|
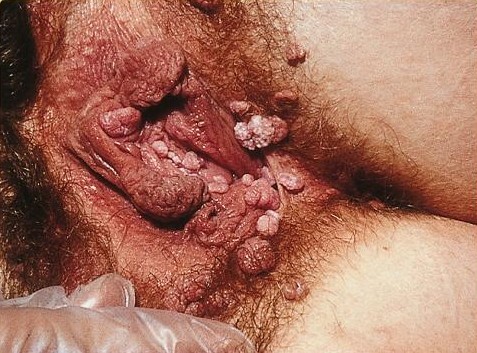
Genital Wart
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). They may be flat or project out from the surface of the skin, and their color may vary; brownish, white, pale yellow, pinkish-red, or gray. There may be a few individual warts or several, either in a cluster or merged together to look cauliflower-shaped. They can be itchy and feel burning. Usually they cause few symptoms, but can occasionally be painful. Typically they appear one to eight months following exposure. Warts are the most easily recognized symptom of genital HPV infection. HPV types 6 and 11 are responsible for causing majority of genital warts whereas HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, and 35 are also occasionally found. It is spread through direct skin-to-skin contact, usually during oral, manual, vaginal, or anal sex with an infected partner. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms and can be confirmed by biopsy. The types of HPV that cause cancer are not the same a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious Disease (medical Specialty)
Infectious diseases (ID), also known as infectiology, is a medical specialty dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of infections. An infectious diseases specialist's practice consists of managing nosocomial (Hospital-acquired infection, healthcare-acquired) infections or community-acquired infections. An ID specialist investigates and determines the cause of a disease (bacteria, virus, parasite, fungus or prions). Once the cause is known, an ID specialist can then run various tests to determine the best drug to treat the disease. While infectious diseases have always been around, the infectious disease specialty did not exist until the late 1900s after scientists and physicians in the 19th century paved the way with research on the sources of infectious disease and the development of vaccines. Scope Infectious diseases specialists typically serve as consultants to other physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immuno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred to as oral intercourse, is sexual activity involving the stimulation of the genitalia of a person by another person using the mouth (including the lips, tongue, or teeth). Cunnilingus is oral sex performed on the vulva while fellatio is oral sex performed on the Human penis, penis. Anilingus, another form of oral sex, is oral stimulation of the Human anus, anus. Oral sex may be performed as foreplay to incite sexual arousal before other sexual activities (such as Sexual intercourse, vaginal or Anal sex, anal intercourse), or as an Eroticism, erotic and physical intimacy, physically intimate act in its own right. Like most forms of sexual activity, oral sex can pose a risk for contracting Sexually transmitted disease, sexually transmitted infections (STIs). However, the transmission risk for oral sex, especially HIV transmission, is significantly lower than for vaginal or anal sex. Oral sex is often regarded as taboo, but most countries do not have l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of Penis
The body or shaft of the penis is the free portion of the human penis that is located outside of the pelvic cavity. It is the continuation of the internal root, which is embedded in the pelvis and extends to the glans. It is made up of the two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum on the underside. The corpora cavernosa are intimately bound to one another with a dorsally fenestrated septum, which becomes a complete one before the penile crura. The body of the penis is homologous to the female clitoral body. Structure The body of the penis is suspended from the pubic symphysis. It has two surfaces; the ''dorsal'' and the ventral or ''urethral''. The penile raphe runs on its ventral surface. The body is surrounded by a bi-layered model of tunica albuginea in which a distal ligament buttresses the glans penis and plays an integral role to the penile fibroskeleton, and the structure is called "os analog", a term coined by Geng Long Hsu in the Encyclopedia of Reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Organ
A sex organ, also known as a reproductive organ, is a part of an organism that is involved in sexual reproduction. Sex organs constitute the primary sex characteristics of an organism. Sex organs are responsible for producing and transporting gametes, as well as facilitating fertilization and supporting the development and birth of offspring. Sex organs are found in many species of animals and plants, with their features varying depending on the species. Sex organs are typically differentiated into male and female types. In animals (including humans), the male sex organs include the testicles, epididymis, epididymides, and penis; the female sex organs include the clitoris, Ovary, ovaries, oviducts, and vagina. The testicle in the male and the ovary in the female are called the ''primary sex organs''. All other sex-related organs are known as ''secondary sex organs''. The outer parts are known as the genitals or external genitalia, visible at birth in both sexes, while the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Anus
In humans, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin ''ānus'', "ring", "circle") is the external opening of the rectum located inside the intergluteal cleft. Two sphincters control the exit of Human feces, feces from the body during an act of defecation, which is the primary function of the anus. These are the internal anal sphincter and the external anal sphincter, which are circular muscles that normally maintain constriction of the orifice and which relax as required by normal physiological functioning. The inner sphincter is involuntary and the outer is voluntary. Above the anus is the perineum, which is also located beneath the vulva or scrotum. In part owing to its exposure to feces, a number of medical conditions may affect the anus, such as hemorrhoids. The anus is the site of potential infections and other conditions, including cancer (see anal cancer). With anal sex, the anus can play a role in Human sexuality, sexuality. Attitudes toward anal sex vary, and it is illeg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Condylomata On Testicles
Small means of insignificant size. Small may also refer to: Science and technology * SMALL, an ALGOL-like programming language * ''Small'' (journal), a nano-science publication * <small>, an HTML element that defines smaller text Arts and entertainment Fictional characters * Small, in the British children's show Big & Small Other uses * Small (surname) * List of people known as the Small * "Small", a song from the album ''The Cosmos Rocks'' by Queen + Paul Rodgers See also * Smal (other) Smal may refer to: People * (1927-2001), Dutch musician * Georges Smal (1928–1988), Belgian writer * Gert Smal (born 1961), South African rugby player * Gijs Smal (born 1997), Dutch football player * (born 1939), Belgian politician; a memb ... * Smalls (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; ; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician and philosopher of the Classical Greece, classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of medicine. He is traditionally referred to as the "Father of Medicine" in recognition of his lasting contributions to the field, such as the use of prognosis and clinical observation, the systematic categorization of diseases, and the (however misguided) formulation of Humorism, humoral theory. His studies set out the basic ideas of modern-day specialties, including surgery, urology, neurology, acute medicine and Orthopedic surgery, orthopedics. The Hippocratic school of medicine revolutionized ancient Greek medicine, establishing it as a discipline distinct from other fields with which it had traditionally been associated (theurgy and philosophy), thus establishing medicine as a profession. However, the achievements of the writers of the Hippocratic Corpus, the practitioners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulating the body's Adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, they help prevent sickness from an infectious disease. When a sufficiently large percentage of a population has been vaccinated, herd immunity results. Herd immunity protects those who may be immunocompromised and cannot get a vaccine because even a weakened version would harm them. The effectiveness of vaccination has been widely studied and verified. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases; widespread immunity due to vaccination is largely responsible for the Eradication of infectious diseases, worldwide eradication of smallpox and the elimination of diseases such as polio and tetanus from much of the world. According to the World Health Organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryotherapy
Cryotherapy, sometimes known as cold therapy, is the local or general use of low temperatures in medical therapy. Cryotherapy can be used in many ways, including whole body exposure for therapeutic health benefits or may be used locally to treat a variety of tissue lesions. Cryotherapy is often used in an effort to prevent or relieve muscle pain, sprains and swelling after soft tissue damage or surgery. When a musculoskeletal injury occurs, the body sends signals to the inflammatory cells, macrophages, which release IGF-1. IGF-1 is a hormone-insulin-like growth factor which initiates the termination of damaged tissue. In some cases, this inflammatory response can be aggravated and cause increased swelling and edema, which can actually prolong the recovery process. For decades, it has been commonly used to accelerate recovery in athletes after exercise. Cryotherapy decreases the temperature of tissue surfaces to minimize hypoxic cell death, edema accumulation, and muscle spasms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podophyllin
Podophyllum resin, also known as podophyllum or podophyllin, is a resin made from the roots of the American mandrake. It is used as a medication to treat genital warts and plantar warts, including in people with HIV/AIDS. It is not recommended in HPV infections without external warts. Application by a healthcare provider to the skin is recommended. Common side effects include redness, itchiness, and pain at the site of use. Severe side effects may include vomiting, abdominal pain, confusion, bone marrow suppression, and diarrhea. It is not recommended for more than a small area at a time. Use during pregnancy is known to be dangerous to the baby. It works mostly via podophyllotoxin which stops cell division. Podophyllin resin has been used to treat warts since at least 1820. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |