|
Genetic Epistemology
Genetic epistemology or 'developmental theory of knowledge' is a study of the origins (genesis) of knowledge (epistemology) established by Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. This theory opposes traditional epistemology and unites constructivism and structuralism. Piaget took epistemology as the starting point and adopted the method of genetics, arguing that all knowledge of the child is generated through interaction with the environment. Aims The goal of genetic epistemology is to link the knowledge to the model of its construction – i.e., the context in which knowledge is gained affects its perception, quality, and degree of retention. Further, genetic epistemology seeks to explain the process of cognitive development (from birth) in four primary stages: sensorimotor (birth to age 2), pre-operational (2–7), concrete operational (7–11), and formal operational (11 years onward). As an example, consider that for children in the sensorimotor stage, teachers should try to p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Epistemology
Epistemology is the branch of philosophy that examines the nature, origin, and limits of knowledge. Also called "the theory of knowledge", it explores different types of knowledge, such as propositional knowledge about facts, practical knowledge in the form of skills, and knowledge by acquaintance as a familiarity through experience. Epistemologists study the concepts of belief, truth, and justification to understand the nature of knowledge. To discover how knowledge arises, they investigate sources of justification, such as perception, introspection, memory, reason, and testimony. The school of skepticism questions the human ability to attain knowledge while fallibilism says that knowledge is never certain. Empiricists hold that all knowledge comes from sense experience, whereas rationalists believe that some knowledge does not depend on it. Coherentists argue that a belief is justified if it coheres with other beliefs. Foundationalists, by contrast, maintain th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
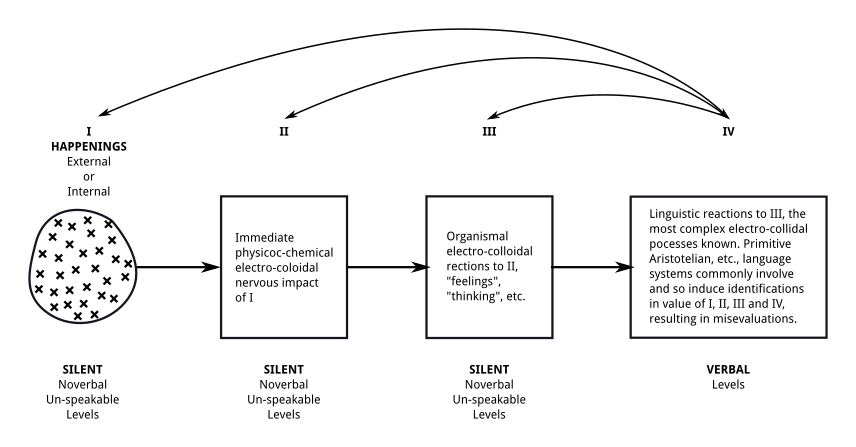
General Semantics
General semantics is a school of thought that incorporates philosophy, philosophic and science, scientific aspects. Although it does not stand on its own as a separate list of schools of philosophy, school of philosophy, a separate science, or an academic discipline, it describes itself as a scientifically empiricism, empirical approach to cognition and problem solving. It has been described by nonproponents as a self-help system, and it has been criticized as having pseudoscience, pseudoscientific aspects, but it has also been favorably viewed by various scientists as a useful set of analysis, analytical tools albeit not its own science. General semantics is concerned with how phenomenon, phenomena (observable events) translate to perceptions, how they are further modified by the names and labelling, labels we apply to them, and how we might gain a measure of control over our own cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses. Proponents characterize general semantics as an ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Developmental Psychology
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of how and why humans grow, change, and adapt across the course of their lives. Originally concerned with infants and children, the field has expanded to include adolescence, adult development, aging, and the entire lifespan. Developmental psychologists aim to explain how thinking, feeling, and behaviors change throughout life. This field examines change across three major dimensions, which are physical development, cognitive development, and social emotional development. Within these three dimensions are a broad range of topics including motor skills, executive functions, moral understanding, language acquisition, social change, personality, emotional development, self-concept, and identity formation. Developmental psychology examines the influences of nature ''and'' nurture on the process of human development, as well as processes of change in context across time. Many researchers are interested in the interactions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Theory Of Cognitive Development
Piaget's theory of cognitive development, or his genetic epistemology, is a comprehensive theory about the nature and development of human intelligence. It was originated by the Swiss developmental psychologist Jean Piaget (1896–1980). The theory deals with the nature of knowledge itself and how humans gradually come to acquire, construct, and use it. Piaget's theory is mainly known as a developmental stage theory. In 1919, while working at the Alfred Binet Laboratory School in Paris, Piaget "was intrigued by the fact that children of different ages made different kinds of mistakes while solving problems". His experience and observations at the Alfred Binet Laboratory were the beginnings of his theory of cognitive development. He believed that children of different ages made different mistakes because of the "quality rather than quantity" of their intelligence. Piaget proposed four stages to describe the development process of children: sensorimotor stage, pre-operational s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ontogeny Recapitulates Phylogeny
Ontogeny (also ontogenesis) is the origination and development of an organism (both physical and psychological, e.g., moral development), usually from the time of fertilization of the ovum, egg to adult. The term can also be used to refer to the study of the entirety of an organism's lifespan. Ontogeny is the developmental history of an organism within its own lifetime, as distinct from phylogeny, which refers to the evolutionary history of a species. Another way to think of ontogeny is that it is the process of an organism going through all of the developmental stages over its lifetime. The developmental history includes all the developmental events that occur during the existence of an organism, beginning with the changes in the egg at the time of fertilization and events from the time of birth or hatching and afterward (i.e., growth, remolding of body shape, development of secondary sexual characteristics, etc.). While developmental (i.e., ontogenetic) processes can influen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Learning Theory (education)
Learning theory describes how students receive, process, and retain knowledge during learning. Cognitive, emotional, and environmental influences, as well as prior experience, all play a part in how understanding, or a worldview, is acquired or changed and knowledge and skills retained. Behaviorists look at learning as an aspect of Operant conditioning, conditioning and advocating a system of rewards and targets in education. Educators who embrace Cognitivism (learning theory), cognitive theory believe that the definition of learning as a change in behaviour is too narrow, and study the learner rather than their environment—and in particular the complexities of human memory. Those who advocate constructivism (learning theory), constructivism believe that a learner's ability to learn relies largely on what they already know and understand, and the acquisition of knowledge should be an individually tailored process of construction. Transformative learning theory focuses on the ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Learning Styles
Learning styles refer to a range of theories that aim to account for differences in individuals' learning. Although there is ample evidence that individuals express personal preferences on how they prefer to receive information, few studies have found validity in using learning styles in education. Many theories share the proposition that humans can be classified according to their "style" of learning, but differ on how the proposed styles should be defined, categorized and assessed. A common concept is that individuals differ in how they learn. The idea of individualized learning styles became popular in the 1970s. This has greatly influenced education despite the criticism that the idea has received from some researchers. Proponents recommend that teachers run a needs analysis to assess the learning styles of their students and adapt their classroom methods to best fit each student's learning style. There are many different types of learning models that have been created and used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Genetic Structuralism
Lucien Goldmann (; 20 July 1913 – 8 October 1970) was a French philosopher and sociologist of Jewish-Romanian origin. A professor at the EHESS in Paris, he was a Marxist theorist. His wife was sociologist Annie Goldmann. Biography Goldmann was born in Bucharest, Romania, but grew up in Botoşani. He studied law at the University of Bucharest and the University of Vienna under the Austromarxist jurist Max Adler.Martin Jay, ''Marxism and Totality: The Adventures of a Concept from Lukács to Habermas'', University of California Press, 1984, pp. 305–06. In 1934, he went to the University of Paris to study political economy, literature, and philosophy. He moved to Switzerland in November 1942, where he was placed in a refugee camp until 1943. Through Jean Piaget's intervention, he was subsequently given a scholarship to the University of Zurich, where he completed his PhD in philosophy in 1945 under the supervision of with a thesis entitled ''Mensch, Gemeinschaft und Welt in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Evolutionary Epistemology
Evolutionary epistemology refers to three distinct topics: (1) the biological evolution of cognitive mechanisms in animals and humans, (2) a theory that knowledge itself evolves by natural selection, and (3) the study of the historical discovery of new abstract entities such as abstract number or abstract value that necessarily precede the individual acquisition and usage of such abstractions. As a branch of inquiry in epistemology, evolutionary epistemology lies at the crossroads of philosophy and evolutionary biology. Cognition in biological evolution can refer to a branch of inquiry in epistemology that applies the concepts of biological evolution to the growth of animal and human cognition. It argues that the mind is in part genetically determined and that its structure and function reflect adaptation, a nonteleological process of interaction between the organism and its environment. A cognitive trait tending to increase inclusive fitness in a given population should th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jean Piaget
Jean William Fritz Piaget (, ; ; 9 August 1896 – 16 September 1980) was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development. Piaget's theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called genetic epistemology. Piaget placed great importance on the education of children. As the Director of the International Bureau of Education, he declared in 1934 that "only education is capable of saving our societies from possible collapse, whether violent, or gradual". His theory of child development has been studied in pre-service education programs. Nowadays, educators and theorists working in the area of early childhood education persist in incorporating constructivist-based strategies. Piaget created the International Center for Genetic Epistemology in Geneva in 1955 while on the faculty of the University of Geneva, and directed the center until his death in 1980. The number of collaborations that its founding made possible, and their impact, ultimately le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Educational Psychology
Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive psychology, cognitive and behavioral psychology, behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, Affect (psychology), affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.Snowman, Jack (1997). Educational Psychology: What Do We Teach, What Should We Teach?. "Educational Psychology", 9, 151-169 Educational psychology can in part be understood through its relationship with other disciplines. It is informed primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of human mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks. In 387 BCE, Plato had suggested that the brain was the seat of the mental processes. In 1637, René Descartes posited that humans are born with innate ideas and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |