|
Gensim
Gensim is an open-source library for unsupervised topic modeling, document indexing, retrieval by similarity, and other natural language processing functionalities, using modern statistical machine learning. Gensim is implemented in Python and Cython for performance. Gensim is designed to handle large text collections using data streaming and incremental online algorithms, which differentiates it from most other machine learning software packages that target only in-memory processing. Main Features Gensim includes streamed parallelized implementations of fastText, word2vec and doc2vec algorithms, as well as latent semantic analysis (LSA, LSI, SVD), non-negative matrix factorization (NMF), latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA), tf-idf and random projections. Some of the novel online algorithms in Gensim were also published in the 2011 PhD dissertation ''Scalability of Semantic Analysis in Natural Language Processing'' of Radim Řehůřek, the creator of Gensim. Uses of Gensi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Word2vec
Word2vec is a technique in natural language processing (NLP) for obtaining vector representations of words. These vectors capture information about the meaning of the word based on the surrounding words. The word2vec algorithm estimates these representations by modeling text in a large corpus. Once trained, such a model can detect synonymous words or suggest additional words for a partial sentence. Word2vec was developed by Tomáš Mikolov, Kai Chen, Greg Corrado, Ilya Sutskever and Jeff Dean at Google, and published in 2013. Word2vec represents a word as a high-dimension vector of numbers which capture relationships between words. In particular, words which appear in similar contexts are mapped to vectors which are nearby as measured by cosine similarity. This indicates the level of semantic similarity between the words, so for example the vectors for ''walk'' and ''ran'' are nearby, as are those for "but" and "however", and "Berlin" and "Germany". Approach Word2vec is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Topic Model
In statistics and natural language processing, a topic model is a type of statistical model for discovering the abstract "topics" that occur in a collection of documents. Topic modeling is a frequently used text-mining tool for discovery of hidden semantic structures in a text body. Intuitively, given that a document is about a particular topic, one would expect particular words to appear in the document more or less frequently: "dog" and "bone" will appear more often in documents about dogs, "cat" and "meow" will appear in documents about cats, and "the" and "is" will appear approximately equally in both. A document typically concerns multiple topics in different proportions; thus, in a document that is 10% about cats and 90% about dogs, there would probably be about 9 times more dog words than cat words. The "topics" produced by topic modeling techniques are clusters of similar words. A topic model captures this intuition in a mathematical framework, which allows examining a set o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
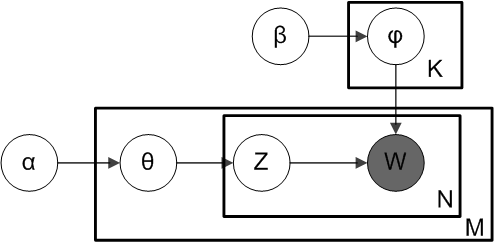
Latent Dirichlet Allocation
In natural language processing, latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) is a Bayesian network (and, therefore, a generative statistical model) for modeling automatically extracted topics in textual corpora. The LDA is an example of a Bayesian topic model. In this, observations (e.g., words) are collected into documents, and each word's presence is attributable to one of the document's topics. Each document will contain a small number of topics. History In the context of population genetics, LDA was proposed by J. K. Pritchard, M. Stephens and P. Donnelly in 2000. LDA was applied in machine learning by David Blei, Andrew Ng and Michael I. Jordan in 2003. Overview Population genetics In population genetics, the model is used to detect the presence of structured genetic variation in a group of individuals. The model assumes that alleles carried by individuals under study have origin in various extant or past populations. The model and various inference algorithms allow sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latent Semantic Analysis
Latent semantic analysis (LSA) is a technique in natural language processing, in particular distributional semantics, of analyzing relationships between a set of documents and the terms they contain by producing a set of concepts related to the documents and terms. LSA assumes that words that are close in meaning will occur in similar pieces of text (the distributional hypothesis). A matrix containing word counts per document (rows represent unique words and columns represent each document) is constructed from a large piece of text and a mathematical technique called singular value decomposition (SVD) is used to reduce the number of rows while preserving the similarity structure among columns. Documents are then compared by cosine similarity between any two columns. Values close to 1 represent very similar documents while values close to 0 represent very dissimilar documents. An information retrieval technique using latent semantic structure was patented in 1988 by Scott D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Science Software
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * ''Free'' (film), a 2001 American dramed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gitter
Gitter is an open-source instant messaging and chat room system for developers and users of GitLab and GitHub repositories. Gitter is provided as software as a service, with a free option providing all basic features and the ability to create a single private chat room, and paid subscription options for individuals and organisations, which allows them to create arbitrary numbers of private chat rooms. Individual chat rooms can be created for individual git repositories on GitHub. Chatroom privacy follows the privacy settings of the associated GitHub repository: thus, a chatroom for a private (i.e. members-only) GitHub repository is also private to those with access to the repository. A graphical badge linking to the chat room can then be placed in the git repository's README file, bringing it to the attention of all users and developers of the project. Users can chat in the chat rooms, or access private chat rooms for repositories they have access to, by logging into Gitter via G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Google Groups
Google Groups is a service from Google that provides discussion groups for people sharing common interests. Until February 2024, the Groups service also provided a gateway to Usenet newsgroups, both reading and posting to them, via a shared user interface. In addition to accessing Google Groups, registered users can also set up mailing list archives for e-mail lists that are hosted elsewhere. Google Groups became operational in February 2001, following Google's acquisition of Deja's Usenet archive. Deja News had been operational since March 1995. Google Groups allows any user to freely conduct and access threaded discussions, via either a web interface or e-mail. There are at least two kinds of discussion groups: forums specific to Google Groups (like mailing lists) and Usenet groups, accessible by NNTP, for which Google Groups acts as gateway and unofficial archive. The Google Groups archive of Usenet newsgroup postings dates back to 1981. On December 15, 2023, Google annou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
GitHub
GitHub () is a Proprietary software, proprietary developer platform that allows developers to create, store, manage, and share their code. It uses Git to provide distributed version control and GitHub itself provides access control, bug tracking system, bug tracking, software feature requests, task management, continuous integration, and wikis for every project. Headquartered in California, GitHub, Inc. has been a subsidiary of Microsoft since 2018. It is commonly used to host open source software development projects. GitHub reported having over 100 million developers and more than 420 million Repository (version control), repositories, including at least 28 million public repositories. It is the world's largest source code host Over five billion developer contributions were made to more than 500 million open source projects in 2024. About Founding The development of the GitHub platform began on October 19, 2005. The site was launched in April 2008 by Tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Locality-sensitive Hashing
In computer science, locality-sensitive hashing (LSH) is a fuzzy hashing technique that hashes similar input items into the same "buckets" with high probability. (The number of buckets is much smaller than the universe of possible input items.) Since similar items end up in the same buckets, this technique can be used for data clustering and nearest neighbor search. It differs from conventional hashing techniques in that hash collisions are maximized, not minimized. Alternatively, the technique can be seen as a way to reduce the dimensionality of high-dimensional data; high-dimensional input items can be reduced to low-dimensional versions while preserving relative distances between items. Hashing-based approximate nearest-neighbor search algorithms generally use one of two main categories of hashing methods: either data-independent methods, such as locality-sensitive hashing (LSH); or data-dependent methods, such as locality-preserving hashing (LPH). Locality-preserving hashin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Non-negative Matrix Factorization
Non-negative matrix factorization (NMF or NNMF), also non-negative matrix approximation is a group of algorithms in multivariate analysis and linear algebra where a matrix is factorized into (usually) two matrices and , with the property that all three matrices have no negative elements. This non-negativity makes the resulting matrices easier to inspect. Also, in applications such as processing of audio spectrograms or muscular activity, non-negativity is inherent to the data being considered. Since the problem is not exactly solvable in general, it is commonly approximated numerically. NMF finds applications in such fields as astronomy, computer vision, document clustering, missing data imputation, chemometrics, audio signal processing, recommender systems, and bioinformatics. History In chemometrics non-negative matrix factorization has a long history under the name "self modeling curve resolution". In this framework the vectors in the right matrix are continuous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |