|
Glaucine
Glaucine (also known as 1,2,9,10-tetramethoxyaporphine, bromcholitin, glauvent, tusidil, and tussiglaucin) is an aporphine alkaloid found in several different plant species in the family Papaveraceae, such as '' Glaucium flavum'', '' Glaucium oxylobum'', and '' Corydalis yanhusuo'', and in other plants such as '' Croton lechleri'' in the family Euphorbiaceae. It has bronchodilator, neuroleptic and antiinflammatory effects, acting as a PDE4 inhibitor and calcium channel blocker, and is used medically as an antitussive in some countries. TLRs plays role in its anti inflammatory effects. Glaucine may produce side effects such as sedation, fatigue, and a hallucinogenic effect characterised by colourful visual images, and has been detected as a novel psychoactive drug. In a 2019 publication,Heng, HL, Chee, CF, Thy, CK, et al. In vitro functional evaluation of isolaureline, dicentrine and glaucine enantiomers at 5‐HT2 and α1 receptors. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2019; 93: 132– 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucium Flavum
''Glaucium flavum'', the yellow horned poppy, yellow hornpoppy or sea poppy, is a summer flowering plant in the family Papaveraceae. It is native to Europe, Northern Africa, Macaronesia and temperate zones in Western Asia. The plant grows on the seashore and is never found inland. All parts of the plant, including the seeds, are toxic. It is classed as a noxious weed in some areas of North America, where it is an introduced species. It is grown in gardens as a short-lived perennial but usually grown as a biennial plant, biennial. Description It has thick, leathery deeply segmented, wavy, bluish-grey leaves, which are coated in a layer of water-retaining wax. The sepal, petals and stamen have a similar structure and form to the Papaver rhoeas, red poppy (''Papaver rhoeas''), except the sepals are not hairy. It grows up to tall, on branched, grey stems. It blooms in summer, between June and October. It has bright yellow or orange flowers, that are across. Later, it produces a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aporphine Alkaloids
Aporphine alkaloids are naturally occurring chemical compounds from the group of alkaloids. After the benzylisoquinoline alkaloids they are the second largest group of isoquinoline alkaloids. At least 85 aporphine alkaloids have been isolated from plants of 15 families. The best known representative is apomorphine. The aporphine alkaloids are of interest mainly because of their similarity to morphine. Occurrence The aporphine alkaloids are most commonly found in plants. For example, isoboldine can be found in the plants in the genera ''Beilschmiedia'', ''Nandina'' (''Nandina domestica''), ''Glaucium'' (horn poppy), and other plants. As the name suggests, glaucine was first found in the horn poppy and usually the name of the alkaloids is derived from the plants in which they were first found. Corydin as a further representative of the aporphine alkaloids is found in ''Corydalis'' (larkspurs) ''Dicentra'' (heart flowers), and also in the horn poppy. Examples Apoglaziovin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2A Receptor
The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor, 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and functions as a GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a cell surface receptor that activates multiple intracellular signalling cascades. Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2A receptor is coupled to the Gq protein, Gq/G11 signaling pathway. It is the primary excitatory receptor subtype among the serotonin-responsive GPCRs. The 5-HT2A receptor was initially noted for its central role as the primary target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. It later regained research prominence when found to mediate, at least in part, the effects of many antipsychotic drugs, particularly atypical antipsychotic, atypical antipsychotics. Downregulation of post-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors is an adaptive response triggered by chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics. Elevated 5-HT2A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corydalis Yanhusuo
''Corydalis yanhusuo'' is a plant species in the genus ''Corydalis''. The Chinese name for ''Corydalis yanhusuo'' is ''yan hu suo'' (). The Japanese common name is engosaku (エンゴサク) and the Korean common name is hyeonhosaek (현호색). English common names include yanhusuo, corydalis, and Asian corydalis. The tuber of this plant, frequently mislabeled as the root, is an important therapeutic agent in traditional Chinese medicine. It is native to high-altitude grasslands across China including in the provinces of Anhui, Henan, Hubei, Hunan, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang, but is more widely cultivated. Description According to the Flora of China, this perennial herbaceous plant produces 5 to 15 purple-blue tubular flowers in clusters that curve out at the opening. The yellow, round tubers are up to in diameter. History Yanhusuo is first mentioned in ''Ben Cao Shi Yi'' (''Omissions from the Materia Medica''), written by Chen Cang-Qi in 720 CE. Chemical compounds The alkaloid de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union, Australia, and New Zealand, as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these designer drugs were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine Receptor
Dopamine receptors are a class of G protein-coupled receptors that are prominent in the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). Dopamine receptors activate different effectors through not only G-protein coupling, but also signaling through different protein (dopamine receptor-interacting proteins) interactions. The neurotransmitter dopamine is the primary endogenous ligand for dopamine receptors. Dopamine receptors are implicated in many neurological processes, including motivational and incentive salience, cognition, memory, learning, and fine motor control, as well as modulation of neuroendocrine signaling. Abnormal dopamine receptor signaling and dopaminergic nerve function is implicated in several neuropsychiatric disorders. Thus, dopamine receptors are common neurologic drug targets; antipsychotics are often dopamine receptor antagonists while psychostimulants are typically indirect agonists of dopamine receptors. Subtypes The existence of multiple types of receptors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronchus
A bronchus ( ; : bronchi, ) is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. These are the widest bronchi, and enter the right lung, and the left lung at each hilum. The main bronchi branch into narrower secondary bronchi or lobar bronchi, and these branch into narrower tertiary bronchi or segmental bronchi. Further divisions of the segmental bronchi are known as 4th order, 5th order, and 6th order segmental bronchi, or grouped together as subsegmental bronchi. The bronchi, when too narrow to be supported by cartilage, are known as bronchioles. No gas exchange takes place in the bronchi. Structure The trachea (windpipe) divides at the carina into two main or primary bronchi, the left bronchus and the right bronchus. The carina of the trachea is located at the level of the sternal angle and the fifth thoracic ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
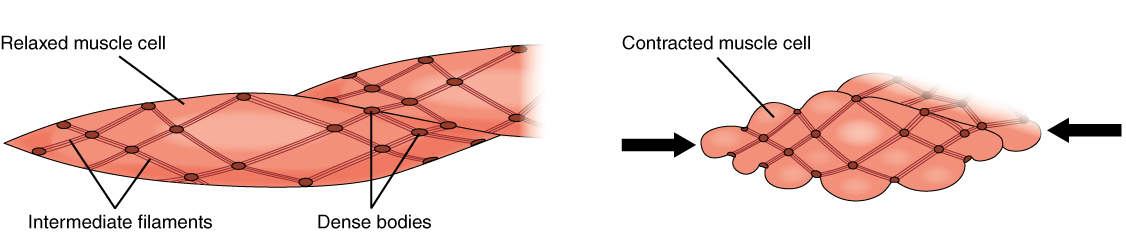
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-type Calcium Channels
The L-type calcium channel (also known as the dihydropyridine channel, or DHP channel) is part of the high-voltage activated family of voltage-dependent calcium channel. "L" stands for long-lasting referring to the length of activation. This channel has four isoforms: Cav1.1, Cav1.2, Cav1.3, and Cav1.4. L-type calcium channels are responsible for the excitation-contraction coupling of skeletal, smooth, cardiac muscle, and for aldosterone secretion in endocrine cells of the adrenal cortex. They are also found in neurons, and with the help of L-type calcium channels in endocrine cells, they regulate neurohormones and neurotransmitters. They have also been seen to play a role in gene expression, mRNA stability, neuronal survival, ischemic-induced axonal injury, synaptic efficacy, and both activation and deactivation of other ion channels. In cardiac myocytes, the L-type calcium channel passes inward Ca2+ current (ICaL) and triggers calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzothiazepine
Thiazepines are substituted thiepins, with a nitrogen replacing a carbon in the seven-membered heterocyclic compound. Depending on the location of the nitrogen, one distinguishes 1,3-thiazepine and 1,4-thiazepine. Benzothiazepines have a single benzene attached to the ring, while dibenzothiazepines have two. Diltiazem, a benzothiazepine, is a calcium channel blocker intermediate in properties between verapamil and the dihydropyridines. It is used to treat variant angina (Prinzmetal's angina Variant angina, also known as Prinzmetal angina, vasospastic angina, angina inversa, coronary vessel spasm, or coronary artery vasospasm, is a syndrome typically consisting of angina (cardiac chest pain). Variant angina differs from stable angin ...), either naturally occurring or drug-induced and stable angina. References External links * {{heterocyclic-stub Thiazepines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |