|
Geocentric Latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east-west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and longitude are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or '' normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of The Earth Into Gauss-Krueger Zones - Globe
Division may refer to: Mathematics *Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication *Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division Military *Division (military), a formation typically consisting of 10,000 to 25,000 troops **Divizion, a subunit in some militaries *Division (naval), a collection of warships Science *Cell division, the process in which biological cells multiply *Continental divide, the geographical term for separation between watersheds *Division (taxonomy), used differently in botany and zoology *Division (botany), a taxonomic rank for plants or fungi, equivalent to phylum in zoology *Division (horticulture), a method of vegetative plant propagation, or the plants created by using this method * Division, a medical/surgical operation involving cutting and separation, see ICD-10 Procedure Coding System Technology *Beam compass, a compass with a beam and sliding sockets for drawing and dividing circles larger than those made by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reference Ellipsoid
An Earth ellipsoid or Earth spheroid is a mathematical figure approximating the Earth's form, used as a reference frame for computations in geodesy, astronomy, and the geosciences. Various different ellipsoids have been used as approximations. It is a spheroid (an ellipsoid of revolution) whose minor axis (shorter diameter), which connects the geographical North Pole and South Pole, is approximately aligned with the Earth's axis of rotation. The ellipsoid is defined by the ''equatorial axis'' () and the ''polar axis'' (); their radial difference is slightly more than 21 km, or 0.335% of (which is not quite 6,400 km). Many methods exist for determination of the axes of an Earth ellipsoid, ranging from meridian arcs up to modern satellite geodesy or the analysis and interconnection of continental geodetic networks. Amongst the different set of data used in national surveys are several of special importance: the Bessel ellipsoid of 1841, the international Hayfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
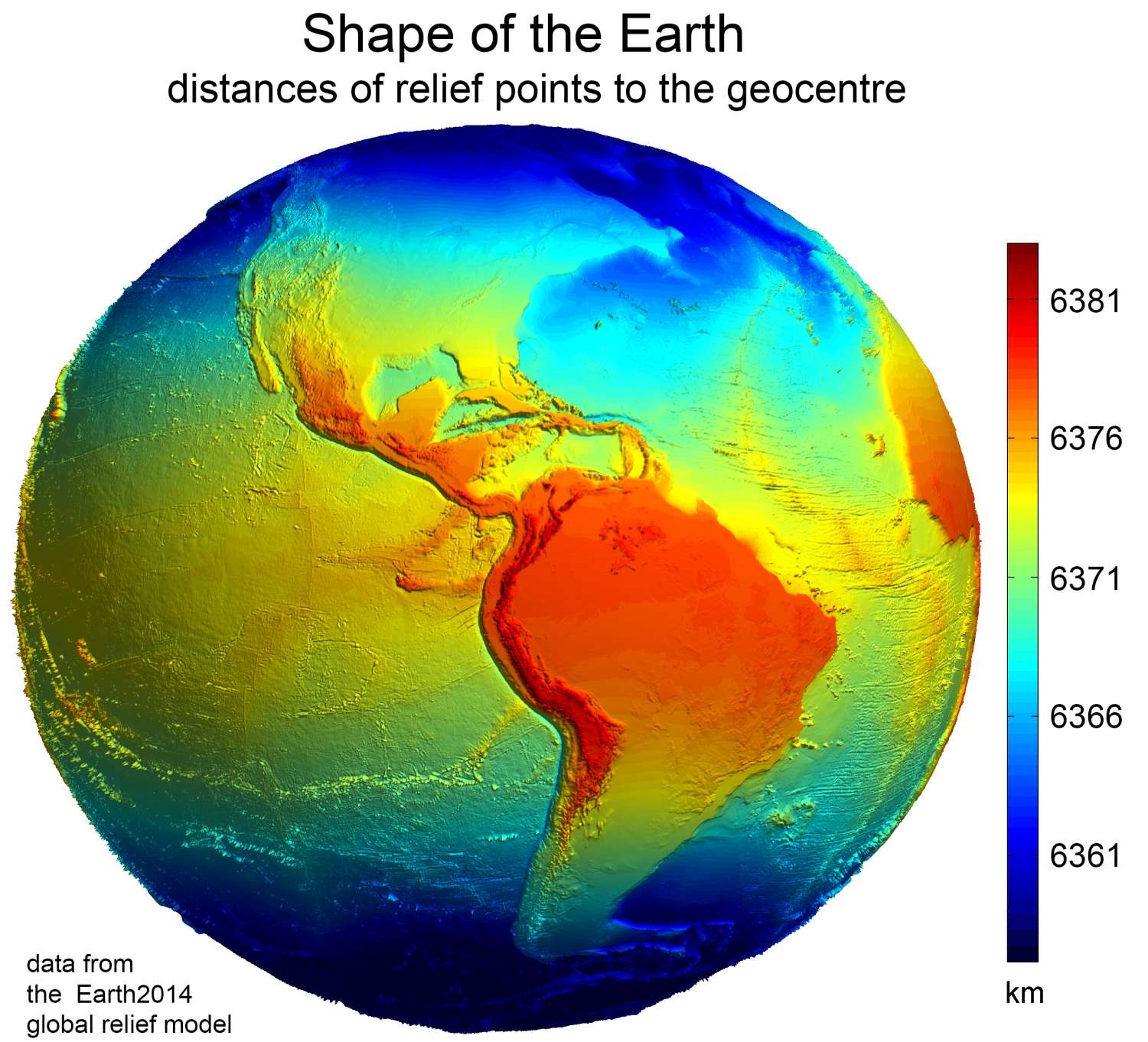
Figure Of The Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is satisfactory for geography, astronomy and many other purposes. Several models with greater accuracy (including ellipsoid) have been developed so that coordinate systems can serve the precise needs of navigation, surveying, cadastre, land use, and various other concerns. Motivation Earth's topographic surface is apparent with its variety of land forms and water areas. This topographic surface is generally the concern of topographers, hydrographers, and geophysicists. While it is the surface on which Earth measurements are made, mathematically modeling it while taking the irregularities into account would be extremely complicated. The Pythagorean concept of a spherical Earth offers a simple surface that is easy to deal with mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodolite
A theodolite () is a precision optical instrument for measuring angles between designated visible points in the horizontal and vertical planes. The traditional use has been for land surveying, but it is also used extensively for building and infrastructure construction, and some specialized applications such as meteorology and rocket launching. It consists of a moveable telescope mounted so it can rotate around horizontal and vertical axes and provide angular readouts. These indicate the orientation of the telescope, and are used to relate the first point sighted through the telescope to subsequent sightings of other points from the same theodolite position. These angles can be measured with accuracies down to microradians or seconds of arc. From these readings a plan can be drawn, or objects can be positioned in accordance with an existing plan. The modern theodolite has evolved into what is known as a total station where angles and distances are measured electronicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian Altitude
{{inline, date=June 2024 Meridian altitude is a method of celestial navigation to determine the latitude of an observer. It notes the altitude angle of an astronomical object above the horizon at culmination. Principle Meridian altitude is the simplest calculation of celestial navigation. An observer determines their latitude by measuring the altitude of an astronomical object at the time of its meridian transit. A meridian is the imaginary plane running north–south and through the zenith, nadir, and celestial poles. This is usually done with the equinox Sun at solar noon to determine the observer's latitude, but can be done with any celestial object. Solar noon is the time when the Sun crosses the meridian. For example, imagine that the equinox Sun is overhead (at the zenith) at a point on the Equator (latitude 0°), and Observer A is standing at this point – the subsolar point. If he were to measure the height of the Sun above the horizon with a sextant, he would find ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space or on the surface of the Earth without relying solely on estimated positional calculations, commonly known as dead reckoning. Celestial navigation is performed without using satellite navigation or other similar modern electronic or digital positioning means. Celestial navigation uses "sights," or timed angular measurements, taken typically between a celestial body (e.g., the Sun, the Moon, a planet, or a star) and the visible horizon. Celestial navigation can also take advantage of measurements between celestial bodies without reference to the Earth's horizon, such as when the Moon and other selected bodies are used in the practice called "lunars" or the Lunar distance (navigation), lunar distance method, used for determining precise time when time is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Latitude
The Greeks studied the results of the measurements of latitude by the explorer Pytheas who voyaged to Britain and beyond, as far as the Arctic Circle (observing the midnight sun), in 325 BC. They used several methods to measure latitude, including the height of the Sun above the horizon at midday, measured using a gnōmōn (a word that originally meant an interpreter or judge); the length of the day at the summer solstice, and the elevation of the Sun at winter solstice. The Greek Marinus of Tyre (CE 70–130) was the first to assign a latitude and longitude to every place on his maps. From the late 9th century CE, the Arabian Kamal was used in equatorial regions, to measure the height of Polaris above the horizon. This instrument could only be used in latitudes where Polaris is close to the horizon. The mariner's astrolabe which gives the angle of the Sun from the horizon at noon, or the angle of a known star at night, was used from around the 15th to the 17th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetographic Latitude
A planetary coordinate system (also referred to as ''planetographic'', ''planetodetic'', or ''planetocentric'') is a generalization of the geographic, geodetic, and the geocentric coordinate systems for planets other than Earth. Similar coordinate systems are defined for other solid celestial bodies, such as in the ''selenographic coordinates'' for the Moon. The coordinate systems for almost all of the solid bodies in the Solar System were established by Merton E. Davies of the Rand Corporation, including Mercury, Venus, Mars, the four Galilean moons of Jupiter, and Triton, the largest moon of Neptune. A planetary datum is a generalization of geodetic datums for other planetary bodies, such as the Mars datum; it requires the specification of physical reference points or surfaces with fixed coordinates, such as a specific crater for the reference meridian or the best-fitting equigeopotential as zero-level surface. Longitude The longitude systems of most of those bodies wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Normal
In geometry, a normal is an object (e.g. a line, ray, or vector) that is perpendicular to a given object. For example, the normal line to a plane curve at a given point is the infinite straight line perpendicular to the tangent line to the curve at the point. A normal vector is a vector perpendicular to a given object at a particular point. A normal vector of length one is called a unit normal vector or normal direction. A curvature vector is a normal vector whose length is the curvature of the object. Multiplying a normal vector by results in the opposite vector, which may be used for indicating sides (e.g., interior or exterior). In three-dimensional space, a surface normal, or simply normal, to a surface at point is a vector perpendicular to the tangent plane of the surface at . The vector field of normal directions to a surface is known as '' Gauss map''. The word "normal" is also used as an adjective: a line ''normal'' to a plane, the ''normal'' component of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Needles
The Needles are a row of three stacks of chalk that rise about out of the sea off the western extremity of the Isle of Wight in the English Channel, United Kingdom, close to Alum Bay and Scratchell's Bay, and part of Totland, the westernmost civil parish of the Isle of Wight. The Needles Lighthouse stands at the outer, western end of the formation. Built in 1859, it has been automated since 1994. The waters and adjoining seabed form part of the Needles Marine Conservation Zone and the Needles along with the shore and heath above are part of the Headon Warren and West High Down Site of Special Scientific Interest. The formation takes its name from a fourth needle-shaped pillar called Lot's wife, which collapsed in a storm in 1764. The remaining rocks are not at all needle-like, but the name has stuck. The Needles were featured on the BBC Two TV programme '' Seven Natural Wonders'' (2005) as one of the wonders of Southern England. During Storm Eunice on 18 February ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decimal Degrees
Decimal degrees (DD) is a notation for expressing latitude and longitude geographic coordinates as decimal fractions of a degree. DD are used in many geographic information systems (GIS), web mapping applications such as OpenStreetMap, and GPS devices. Decimal degrees are an alternative to using degrees-minutes-seconds ( DMS) notation. As with latitude and longitude, the values are bounded by ±90° and ±180° respectively. Positive latitudes are north of the equator, negative latitudes are south of the equator. Positive longitudes are east of the Prime Meridian; negative longitudes are west of the Prime Meridian. Latitude and longitude are usually expressed in that sequence, latitude before longitude. The abbreviation LLhas been used in the scientific literature with locations in texts being identified as a tuple within square brackets, for example 4.5798, −3.5820 The appropriate decimal places are used, negative values are given using a hyphen-minus character. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcminute
A minute of arc, arcminute (abbreviated as arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a degree. Since one degree is of a turn, or complete rotation, one arcminute is of a turn. The nautical mile (nmi) was originally defined as the arc length of a minute of latitude on a spherical Earth, so the actual Earth's circumference is very near . A minute of arc is of a radian. A second of arc, arcsecond (abbreviated as arcsec), or arc second, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of a minute of arc, of a degree, of a turn, and (about ) of a radian. These units originated in Babylonian astronomy as sexagesimal (base 60) subdivisions of the degree; they are used in fields that involve very small angles, such as astronomy, optometry, ophthalmology, optics, navigation, land surveying, and marksmanship. To express even smaller angles, standard SI prefixes can be employed; the milliarcse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |