|
Global Biodiversity
Global biodiversity is the measure of biodiversity on planet Earth and is defined as the total variability of life forms. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates on the number of Earth's current species range from 2 million to 1 trillion, but most estimates are around 11 million species or fewer. About 1.74 million species were databased as of 2018, and over 80 percent have not yet been described. The total amount of DNA base pairs on Earth, as a possible approximation of global biodiversity, is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon). In other related studies, around 1.9 million extant species are believed to have been described currently, but some scientists believe 20% are synonyms, reducing the total valid described species to 1.5 million. In 2013, a study published in Science estimated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Animals
Kingdom commonly refers to: * A Monarchy, monarchic state or realm ruled by a king or queen. ** A monarchic chiefdom, represented or governed by a king or queen. * Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy Kingdom may also refer to: Arts and media Television * Kingdom (British TV series), ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama starring Stephen Fry * Kingdom (American TV series), ''Kingdom'' (American TV series), a 2014 US television drama starring Frank Grillo * Kingdom (South Korean TV series), ''Kingdom'' (South Korean TV series), a 2019 South Korean television series *''Kingdom: Legendary War'', a 2021 South Korean television series * Kingdom (Friday Night Lights), an episode of the TV series Friday Night Lights * Kingdom (Runaways), "Kingdom" (''Runaways''), an episode of ''Runaways'' Music * Kingdom (group), a South Korean boy band * Kingdom (Koda Kumi album), ''Kingdom'' (Koda Kumi album), 2008 * Kingdom (Bilal Hassani album), ''Kingdom'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction Event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are animals that neither develop nor retain a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''spine'' or ''backbone''), which evolved from the notochord. It is a paraphyletic grouping including all animals excluding the chordate subphylum Vertebrata, i.e. vertebrates. Well-known phyla of invertebrates include arthropods, molluscs, annelids, echinoderms, flatworms, cnidarians, and sponges. The majority of animal species are invertebrates; one estimate puts the figure at 97%. Many invertebrate taxa have a greater number and diversity of species than the entire subphylum of Vertebrata. Invertebrates vary widely in size, from 10 μm (0.0004 in) myxozoans to the 9–10 m (30–33 ft) colossal squid. Some so-called invertebrates, such as the Tunicata and Cephalochordata, are actually sister chordate subphyla to Vertebrata, being more closely related to vertebrates than to other invertebrates. This makes the "invertebrates" paraphyletic, so the term has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalochordata
The lancelets ( ), also known as amphioxi (: amphioxus ), consist of 32 described species of somewhat fish-like benthic filter feeding chordates in the subphylum Cephalochordata, class Leptocardii, and family Branchiostomatidae. Lancelets diverged from other chordates during or prior to the Cambrian period. A number of fossil chordates have been suggested to be closely related to lancelets, including '' Pikaia'' and '' Cathaymyrus'' from the Cambrian and '' Palaeobranchiostoma'' from the Permian, but their close relationship to lancelets has been doubted by other authors. Molecular clock analysis suggests that modern lancelets probably diversified much more recently, during the Cretaceous or Cenozoic. They are of interest to Zoologists as lancelets contain many organs and organ systems that are homologous to those of modern fish. Therefore, they provide a number of examples of possible evolutionary exaptation. For example, the gill-slits of lancelets are used for feeding only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
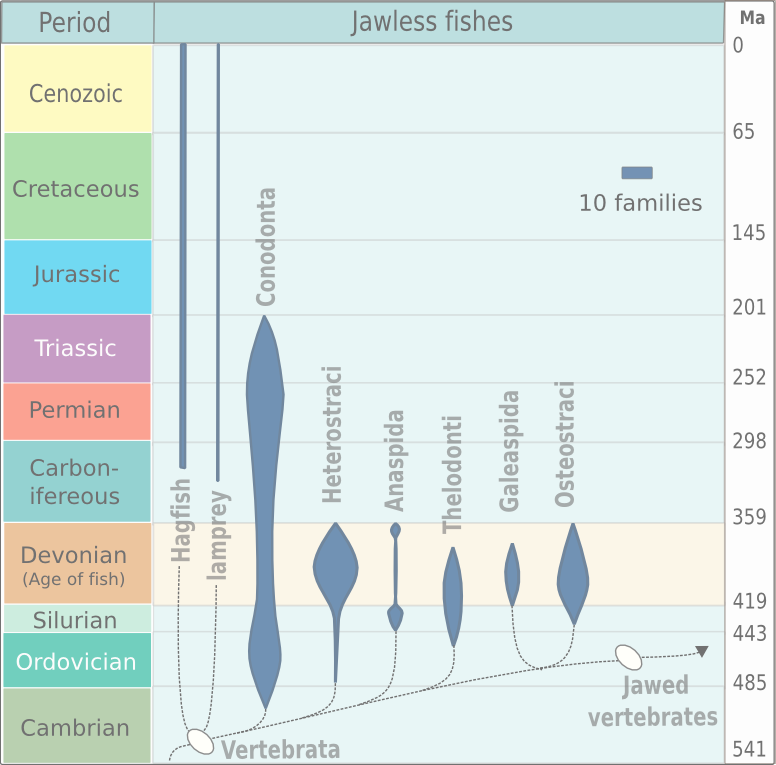
Agnatha
Agnatha (; ) or jawless fish is a paraphyletic infraphylum of animals in the subphylum Vertebrata of the phylum Chordata, characterized by the lack of jaws. The group consists of both extant taxon, living (Cyclostomi, cyclostomes such as hagfishes and lampreys) and Extinction, extinct clades (e.g. conodonts and Cephalaspidomorphi, cephalaspidomorphs, among others). They are sister taxon, sister to vertebrates with jaws known as gnathostomes, who evolution, evolved from jawless ancestors during the early Silurian by developing folding joint, articulations in the first pairs of gill arches. Sequencing, Molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as Embryology, embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that both groups of living agnathans, hagfishes and lampreys, are more closely related to each other than to Gnathostomata, jawed fish, forming the Class (biology), superclass Cyclostomi. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian. Living jawless fish c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fishes
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphibia
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniotic, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all tetrapods, but excluding the amniotes (tetrapods with an amniotic membrane, such as modern reptiles, birds and mammals). All extant (living) amphibians belong to the monophyletic subclass Lissamphibia, with three living orders: Anura (frogs and toads), Urodela (salamanders), and Gymnophiona (caecilians). Evolved to be mostly semiaquatic, amphibians have adapted to inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living in freshwater, wetland or terrestrial ecosystems (such as riparian woodland, fossorial and even arboreal habitats). Their life cycle typically starts out as aquatic larvae with gills known as tadpoles, but some species have developed behavioural adaptations to bypass this. Young amphibians generally undergo metamorphosis from an aquatic larval form with gills to an air-breathi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as commonly defined, are a group of tetrapods with an ectothermic metabolism and Amniotic egg, amniotic development. Living traditional reptiles comprise four Order (biology), orders: Testudines, Crocodilia, Squamata, and Rhynchocephalia. About 12,000 living species of reptiles are listed in the Reptile Database. The study of the traditional reptile orders, customarily in combination with the study of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. Reptiles have been subject to several conflicting Taxonomy, taxonomic definitions. In Linnaean taxonomy, reptiles are gathered together under the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), which corresponds to common usage. Modern Cladistics, cladistic taxonomy regards that group as Paraphyly, paraphyletic, since Genetics, genetic and Paleontology, paleontological evidence has determined that birds (class Aves), as members of Dinosauria, are more closely related to living crocodilians than to other reptiles, and are thus nested among re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight Bird skeleton, skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the common ostrich. There are over 11,000 living species and they are split into 44 Order (biology), orders. More than half are passerine or "perching" birds. Birds have Bird wing, wings whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the Flightless bird, loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemism, endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles and birds, from which their ancestors diverged in the Carboniferous Period over 300 million years ago. Around 6,640 extant species of mammals have been described and divided into 27 orders. The study of mammals is called mammalogy. The largest orders of mammals, by number of species, are the rodents, bats, and eulipotyphlans (including hedgehogs, moles and shrews). The next three are the primates (including humans, monkeys and lemurs), the even-toed ungulates (including pigs, camels, and whales), and the Carnivora (including cats, dogs, and seals). Mammals are the only living members of Synapsida; this clade, together with Sauropsida (reptiles and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordates
A chordate ( ) is a bilaterian animal belonging to the phylum Chordata ( ). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics ( synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post- anal tail. In addition to the morphological characteristics used to define chordates, analysis of genome sequences has identified two conserved signature indels (CSIs) in their proteins: cyclophilin-like protein and inner mitochondrial membrane protease ATP23, which are exclusively shared by all vertebrates, tunicates and cephalochordates. These CSIs provide molecular means to reliably distinguish chordates from all other animals. Chordates are divided into three subphyla: Vertebrata (fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals), whose notochords are replaced by a cartilaginous/ bony axial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |