|
Glycitein
Glycitein is an O-methylated isoflavone which accounts for 5-10% of the total isoflavones in soy food products. Glycitein is a phytoestrogen with weak estrogenic activity, comparable to that of the other soy isoflavones. Glycitin (glycitein 7-''O''-glucoside) can be transformed to glycetein by human intestinal flora. References O-methylated isoflavones {{aromatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-methylated Isoflavone
The O-methylated flavonoids or methoxyflavonoids are flavonoids with methylations on hydroxyl groups (methoxy bonds). O-methylation has an effect on the solubility of flavonoids. Enzymes O-methylated flavonoids formation implies the presence of specific O-methyltransferase (OMT) enzymes which accept a variety of substrates. Those enzymes mediate the O-methylation on a specific hydroxyl group, like on 4' (example in ''Catharanthus roseus'') or 3' (example in rice) positions. Those positions can be Arene substitution patterns, ortho, meta, para and there can be a special 3-O-methyltransferase for the 3-OH position. Calamondin orange (''Citrus mitis'') exhibits all of those activities. Plant enzymes * Apigenin 4'-O-methyltransferase * 8-hydroxyquercetin 8-O-methyltransferase * Isoflavone 4'-O-methyltransferase * Isoflavone 7-O-methyltransferase * Isoliquiritigenin 2'-O-methyltransferase * Isoorientin 3'-O-methyltransferase * Kaempferol 4'-O-methyltransferase * Luteolin O-methyltransfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycitin
Glycitin (glycitein 7-''O''-glucoside) is an isoflavone found in soy, and remains to various degrees in soy products like tofu, soymilk and soy sauce. Although glycitin has its own health associated properties (below), it can be transformed to glycitein by human intestinal flora by the action of beta-glucosidases. Properties Some interesting effects of glycitin include human dermal fibroblast cell proliferation and migration via TGF‐β signaling, glycitin treatment produces anti-photoaging effects such as collagen type I and collagen type III increase at both the mRNA and protein levels. Other noted effects decreased elastase, and decreased β‐galactosidase activation. In conjunction with 4′,6,7-trimethoxyisoflavone (TMF), an isoflavone that promotes fibroblast migration but not proliferation, wound healing and anti-scarring A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
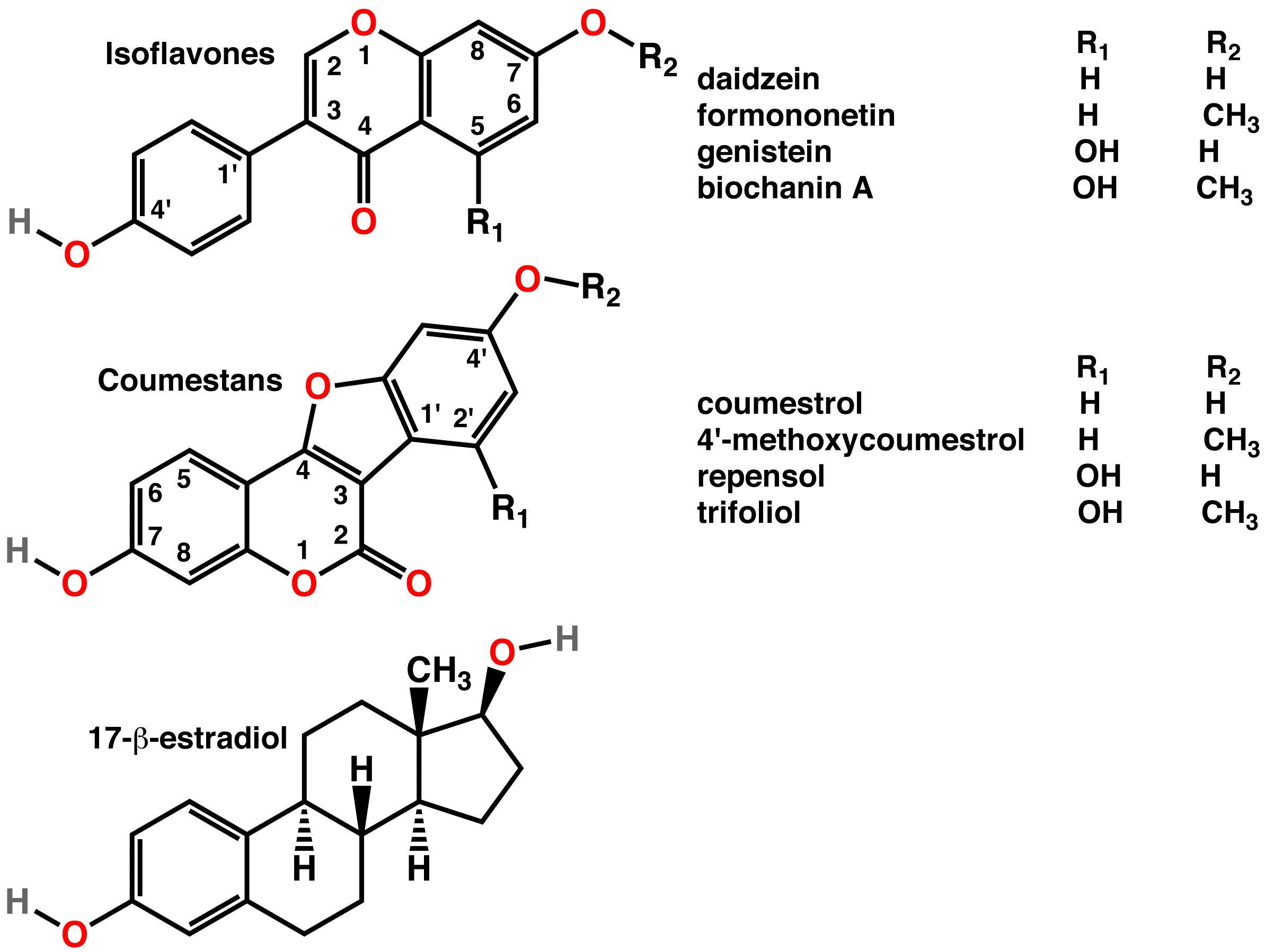
Phytoestrogen
A phytoestrogen is a plant-derived xenoestrogen (a type of estrogen produced by organisms other than humans) not generated within the endocrine system, but consumed by eating plants or manufactured foods. Also called a "dietary estrogen", it is a diverse group of naturally occurring nonsteroidal plant compounds that, because of its structural similarity to estradiol (17-β-estradiol), have the ability to cause both estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects. Phytoestrogens are not essential nutrients because their absence from the diet does not cause a disease, nor are they known to participate in any normal biological function. Common foods containing phytoestrogens are soybeans and soy protein concentrate, miso, tempeh, and tofu. Some soy-based infant formulas manufactured with soy protein contain isoflavones. Its name comes from the Greek ''phyto'' ("plant") and ''estrogen'', the hormone which gives fertility to female mammals. The word "estrus" (Greek οίστρος) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Flora
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses, that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density of any human-associated microbial community studied so far, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. About 55% of the dry mass of feces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |