|
Glitazone
The thiazolidinediones , abbreviated as TZD, also known as glitazones after the prototypical drug ciglitazone, are a class of heterocyclic compounds consisting of a five-membered C3NS ring. The term usually refers to a family of drugs used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 that were introduced in the late 1990s. As of 2024, there are two FDA-approved drugs in this class, pioglitazone and rosiglitazone. Mechanism of action Thiazolidinediones or TZDs act by activating PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors), a group of nuclear receptors, specific for ''PPARγ'' (PPAR-gamma, PPARG). They are thus the PPARG agonists subset of PPAR agonists. The endogenous ligands for these receptors are free fatty acids (FFAs) and eicosanoids. When activated, the receptor binds to DNA in complex with the retinoid X receptor (RXR), another nuclear receptor, increasing transcription of a number of specific genes and decreasing transcription of others. The main effect of expre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosiglitazone
Rosiglitazone (trade name Avandia) is an antidiabetic drug in the thiazolidinedione class. It works as an insulin sensitizer, by binding to the PPAR in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin. It is marketed by the pharmaceutical company GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) as a stand-alone drug or for use in combination with metformin or with glimepiride. First released in 1999, annual sales peaked at approximately $2.5-billion in 2006; however, following a meta-analysis in 2007 that linked the drug's use to an increased risk of heart attack, sales plummeted to just $9.5-million in 2012. The drug's patent expired in 2012. It was patented in 1987 and approved for medical use in 1999. Despite rosiglitazone's effectiveness at decreasing blood sugar in type 2 diabetes mellitus, its use decreased dramatically as studies showed apparent associations with increased risks of heart attacks and death. Adverse effects alleged to be caused by rosiglitazone were the subject of over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioglitazone
Pioglitazone, sold under the brand name Actos among others, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It may be used with metformin, a sulfonylurea, or insulin. Use is recommended together with exercise and diet. It is not recommended in type 1 diabetes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include headaches, muscle pains, inflammation of the throat, and swelling. Serious side effects may include bladder cancer, low blood sugar, heart failure, and osteoporosis. Use is not recommended in pregnancy or breastfeeding. It is in the thiazolidinedione (TZD) class and works by improving sensitivity of tissues to insulin. Pioglitazone was patented in 1985, and came into medical use in 1999. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 120th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. It was withdrawn in France and Germany in 2011. Medical uses Pioglitazone is used to lower blood glucose lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazolidinedione Functional Group
The thiazolidinediones , abbreviated as TZD, also known as glitazones after the prototypical drug ciglitazone, are a class of heterocyclic compounds consisting of a five-membered C3NS ring. The term usually refers to a family of drugs used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2 that were introduced in the late 1990s. As of 2024, there are two FDA-approved drugs in this class, pioglitazone and rosiglitazone. Mechanism of action Thiazolidinediones or TZDs act by activating PPARs (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors), a group of nuclear receptors, specific for '' PPARγ'' (PPAR-gamma, PPARG). They are thus the PPARG agonists subset of PPAR agonists. The endogenous ligands for these receptors are free fatty acids (FFAs) and eicosanoids. When activated, the receptor binds to DNA in complex with the retinoid X receptor (RXR), another nuclear receptor, increasing transcription of a number of specific genes and decreasing transcription of others. The main effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciglitazone
Ciglitazone ( INN) is a thiazolidinedione. Developed by Takeda Pharmaceuticals in the early 1980s, it is considered the prototypical compound for the thiazolidinedione class. Ciglitazone was never used as a medication, but it sparked interest in the effects of thiazolidinediones. Several analogues were later developed, some of which—such as pioglitazone and troglitazone—made it to the market. Ciglitazone significantly decreases VEGF production by human granulosa cells in an in vitro study, and may potentially be used in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Ciglitazone is a potent and selective PPARγ ligand. It binds to the PPARγ ligand-binding domain with an EC50 ] Half maximal effective concentration (EC50) is a measure of the concentration of a drug, antibody or toxicant which induces a stimulus–response model, biological response halfway between the baseline and maximum after a specified exposure tim ... of 3.0 μM. Ciglitazone is active in vivo as an anti-hyperg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PPARγ
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ or PPARG), also known as the glitazone reverse insulin resistance receptor, or NR1C3 (nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group C, member 3) is a type II nuclear receptor functioning as a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the ''PPARG'' gene. Tissue distribution PPARG is mainly present in adipose tissue, colon and macrophages. Two isoforms of PPARG are detected in the human and in the mouse: PPAR-γ1 (found in nearly all tissues except muscle) and PPAR-γ2 (mostly found in adipose tissue and the intestine). Gene expression This gene encodes a member of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) subfamily of nuclear receptors. PPARs form heterodimers with retinoid X receptors (RXRs) and these heterodimers regulate transcription of various genes. Three subtypes of PPARs are known: PPAR-alpha, PPAR-delta, and PPAR-gamma. The protein encoded by this gene is PPAR-gamma and is a regulator of adipocyte dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
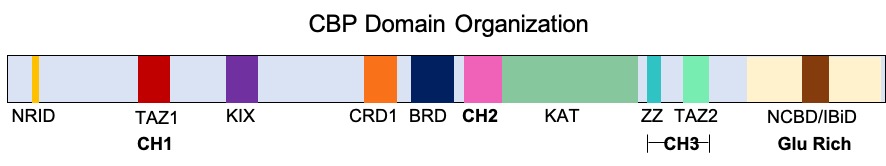
CREB Binding Protein
CREB-binding protein, also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, (where CREB is cAMP response element-binding protein) is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies including colorectal cancer as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Dimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or protein multimer, multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually Non-covalent interaction, non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", ''wikt:di-#Prefix, di-'' + ''wikt:-mer#Suffix, -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein IKBKG, NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hormone Response Element
''Response elements'' are short sequences of DNA within a gene promoter or enhancer region that are able to bind specific transcription factors and regulate transcription of genes. Under conditions of stress, a transcription activator protein binds to the response element and stimulates transcription. If the same response element sequence is located in the control regions of different genes, then these genes will be activated by the same stimuli, thus producing a coordinated response. Hormone response element A hormone response element (HRE) is a short sequence of DNA within the promoter of a gene, that is able to bind to a specific hormone receptor complex and therefore regulate transcription. The sequence is most commonly a pair of inverted repeats separated by three nucleotides, which also indicates that the receptor binds as a dimer. Specifically, HRE responds to steroid hormones, as the activated steroid receptor is the transcription factor binding HRE. This regulates the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coactivator (genetics)
A coactivator is a type of transcriptional coregulator that binds to an activator (a transcription factor) to increase the rate of transcription of a gene or set of genes. The activator contains a DNA binding domain that binds either to a DNA promoter site or a specific DNA regulatory sequence called an enhancer. Binding of the activator-coactivator complex increases the speed of transcription by recruiting general transcription machinery to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. The use of activators and coactivators allows for highly specific expression of certain genes depending on cell type and developmental stage. Some coactivators also have histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity. HATs form large multiprotein complexes that weaken the association of histones to DNA by acetylating the N-terminal histone tail. This provides more space for the transcription machinery to bind to the promoter, therefore increasing gene expression. Activators are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 1
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1), also called steroid receptor coactivator-1 (SRC-1), is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor–interacting domains and possesses intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. It is encoded by the gene ''NCOA1''. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promoter sites by ligand-activated nuclear receptors. NCOA1, in turn, acylates histones, which makes downstream DNA more accessible to transcription. Hence, NCOA1 assists nuclear receptors in the upregulation of DNA expression as a coactivator. Interactions Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 possesses a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain and has been shown to interact with: * Androgen receptor, * C-Fos, * C-jun, * CIITA, * CREB-binding protein, * Cyclin D1, * Estrogen receptor alpha, * Glucocorticoid receptor, * NFKB1, * PCAF, * PPARGC1A, * Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, * SNW1, * STAT3 Signal transducer and activator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cell (biology), cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesis. In cell culture, adipocyte progenitors can also form osteoblasts, myocytes and other cell types. There are two types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT), which are also known as white and brown fat, respectively, and comprise two types of fat cells. Structure White fat cells White fat cells contain a single large lipid droplet surrounded by a layer of cytoplasm, and are known as unilocular. The Cell nucleus, nucleus is flattened and pushed to the periphery. A typical fat cell is 0.1 mm in diameter with some being twice that size, and others half that size. However, these numerical estimates of fat cell size depend largely on the measurement method and the location of the adi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |