be inside the particle essentially ceases to exist. In order to move past the particle some new boundary must be created, and this is energetically unfavourable. While the region of boundary near the particle is pinned, the rest of the boundary continues trying to move forward under its own driving force. This r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abnormal Grain Growth
In materials science, abnormal or discontinuous grain growth, also referred to as exaggerated or secondary recrystallisation grain growth, is a grain growth phenomenon in which certain energetically favorable grains (crystallites) grow rapidly in a matrix of finer grains, resulting in a bimodal distribution of grain size. In ceramic materials, this phenomenon can result in the formation of elongated prismatic, acicular (needle-like) grains in a densified matrix. This microstructure has the potential to improve fracture toughness by impeding the propagation of cracks. Mechanisms Abnormal grain growth (AGG) is encountered in metallic or ceramic systems exhibiting one or more of several characteristics: # Systems with secondary phase inclusions, precipitates or impurities above a certain threshold concentration. # Systems with a highly anisotropic surface energy. # Systems far from chemical equilibrium. Abnormal grain growth occurs due to very high local rates of interface ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mats Hillert
Mats Hillert (28 November 1924 – 2 November 2022) was a Swedish metallurgist who was an emeritus professor in metallography (physical metallurgy) at the Royal Institute of Technology (KTH).Thermodynamics and Phase Transformations - The Selected works of Mats Hillert. (2006) s. iii. A short presentation of Mats Hillert Hillert was born in Gothenburg on 28 November 1924. He graduated from Chalmers University of Technology in 1947 with a major in chemical engineering. After finishing his military service, he joined the Swedish Institute for Metals Research in 1948. He investigated his options for postgraduate studies related to his new area, and took additional physics courses at KTH. In 1953, he moved to the United States for postgraduate studies at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he earned an Sc.D. in 1956, after which he returned to Sweden. He was made a professor at KTH in 1961. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ostwald Ripening
Ostwald ripening is a phenomenon observed in solid solutions and liquid sols that involves the change of an inhomogeneous structure over time, in that small crystals or sol particles first dissolve and then redeposit onto larger crystals or sol particles. Dissolution of small crystals or sol particles and the redeposition of the dissolved species on the surfaces of larger crystals or sol particles was first described by Wilhelm Ostwald in 1896. For colloidal systems, Ostwald ripening is also found in water-in-oil emulsions, while flocculation is found in oil-in-water emulsions. Mechanism This thermodynamically-driven spontaneous process occurs because larger particles are more energetically favored than smaller particles. This stems from the fact that molecules on the surface of a particle are energetically less stable than the ones in the interior. Consider a cubic crystal of atoms: all the atoms inside are bonded to 6 neighbours and are quite stable, but atoms on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolution Of A Single Growing Grain
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book ''On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) traits vary among individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |