|
Graduation (scale)
A graduation is a marking used to indicate points on a visual scale, which can be present on a container, a measuring device, or the axes of a line plot, usually one of many along a line or curve, each in the form of short line segments perpendicular to the line or curve. Often, some of these line segments are longer and marked with a numeral, such as every fifth or tenth graduation. The scale itself can be linear (the graduations are spaced at a constant distance apart) or nonlinear. Linear graduation of a scale occurs mainly (but not exclusively) on straight measuring devices, such as a rule or measuring tape, using units such as inches or millimetres. Graduations can also be spaced at varying spatial intervals, such as when using a logarithmic, for instance on a measuring cup, can vary in scale due to the container's non-cylindrical shape. Graduations along a curve Circular graduations of a scale occur on a circular arc or limb of an instrument. In some cases, non-circ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
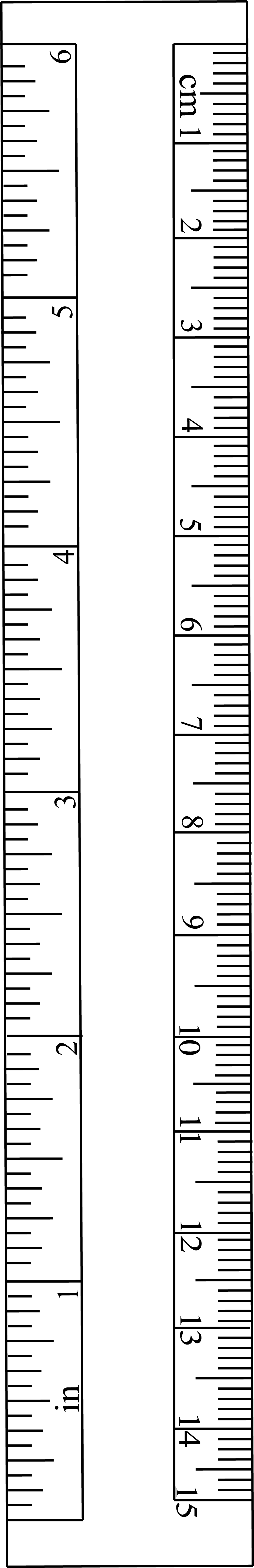
Ruler Figure
A ruler, sometimes called a rule, scale, line gauge, or metre/meter stick, is an instrument used to make length measurements, whereby a length is read from a series of markings called "rules" along an edge of the device. Usually, the instrument is rigid and the edge itself is a straightedge ("ruled straightedge"), which additionally allows one to draw straighter lines. Rulers are an important tool in geometry, geography and mathematics. They have been used since at least 2650 BC. Variants Rulers have long been made from different materials and in multiple sizes. Historically, they were mainly wood but plastics have also been used. They can be created with length markings instead of being scribed. Metal is also used for more durable rulers for use in the workshop; sometimes a metal edge is embedded into a wooden desk ruler to preserve the edge when used for straight-line cutting. Typically in length, though some can go up to 100 cm, it is useful for a ruler to be on a des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclinometer
An inclinometer or clinometer is an measuring instrument, instrument used for measuring angles of slope, elevation, or depression (geology), depression of an object with respect to gravity's direction. It is also known as a ''tilt indicator'', ''tilt sensor'', tiltmeter, ''tilt meter'', ''slope alert'', ''slope gauge'', ''gradient meter'', ''gradiometer'', ''level gauge'', ''level meter'', ''declinometer'', and ''pitch & roll indicator''. Clinometers measure both inclines and declines using three different units of measure: degree (angle), degrees, percentage points, and topos. The Astrolabes, astrolabe is an example of an inclinometer that was used for celestial navigation and location of astronomical objects from ancient history, ancient times to the Renaissance. A ''tilt sensor'' can measure the wikt:tilt, tilting in often two axes of a reference plane in two axes. In contrast, a full motion would use at least three axes and often additional sensors. One way to measure tilt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
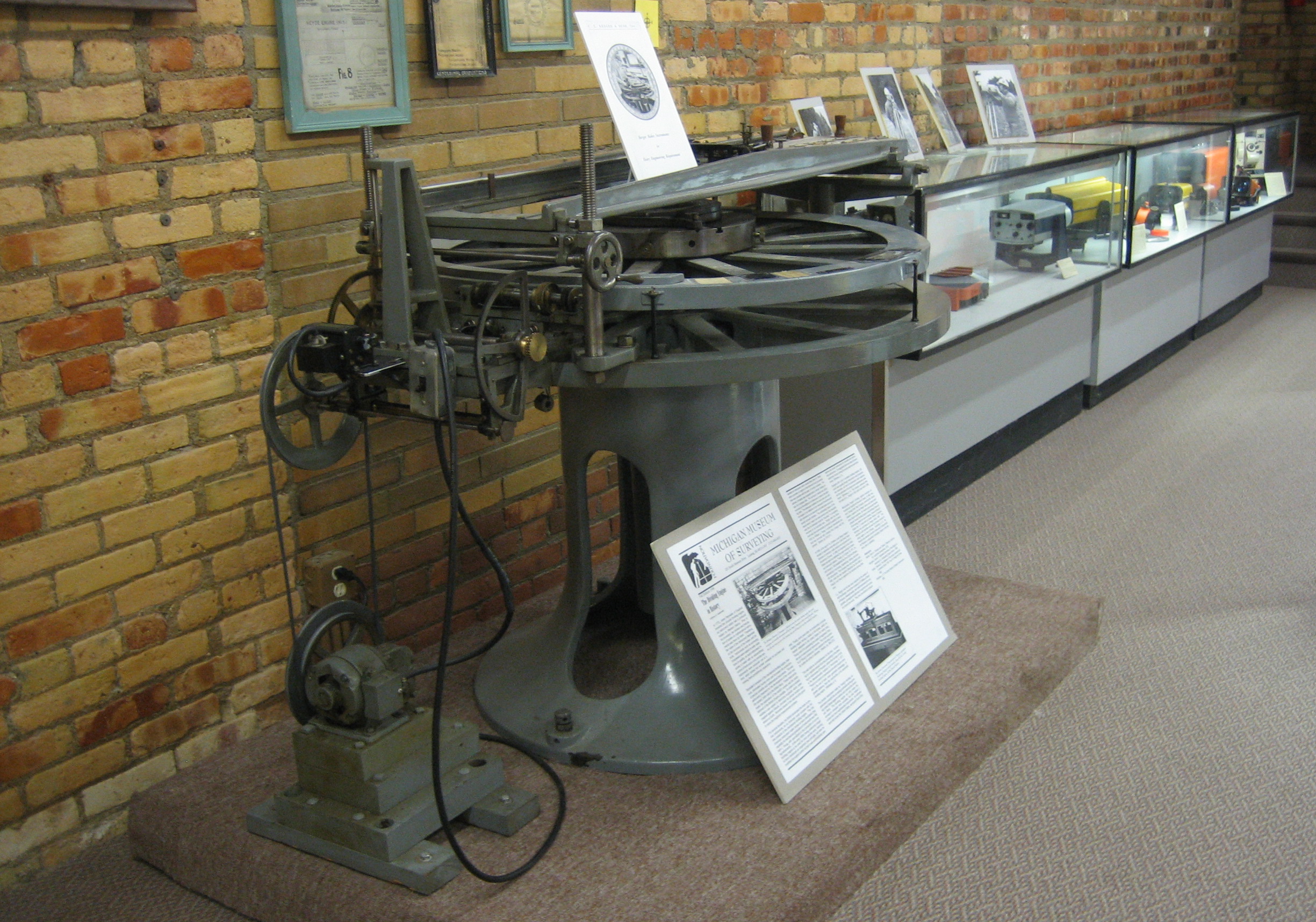
Dividing Engine
A dividing engine is a device employed to mark graduations on measuring instruments. History There has always been a need for accurate measuring instruments. Whether it is a linear device such as a ruler or vernier or a circular device such as a protractor, astrolabe, sextant, theodolite, or setting circles for astronomical telescopes, the desire for ever greater precision has always existed. For every improvement in the measuring instruments, such as better alidades or the introduction of telescopic sights, the need for more exact graduations immediately followed. In early instruments, graduations were typically etched or scribed lines in wood, ivory or brass. Instrument makers devised various devices to perform such tasks. Early Islamic instrument makers must have had techniques for the fine division of their instruments, as this accuracy is reflected in the accuracy of the readings they made. This skill and knowledge seems to have been lost, given that small quadrants an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human beings, whose use of stone tools dates back hundreds of millennia, have been observed using tools to make other tools. Early human tools, made of such materials as Rock (geology), stone, bone, and wood, were used for the preparation of food, hunting, the manufacture of weapons, and the working of materials to produce clothing and useful Cultural artifact, artifacts and crafts such as pottery, along with the construction of housing, businesses, infrastructure, and transportation. The development of metalworking made additional types of tools possible. Harnessing energy sources, such as Working animal, animal power, wind, or steam, allowed increasingly complex tools to produce an even larger range of items, with the Industrial Revolution markin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of printing as applied to paper was woodblock printing, which appeared in China before 220 AD for cloth printing. However, it would not be applied to paper until the seventh century.Shelagh Vainker in Anne Farrer (ed), "Caves of the Thousand Buddhas", 1990, British Museum publications, Later developments in printing technology include the movable type invented by Bi Sheng around 1040 AD and the printing press invented by Johannes Gutenberg in the 15th century. The technology of printing played a key role in the development of the Renaissance and the Scientific Revolution and laid the material basis for the modern knowledge-based economy and the spread of learning to the masses. History Woodblock printing Woodblo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painting
Painting is a Visual arts, visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or "Support (art), support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual arts, visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, Composition (visual art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design on a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a Burin (engraving), burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or Glass engraving, glass are engraved, or may provide an Intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing images on paper as prints or illustrations; these images are also called "engravings". Engraving is one of the oldest and most important techniques in printmaking. Wood engravings, a form of relief printing and stone engravings, such as petroglyphs, are not covered in this article. Engraving was a historically important method of producing images on paper in artistic printmaking, in mapmaking, and also for commercial reproductions and illustrations for books and magazines. It has long been replaced by various photographic processes in its commercial applications and, partly because of the difficulty of learning the techni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Etching
Chemical milling or industrial etching is the subtractive manufacturing process of using baths of temperature-regulated etching chemicals to remove material to create an object with the desired shape. Other names for chemical etching include photo etching, chemical etching, photo chemical etching and photochemical machining. It is mostly used on metals, though other materials are increasingly important. It was developed from armor-decorating and printing etching processes developed during the Renaissance as alternatives to engraving on metal. The process essentially involves bathing the cutting areas in a corrosive chemical known as an etchant, which reacts with the material in the area to be cut and causes the solid material to be dissolved; inert substances known as maskants are used to protect specific areas of the material as resists. History Organic chemicals such as lactic acid and citric acid have been used to etch metals and create products as early as 400 BCE ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protractor Rapporteur Degrees V3
A goniometer is an instrument that either measures an angle or allows an object to be rotated to a precise angular position. The term goniometry derives from two Greek words, γωνία (''gōnía'') 'angle' and μέτρον (''métron'') ' measure'. The protractor is a commonly used type in the fields of mechanics, engineering, and geometry. The first known description of a goniometer, based on the astrolabe, was by Gemma Frisius in 1538. Protractor A protractor is a measuring instrument, typically made of transparent plastic, for measuring angles. Some protractors are simple half-discs or full circles. More advanced protractors, such as the bevel protractor, have one or two swinging arms, which can be used to help measure the angle. Most protractors measure angles in degrees (°). Radian-scale protractors measure angles in radians. Most protractors are divided into 180 equal parts. Some precision protractors further divide degrees into arcminutes. A protractor divided i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slide Rule Scales Back
Slide or Slides may refer to: Places *Slide, California, former name of Fortuna, California Arts, entertainment, and media Music Albums * ''Slide'' (Lisa Germano album), 1998 * ''Slide'' (George Clanton album), 2018 *''Slide'', by Patrick Gleeson, 2007 * ''Slide'' (Luna EP), 1993 * ''Slide'' (Madeline Merlo EP), 2022 Songs * "Slide" (Slave song), 1977 * "Slide" (The Big Dish song), 1986 * "Slide" (Goo Goo Dolls song), 1998 * "Slide" (Calvin Harris song), 2017 * "Slide" (FBG Duck song), 2018 * "Slide" (French Montana song), 2019 * "Slide" (H.E.R. song), 2019 * "Slide" (Madeline Merlo song), 2022 * "Slide" (¥$ song), 2024 * "Step Back"/"Slide", by Superheist, 2001 *"Slide", by Chris Brown from '' Breezy'' *"Slide", by Dido from '' No Angel'' *"Slide", by Doechii from ''Alligator Bites Never Heal'' *"The Slide", by Cowboy Junkies from '' One Soul Now'' Other uses in music *Slide (musical ornament), a musical embellishment found particularly in Baroque music *Slide (tune type), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduated Cylinder
A graduated cylinder, also known as a measuring cylinder or mixing cylinder, is a common piece of laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of a liquid. It has a narrow cylindrical shape. Each marked line on the graduated cylinder represents the amount of liquid that has been measured. Materials and structure Large graduated cylinders are usually made of polypropylene for its excellent chemical resistance or polymethylpentene for its transparency, making them lighter and less fragile than glass. Polypropylene (PP) is easy to repeatedly autoclave; however, autoclaving in excess of about (depending on the chemical formulation: typical commercial grade polypropylene melts in excess of ), can warp or damage polypropylene graduated cylinders, affecting accuracy. A traditional graduated cylinder is usually narrow and tall so as to increase the accuracy and precision of volume measurement. It has a plastic or glass base (stand, foot, support) and a "spout" for easy pouring o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Slide Rule
A slide rule is a hand-operated mechanical calculator consisting of slidable rulers for conducting mathematical operations such as multiplication, division, exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is one of the simplest analog computers. Slide rules exist in a diverse range of styles and generally appear in a linear, circular or cylindrical form. Slide rules manufactured for specialized fields such as aviation or finance typically feature additional scales that aid in specialized calculations particular to those fields. The slide rule is closely related to nomograms used for application-specific computations. Though similar in name and appearance to a standard ruler, the slide rule is not meant to be used for measuring length or drawing straight lines. Maximum accuracy for standard linear slide rules is about three decimal significant digits, while scientific notation is used to keep track of the order of magnitude of results. English mathematician and clergyman R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |