|
Glypicans
Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypicans have been identified, and these are referred to as dally (division abnormally delayed) and dally-like. One glypican has been identified in ''C. elegans''. Glypicans seem to play a vital role in developmental morphogenesis, and have been suggested as regulators for the Wnt and Hedgehog cell signaling pathways. They have additionally been suggested as regulators for fibroblast growth factor and bone morphogenic protein signaling. Structure While six glypicans have been identified in mammals, several characteristics remain consistent between these different proteins. First, the core protein of all glypicans is similar in size, approximately ranging between 60 and 70 kDa. Additionally, in terms of amino acid sequence, the location of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC6
Glypican-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPC6'' gene. The glypicans comprise a family of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored heparan sulfate proteoglycans. The glypicans have been implicated in the control of cell growth and division. Glypican 6 is a putative cell surface coreceptor for growth factors, extracellular matrix proteins, proteases and anti-proteases. See also * Glypican Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypica ... References Further reading * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heparan Sulfate
Heparan sulfate (HS) is a linear polysaccharide found in all animal tissues. It occurs in a proteoglycan (HSPG, i.e. Heparan Sulfate ProteoGlycan) in which two or three HS chains are attached in close proximity to cell surface or extracellular matrix proteins. In this form, HS binds to a variety of protein ligands, including Wnt signaling pathway, Wnt, and regulates a wide range of biological activities, including developmental processes, angiogenesis, blood coagulation, abolishing detachment activity by GrB (Granzyme B), and tumour metastasis. HS has also been shown to serve as cellular receptor for a number of viruses, including the respiratory syncytial virus. One study suggests that cellular heparan sulfate has a role in SARS-CoV-2 infection, particularly when the virus attaches with ACE2. Proteoglycans The major cell membrane HSPGs are the transmembrane syndecans and the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored glypicans. Other minor forms of membrane HSPG include betaglyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC1
Glypican-1 (GPC1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPC1'' gene. GPC1 is encoded by human ''GPC1'' gene located at 2q37.3. GPC1 contains 558 amino acids with three predicted heparan sulfate chains. Function Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with three heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. Interactions Glypican 1 has been shown to interact with SLIT2. Clinical significance This protein is involved in the misfolding of normal prion proteins in the cell membrane to the infectious prion form. In 2015 it was reported that the presence of this protein in exosomes in patients' blood is able to detect early pancreatic cancer with absolute s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
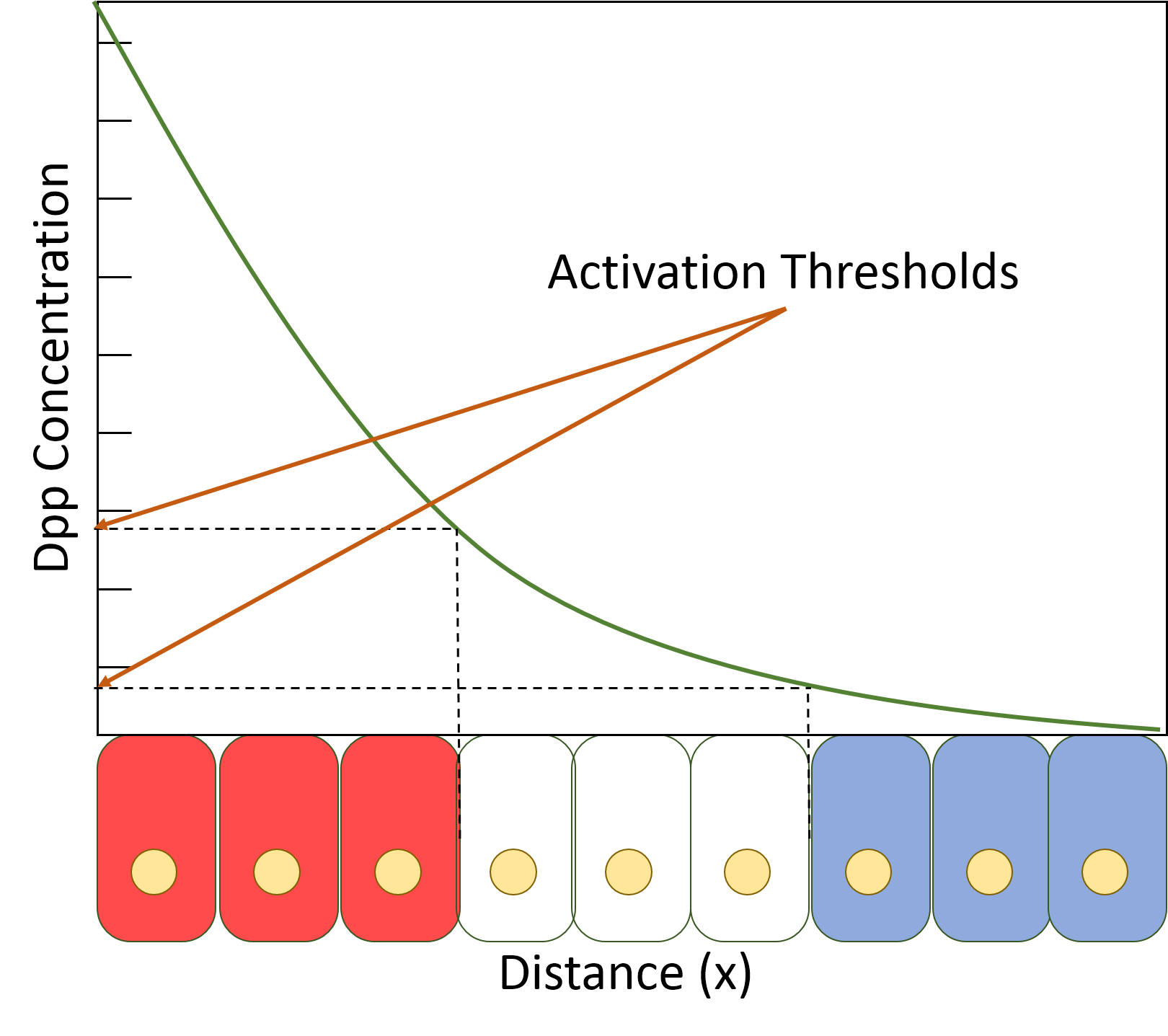
Decapentaplegic
''Decapentaplegic'' (''Dpp'') is a key morphogen involved in the development of the fruit fly ''Drosophila melanogaster'' and is the first validated secreted morphogen. It is known to be necessary for the correct patterning and development of the early ''Drosophila'' embryo and the fifteen imaginal discs, which are tissues that will become limbs and other organs and structures in the adult fly. It has also been suggested that ''Dpp'' plays a role in regulating the growth and size of tissues. Flies with mutations in decapentaplegic fail to form these structures correctly, hence the name (''decapenta''-, fifteen; -''plegic'', paralysis). ''Dpp'' is the ''Drosophila'' homolog of the vertebrate bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs), which are members of the transforming growth factor beta superfamily, TGF-β superfamily, a class of proteins that are often associated with their own specific signaling pathway. Studies of ''Dpp'' in ''Drosophila'' have led to greater understanding of the func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC3
Glypican-3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''GPC3'' gene. The ''GPC3'' gene is located on human X chromosome (Xq26) where the most common gene (Isoform 2, GenBank Accession No.: NP_004475) encodes a 70-kDa core protein with 580 amino acids. Three variants have been detected that encode alternatively spliced forms termed Isoforms 1 (NP_001158089), Isoform 3 (NP_001158090) and Isoform 4 (NP_001158091). Structure and function The protein core of GPC3 consists of two subunits, where the N-terminal subunit has a size of ~40 kDa and the C-terminal subunit is ~30 kDa. Six glypicans (GPC1-6) have been identified in mammals. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC5
Glypican-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPC5'' gene. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. See also * Glypican Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypica ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * {{gene-13-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC4
Glypican-4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GPC4'' gene. Cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans are composed of a membrane-associated protein core substituted with a variable number of heparan sulfate chains. Members of the glypican-related integral membrane proteoglycan family (GRIPS) contain a core protein anchored to the cytoplasmic membrane via a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol linkage. These proteins may play a role in the control of cell division and growth regulation. The GPC4 gene is adjacent to the 3' end of GPC3 and may also play a role in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome. See also * Glypican Glypicans constitute one of the two major families of heparan sulfate proteoglycans, with the other major family being syndecans. Six glypicans have been identified in mammals, and are referred to as GPC1 through GPC6. In ''Drosophila'' two glypica ... References Further reading * * * * * * * External links GeneReviews/NIH/NCBI/UW entry on Sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouse Brain
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus''). Mice are also popular as pets. In some places, certain kinds of Apodemus, field mice are locally common. They are known to invade homes for food and shelter. Mice are typically distinguished from rats by their size. Generally, when a muroid rodent is discovered, its common name includes the term ''mouse'' if it is smaller, or ''rat'' if it is larger. The common terms ''rat'' and ''mouse'' are not Taxonomy (biology), taxonomically specific. Typical mice are classified in the genus ''Mus (genus), Mus'', but the term ''mouse'' is not confined to members of ''Mus'' and can also apply to species from other genera such as the deer mouse, deer mouse (''Peromyscus''). Fancy mouse, Domestic mice sold as pets often differ substantially in size f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hedgehog (cell Signaling)
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway also has roles in the adult. Diseases associated with the malfunction of this pathway include cancer. The Hedgehog signaling pathway is one of the key regulators of animal development and is present in all bilaterians. The pathway takes its name from its polypeptide ligand, an intracellular signaling molecule called Hedgehog (''Hh'') found in fruit flies of the genus '' Drosophila''; fruit fly larvae lacking the ''Hh'' gene are said to resemble hedgehogs. ''Hh'' is one of Drosophila's segment polarity gene products, involved in establishing the basis of the fly body plan. The molecule remains important during later stages of embryogenesis and metamorphosis. Mammals have three Hedgehog homologues, Desert (DHH), Indian (IHH), and Soni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dally (gene)
Dally (division abnormally delayed) is the name of a gene that encodes a HS-modified-protein found in the fruit fly (''Drosophila melanogaster''). The protein has to be processed after being codified, and in its mature form it is composed by 626 amino acids,Uniprot KB forming a proteoglycan rich in heparin sulfate which is anchored to the cell surface via covalent linkage to glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI), so we can define it as a glypican. For its normal biosynthesis it requires sugarless (''sgl''), a gene that encodes an enzyme which plays a critical role in the process of modification of dally. Dally’s function  Dally works as a co-receptor of so ...
Dally works as a co-receptor of so ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GPC2
Glypican 2 (GPC2), also known cerebroglycan, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''GPC2'' gene. The ''GPC2'' gene is at locus 7q22.1 and encodes for a 579 amino acid protein. The C-terminus of GPC2 has the GPI attachment site, at G554, and the N-terminus encodes a signal peptide, from M1 to S24. Multiple GPC2 mRNA transcripts have been identified. ''GPC2-201'' is the isoform overexpressed in pediatric cancers. Tumor-associated exon 3 of GPC2 shows the lowest expression in normal tissues compared with other exons. Function Cerebroglycan is a glycophosphatidylinositol-linked integral membrane heparan sulfate proteoglycan found in the developing nervous system. Cerebroglycan participates in cell adhesion and is thought to regulate the growth and guidance of axons. Cerebroglycan has especially high affinity for laminin-1. Implications in cancer GPC2 has been identified as a therapeutic target in neuroblastoma in two independent studies published by Mitchell Ho's l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson–Golabi–Behmel Syndrome
Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome (SGBS) is a rare inherited congenital disorder that can cause craniofacial, skeletal, vascular, cardiac, and renal abnormalities. There is a high prevalence of cancer associated in those with SGBS which includes wilms tumors, neuroblastoma, tumors of the adrenal gland, liver, lungs and abdominal organs. The syndrome is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. Females that possess one copy of the mutation are considered to be carriers of the syndrome but may still express varying degrees of the phenotype, suffering mild to severe malady. Males experience a higher likelihood of fetal death. Types There are two types of SGBS, each associated with mutations on a different gene: SGBS is also considered to be an overgrowth syndrome (OGS). OGS is characterized by a two to three standard deviation increase in weight, height, or head circumference above the average for sex and age. One of the most noted features of OGS is the increased risk of neopla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |