|
Generalizability
Generalizability theory, or G theory, is a statistical framework for conceptualizing, investigating, and designing reliable observations. It is used to determine the reliability (i.e., reproducibility) of measurements under specific conditions. It is particularly useful for assessing the reliability of performance assessments. It was originally introduced by Lee Cronbach, N. Rajaratnam, and Goldine Gleser in 1963. Overview In G theory, sources of variation are referred to as ''facets''. Facets are similar to the "factors" used in analysis of variance, and may include persons, raters, items/forms, time, and settings among other possibilities. These facets are potential sources of error and the purpose of generalizability theory is to quantify the amount of error caused by each facet and interaction of facets. The usefulness of data gained from a G study is crucially dependent on the design of the study. Therefore, the researcher must carefully consider the ways in which he/she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Cronbach
Lee Joseph Cronbach (April 22, 1916 – October 1, 2001) was an American educational psychologist who made contributions to psychological testing and measurement. At the University of Illinois, Urbana, Cronbach produced many of his works: the "Alpha" paper (Cronbach, 1951), as well as an essay titled "The Two Disciplines of Scientific Psychology", in the ''American Psychologist'' magazine in 1957, where he discussed his thoughts on the increasing divergence between the fields of experimental psychology and correlational psychology (to which he himself belonged). Cronbach was the president of the American Psychological Association, president of the American Educational Research Association, Vida Jacks Professor of Education at Stanford University and a member of the United States National Academy of Sciences, the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, and the American Philosophical Society. Cronbach is considered to be "one of the most prominent and influential educational psyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goldine Gleser
Goldine C. Gleser (1915 – 2004) was an American psychologist and statistician known for her research on the statistics of psychological testing, on generalizability theory, on defence mechanisms, on the psychological effects on child survivors of the Buffalo Creek flood, for her work with Mildred Trotter on estimation of stature, and for her participation in the Cincinnati Radiation Experiments. She was a professor of psychiatry and psychology at the University of Cincinnati. Early life and education Gleser was originally from St. Louis, Missouri. She studied mathematics at Washington University in St. Louis, graduating Phi Beta Kappa in 1935 and earning a master's degree in 1936. Although she was working towards a doctorate in mathematics, she interrupted her studies to marry a civil engineer, and later switched to psychology, completing a Ph.D. at Washington University in 1950. Career Gleser began part-time work at the University of Cincinnati in 1956, and in 1964 beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Test Theory
Classical test theory (CTT) is a body of related psychometric theory that predicts outcomes of psychological Test (assessment), testing such as the difficulty of items or the ability of test-takers. It is a theory of testing based on the idea that a person's observed or obtained score on a test is the sum of a true score (error-free score) and an error score. Generally speaking, the aim of classical test theory is to understand and improve the Reliability (psychometric), reliability of psychological tests. ''Classical test theory'' may be regarded as roughly synonymous with ''true score theory''. The term "classical" refers not only to the chronology of these models but also contrasts with the more recent psychometric theories, generally referred to collectively as item response theory, which sometimes bear the appellation "modern" as in "modern latent trait theory". Classical test theory as we know it today was codified by and described in classic texts such as and . The descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation
Observation in the natural sciences is an act or instance of noticing or perceiving and the acquisition of information from a primary source. In living beings, observation employs the senses. In science, observation can also involve the perception and recording of data via the use of scientific instruments. The term may also refer to any data collected during the scientific activity. Observations can be qualitative, that is, the absence or presence of a property is noted and the observed phenomenon described, or quantitative if a numerical value is attached to the observed phenomenon by counting or measuring. Science The scientific method requires observations of natural phenomena to formulate and test hypotheses. It consists of the following steps: # Ask a question about a phenomenon # Make observations of the phenomenon # Formulate a hypothesis that tentatively answers the question # Predict logical, observable consequences of the hypothesis that have not yet been inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability (statistics)
In statistics and psychometrics, reliability is the overall consistency of a measure. A measure is said to have a high reliability if it produces similar results under consistent conditions:It is the characteristic of a set of test scores that relates to the amount of random error from the measurement process that might be embedded in the scores. Scores that are highly reliable are precise, reproducible, and consistent from one testing occasion to another. That is, if the testing process were repeated with a group of test takers, essentially the same results would be obtained. Various kinds of reliability coefficients, with values ranging between 0.00 (much error) and 1.00 (no error), are usually used to indicate the amount of error in the scores. For example, measurements of people's height and weight are often extremely reliable.The Marketing Accountability Standards Board (MASB) endorses this definition as part of its ongoinCommon Language: Marketing Activities and Metrics Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analysis Of Variance
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a family of statistical methods used to compare the Mean, means of two or more groups by analyzing variance. Specifically, ANOVA compares the amount of variation ''between'' the group means to the amount of variation ''within'' each group. If the between-group variation is substantially larger than the within-group variation, it suggests that the group means are likely different. This comparison is done using an F-test. The underlying principle of ANOVA is based on the law of total variance, which states that the total variance in a dataset can be broken down into components attributable to different sources. In the case of ANOVA, these sources are the variation between groups and the variation within groups. ANOVA was developed by the statistician Ronald Fisher. In its simplest form, it provides a statistical test of whether two or more population means are equal, and therefore generalizes the Student's t-test#Independent two-sample t-test, ''t''- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
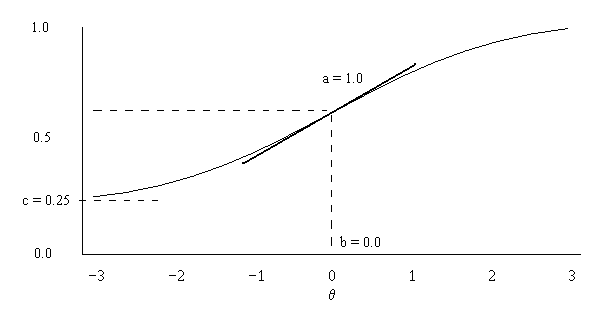
Item Response Theory
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT, also known as latent trait theory, strong true score theory, or modern mental test theory) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of Test (student assessment), tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measurement, measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which ''"''All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments". By contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |