 |
Gold Cluster
Gold clusters, a part of cluster chemistry, is a term used to describe molecular clusters of gold or larger colloidal particles. Both types can described as nanoparticles, with diameters of less than one micrometer. Gold nanoclusters have, despite intense efforts, as yet no commercial applications. Their optoelectronic and catalytic properties continue to attract attention. Bare gold clusters Bare gold clusters, i.e., clusters without stabilizing ligand shells can be synthesized and studied in vacuum using molecular beam techniques. Their structures have been experimentally studied using, e.g., anion photoelectron spectroscopy, far-infrared spectroscopy, as well as measurements of their ion mobility and electron diffraction studies in conjunction with quantum chemical calculations. The structures of such clusters differ strongly from those of the ligand-stabilized ones, indicating an pivotal influence of the chemical environment on the cluster structure. A notable example is Au2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cluster Chemistry
Nanoclusters are atomically precise, crystalline materials most often existing on the 0-2 nanometer scale. They are often considered kinetically stable intermediates that form during the synthesis of comparatively larger materials such as semiconductor and metallic nanocrystals. The majority of research conducted to study nanoclusters has focused on characterizing their crystal structures and understanding their role in the nucleation and growth mechanisms of larger materials. Materials can be categorized into three different regimes, namely bulk, nanoparticles and nanoclusters. Bulk metals are electrical conductors and good optical reflectors and metal nanoparticles display intense colors due to surface plasmon resonance. However, when the size of metal nanoclusters is further reduced to form a nanocluster, the band structure becomes discontinuous and breaks down into discrete energy levels, somewhat similar to the energy levels of molecules. This gives nanoclusters similar q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Alkanethiol
In organic chemistry, a thiol (; ), or thiol derivative, is any organosulfur compound of the form , where R represents an alkyl or other organic substituent. The functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group, or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols (that is, sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl () group of an alcohol), and the word is a blend of "''thio-''" with "alcohol". Many thiols have strong odors resembling that of garlic, cabbage or rotten eggs. Thiols are used as odorants to assist in the detection of natural gas (which in pure form is odorless), and the smell of natural gas is due to the smell of the thiol used as the odorant. Nomenclature Thiols are sometimes referred to as mercaptans () or mercapto compounds, a term introduced in 1832 by William Christopher Zeise and is derived from the Latin ('capturing mercury')''Oxford American Dictionaries'' (Mac OS X Leopard). because the thiolate group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy's (DOE) Office of Science. The main campus of the laboratory is in Richland, Washington, with additional research facilities around the country. Originally named the Pacific Northwest Laboratory, PNL was established in 1965 when research and development at the Hanford Site was separated from other Hanford operations. In 1995, the laboratory was renamed the Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL). Research facilities The Environmental Molecular Sciences Laboratory (EMSL) is a U.S. Department of Energy national scientific user facility. EMSL provides researchers around the world with integrated capabilities in oxide and mineral interface chemistry, high-performance computing and computational chemistry software, mass spectrometry, high-field magnetic resonance, and subsurface flow and transport research. The Biopr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Bismuth Cluster
Bismuth polycations are polyatomic ions of the formula . They were originally observed in solutions of bismuth metal in molten bismuth chloride. It has since been found that these clusters are present in the solid state, particularly in salts where germanium tetrachloride or tetrachloroaluminate serve as the counteranions, but also in amorphous phases such as glasses and gels. Bismuth endows materials with a variety of interesting optical properties that can be tuned by changing the supporting material. Commonly-reported structures include the trigonal bipyramidal cluster, the octahedral cluster, the square antiprismatic cluster, and the tricapped trigonal prismatic cluster. Known materials Crystalline * Bi5(AlCl4)3 * Bi8(AlCl4)2 * Bi5(GaCl4)3 * Bi8(GaCl4)2 Metal complexes * uBi8AlCl4]3 * u(Bi8)2sup>6+ * u2Bi14Br4AlCl4]4 Structure and bonding Bismuth polycations form despite the fact that they possess fewer total valence electrons than would seem necessary for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Thiolate-protected Gold Cluster
Thiolate-protected gold clusters are a type of ligand-protected metal cluster, synthesized from gold ions and thin layer compounds that play a special role in cluster physics because of their unique stability and electronic properties. They are considered to be stable compounds. These clusters can range in size up to hundreds of gold atoms, above which they are classified as passivated gold nanoparticles. Synthesis Wet chemical synthesis The wet chemical synthesis of thiolate-protected gold clusters is achieved by the reduction of gold(III) salt solutions, using a mild reducing agent in the presence of thiol compounds. This method starts with gold ions and synthesizes larger particles from them, therefore this type of synthesis can be regarded as a "bottom-up approach" in nanotechnology to the synthesis of nanoparticles. The reduction process depends on the equilibrium between different oxidation states of the gold and the oxidized or reduced forms of the reducing agent, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Science (journal)
''Science'' is the peer review, peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' cover the full range of List of academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Surface Plasmon Resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is a phenomenon that occurs where electrons in a thin metal sheet become excited by light that is directed to the sheet with a particular angle of incidence (optics), angle of incidence, and then travel parallel to the sheet. Assuming a constant light source wavelength and that the metal sheet is thin, the angle of incidence that triggers SPR is related to the refractive index of the material and even a small change in the refractive index will cause SPR to not be observed. This makes SPR a possible technique for detecting particular substances (analytes) and SPR biosensors have been developed to detect various important biomarkers. Explanation The surface plasmon polariton is a non-radiative Surface wave#Electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic surface wave that propagates in a direction parallel to the negative permittivity/dielectric material interface. Since the wave is on the boundary of the conductor and the external medium (air, water or vacuu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the spectral band, band of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' (or simply light). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well, known collectively as ''optical radiation''. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 Terahertz (unit), terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions, these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal, a group 11 element, and one of the noble metals. It is one of the least reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemical elements, being the second-lowest in the reactivity series. It is solid under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions. Gold often occurs in free elemental (native state (metallurgy), native state), as gold nugget, nuggets or grains, in rock (geology), rocks, vein (geology), veins, and alluvial deposits. It occurs in a solid solution series with the native element silver (as in electrum), naturally alloyed with other metals like copper and palladium, and mineral inclusions such as within pyrite. Less commonly, it occurs in minerals as gold compounds, often with tellurium (gold tellurides). Gold is resistant to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
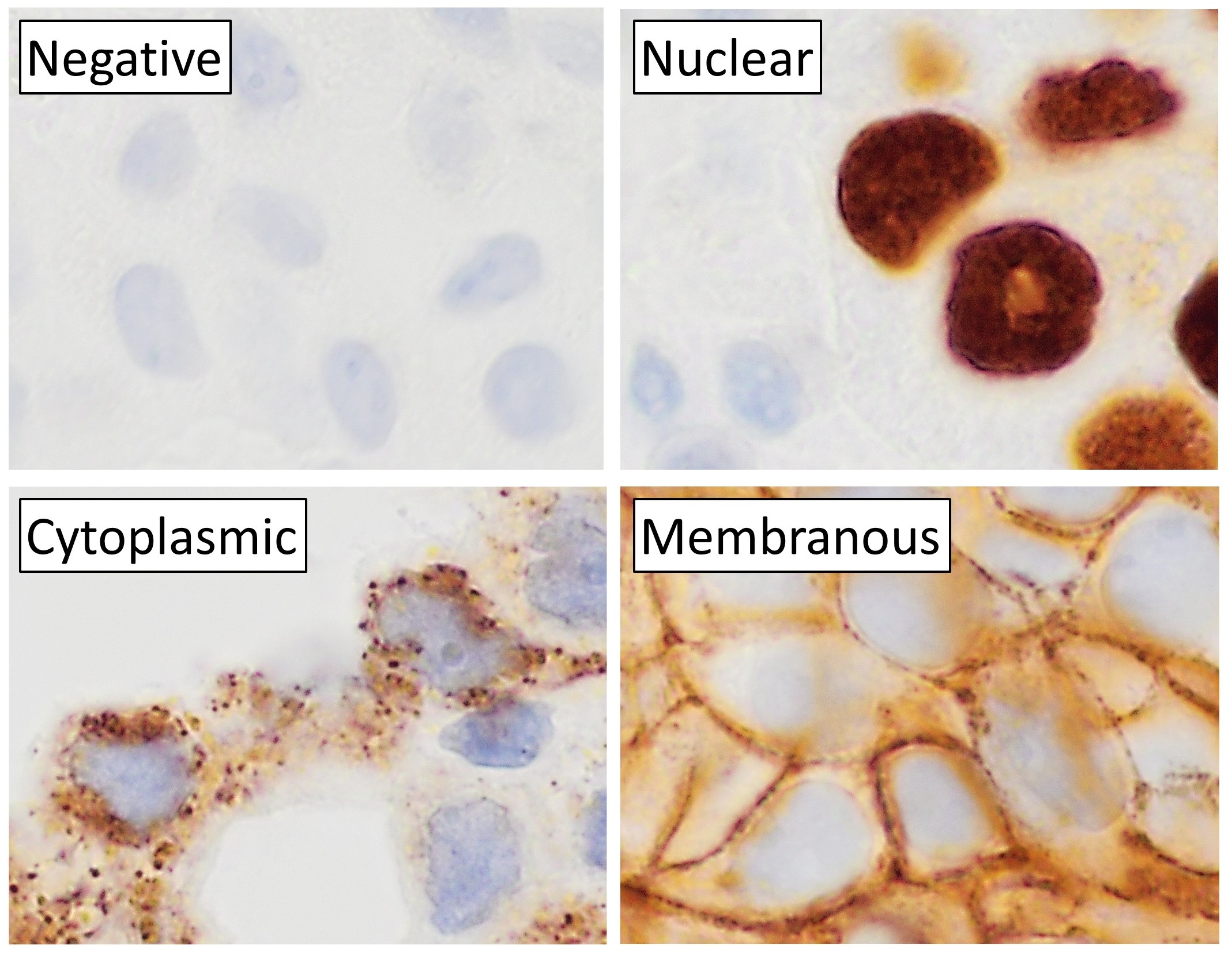 |
Immunohistochemical Staining
Immunohistochemistry is a form of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens in cells and tissue, by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. Albert Hewett Coons, Ernest Berliner, Norman Jones and Hugh J Creech was the first to develop immunofluorescence in 1941. This led to the later development of immunohistochemistry. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diagnosis of abnormal cells such as those found in cancerous tumors. In some cancer cells certain tumor antigens are expressed which make it possible to detect. Immunohistochemistry is also widely used in basic research, to understand the distribution and localization of biomarkers and differentially expressed proteins in different parts of a biological tissue. Sample preparation Immunohistochemistry can be performed on tissue that has been fixed and embedded in paraffin, but also cryopreservated (frozen) tissue. Based on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
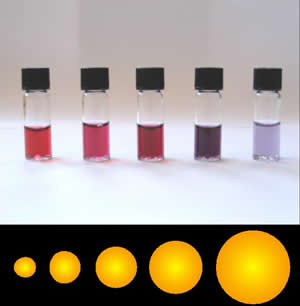 |
Colloidal Gold
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is coloured usually either wine red (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue-purple (for larger spherical particles or nanorods). Due to their optical, electronic, and molecular-recognition properties, gold nanoparticles are the subject of substantial research, with many potential or promised applications in a wide variety of areas, including electron microscopy, electronics, nanotechnology, materials science, and biomedicine. The properties of colloidal gold nanoparticles, and thus their potential applications, depend strongly upon their size and shape. For example, rodlike particles have both a transverse and longitudinal absorption peak, and anisotropy of the shape affects their self-assembly. History Used since ancient times as a method of staining glass, colloidal gold was used in the 4th-century Lycurgus Cup, which changes color dependi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |